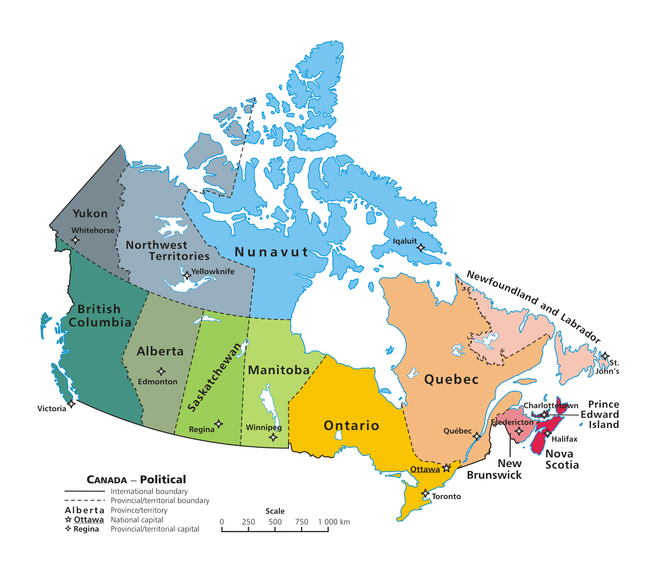
List of regions of Canada
National regions
Although these regions have no official status or defined boundaries the Provinces and territories are sometimes informally grouped into the following regions (generally from west to east):
| All provinces and territories | Senate divisions | Seven-region model[1] | Six-region model | Five-region model | Four-region model | Three-region model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| British Columbia | Western Canada (24 seats) | British Columbia | Pacific Canada | Western Canada | Western Canada | Western Canada |
| Alberta | Alberta | Prairies | ||||
| Saskatchewan | Saskatchewan and Manitoba | |||||
| Manitoba | ||||||
| Ontario | Ontario (24 seats) | Ontario | Ontario | Ontario | Central Canada | Eastern Canada |
| Quebec | Quebec (24 seats) | Quebec | Quebec | Quebec | ||
| New Brunswick | The Maritimes (24 seats) | Atlantic Canada | Atlantic Canada | Atlantic Canada | Atlantic Canada | |
| Prince Edward Island | ||||||
| Nova Scotia | ||||||
| Newfoundland and Labrador | Newfoundland and Labrador (6 seats) | |||||
| Yukon | The North (Territories) (3 seats) | Northern Canada | Northern Canada | Northern Canada | Northern Canada | Northern Canada |
| Northwest Territories | ||||||
| Nunavut |
Other regions are:
- French Canada
- English Canada, sometimes known as the Rest of Canada (excluding Quebec) when considering topics of language
- Acadia
- Quebec City–Windsor Corridor
Seats in the Senate are equally divided among four regions: Maritimes, Quebec, Ontario, and the West, with special status for Newfoundland and Labrador, and Northern Canada ('the North').
Provincial regions
The provinces and territories are all sub-divided into regions for a variety of official and unofficial purposes. In some provinces, the regions have been officially defined by their respective governments. In others, the "regions" have no official status.
See also
References
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||