List of fallacies
A fallacy is incorrect argument in logic and rhetoric which undermines an argument's logical validity or more generally an argument's logical soundness. Fallacies are either formal fallacies or informal fallacies.
Formal fallacies
A formal fallacy is an error in logic that can be seen in the argument's form.[1] All formal fallacies are specific types of non sequiturs.
- Anecdotal fallacy - using a personal experience or an isolated example instead of sound reasoning or compelling evidence.
- Appeal to probability – is a statement that takes something for granted because it would probably be the case (or might be the case).[2][3]
- Argument from fallacy – assumes that if an argument for some conclusion is fallacious, then the conclusion is false.[4]
- Base rate fallacy – making a probability judgment based on conditional probabilities, without taking into account the effect of prior probabilities.[5]
- Conjunction fallacy – assumption that an outcome simultaneously satisfying multiple conditions is more probable than an outcome satisfying a single one of them.[6]
- Masked man fallacy (illicit substitution of identicals) – the substitution of identical designators in a true statement can lead to a false one.[7]
- Unwarranted assumption fallacy - The fallacy of unwarranted assumption is committed when the conclusion of an argument is based on a premise (implicit or explicit) that is false or unwarranted. An assumption is unwarranted when it is false - these premises are usually suppressed or vaguely written. An assumption is also unwarranted when it is true but does not apply in the given context.
Propositional fallacies
A propositional fallacy is an error in logic that concerns compound propositions. For a compound proposition to be true, the truth values of its constituent parts must satisfy the relevant logical connectives that occur in it (most commonly: <and>, <or>, <not>, <only if>, <if and only if>). The following fallacies involve inferences whose correctness is not guaranteed by the behavior of those logical connectives, and hence, which are not logically guaranteed to yield true conclusions.
Types of Propositional fallacies:
- Affirming a disjunct – concluded that one disjunct of a logical disjunction must be false because the other disjunct is true; A or B; A; therefore not B.[8]
- Affirming the consequent – the antecedent in an indicative conditional is claimed to be true because the consequent is true; if A, then B; B, therefore A.[8]
- Denying the antecedent – the consequent in an indicative conditional is claimed to be false because the antecedent is false; if A, then B; not A, therefore not B.[8]
Quantification fallacies
A quantification fallacy is an error in logic where the quantifiers of the premises are in contradiction to the quantifier of the conclusion.
Types of Quantification fallacies:
- Existential fallacy – an argument has a universal premise and a particular conclusion.[9]
Formal syllogistic fallacies
Syllogistic fallacies – logical fallacies that occur in syllogisms.
- Affirmative conclusion from a negative premise (illicit negative) – when a categorical syllogism has a positive conclusion, but at least one negative premise.[9]
- Fallacy of exclusive premises – a categorical syllogism that is invalid because both of its premises are negative.[9]
- Fallacy of four terms (quaternio terminorum) – a categorical syllogism that has four terms.[10]
- Illicit major – a categorical syllogism that is invalid because its major term is not distributed in the major premise but distributed in the conclusion.[9]
- Illicit minor – a categorical syllogism that is invalid because its minor term is not distributed in the minor premise but distributed in the conclusion.[9]
- Negative conclusion from affirmative premises (illicit affirmative) – when a categorical syllogism has a negative conclusion but affirmative premises. [9]
- Fallacy of the undistributed middle – the middle term in a categorical syllogism is not distributed.[11]
Informal fallacies
Informal fallacies – arguments that are fallacious for reasons other than structural (formal) flaws and usually require examination of the argument's content.[12]
- Appeal to the stone (argumentum ad lapidem) – dismissing a claim as absurd without demonstrating proof for its absurdity.[13]
- Argument from ignorance (appeal to ignorance, argumentum ad ignorantiam) – assuming that a claim is true because it has not been or cannot be proven false, or vice versa.[14]
- Argument from (personal) incredulity (divine fallacy, appeal to common sense) – I cannot imagine how this could be true, therefore it must be false.[15][16]
- Argument from repetition (argumentum ad infinitum) – signifies that it has been discussed extensively until nobody cares to discuss it anymore.[17][18]
- Argument from silence (argumentum e silentio) – where the conclusion is based on the absence of evidence, rather than the existence of evidence.[19][20]
- Argument to moderation (false compromise, middle ground, fallacy of the mean, argumentum ad temperantiam) – assuming that the compromise between two positions is always correct.[21]
- Argumentum ad hominem – the evasion of the actual topic by directing an attack at your opponent.
- ergo decedo – where a critic's perceived affiliation is seen as the underlying reason for the criticism and the critic is asked to stay away from the issue altogether.
- Argumentum verbosium – See Proof by verbosity, below.
- Begging the question (petitio principii) – providing what is essentially the conclusion of the argument as a premise.[22][23][24][25]
- (shifting the) Burden of proof (see – onus probandi) – I need not prove my claim, you must prove it is false.
- Circular reasoning (circulus in demonstrando) – when the reasoner begins with what he or she is trying to end up with; sometimes called assuming the conclusion.
- Circular cause and consequence – where the consequence of the phenomenon is claimed to be its root cause.
- Continuum fallacy (fallacy of the beard, line-drawing fallacy, sorites fallacy, fallacy of the heap, bald man fallacy) – improperly rejecting a claim for being imprecise.[26]
- Correlative-based fallacies
- Correlation proves causation (cum hoc ergo propter hoc) – a faulty assumption that correlation between two variables implies that one causes the other.[27]
- Suppressed correlative – where a correlative is redefined so that one alternative is made impossible.[28]
- Equivocation – the misleading use of a term with more than one meaning (by glossing over which meaning is intended at a particular time).[29]
- Ambiguous middle term – a common ambiguity in syllogisms in which the middle term is equivocated.[30]
- Ecological fallacy – inferences about the nature of specific individuals are based solely upon aggregate statistics collected for the group to which those individuals belong.[31]
- Etymological fallacy – which reasons that the original or historical meaning of a word or phrase is necessarily similar to its actual present-day usage.[32]
- Fallacy of accent – a specific type of ambiguity that arises when the meaning of a sentence is changed by placing an unusual prosodic stress, or when, in a written passage, it's left unclear which word the emphasis was supposed to fall on.
- Fallacy of composition – assuming that something true of part of a whole must also be true of the whole.[33]
- Fallacy of division – assuming that something true of a thing must also be true of all or some of its parts.[34]
- False attribution – an advocate appeals to an irrelevant, unqualified, unidentified, biased or fabricated source in support of an argument.
- Fallacy of quoting out of context (contextomy) – refers to the selective excerpting of words from their original context in a way that distorts the source's intended meaning.[35]
- False authority (single authority) – using an expert of dubious credentials or using only one opinion to sell a product or idea. Related to the appeal to authority fallacy.
- False dilemma (false dichotomy, fallacy of bifurcation, black-or-white fallacy) – two alternative statements are held to be the only possible options, when in reality there are more.[36]
- False equivalence – describing a situation of logical and apparent equivalence, when in fact there is none.
- Fallacy of many questions (complex question, fallacy of presupposition, loaded question, plurium interrogationum) – someone asks a question that presupposes something that has not been proven or accepted by all the people involved. This fallacy is often used rhetorically, so that the question limits direct replies to those that serve the questioner's agenda.
- Fallacy of the single cause (causal oversimplification[37]) – it is assumed that there is one, simple cause of an outcome when in reality it may have been caused by a number of only jointly sufficient causes.
- Furtive fallacy – outcomes are asserted to have been caused by the malfeasance of decision makers.
- Gambler's fallacy – the incorrect belief that separate, independent events can affect the likelihood of another random event. If a fair coin lands on heads 10 times in a row, the belief that it is "due to the number of times it had previously landed on tails" is incorrect.[38]
- Hedging – using words with ambiguous meanings, then changing the meaning of them later.
- Historian's fallacy – occurs when one assumes that decision makers of the past viewed events from the same perspective and having the same information as those subsequently analyzing the decision.[39] (Not to be confused with presentism, which is a mode of historical analysis in which present-day ideas, such as moral standards, are projected into the past.)
- Homunculus fallacy – where a "middle-man" is used for explanation, this sometimes leads to regressive middle-men. Explains without actually explaining the real nature of a function or a process. Instead, it explains the concept in terms of the concept itself, without first defining or explaining the original concept. Explaining thought as something produced by a little thinker, a sort of homunculus inside the head, merely explains it as another kind of thinking (as different but the same).[40]
- Inflation of conflict – The experts of a field of knowledge disagree on a certain point, so the scholars must know nothing, and therefore the legitimacy of their entire field is put to question.[41]
- If-by-whiskey – an argument that supports both sides of an issue by using terms that are selectively emotionally sensitive.
- Incomplete comparison – in which insufficient information is provided to make a complete comparison.
- Inconsistent comparison – where different methods of comparison are used, leaving one with a false impression of the whole comparison.
- Intentionality fallacy – the insistence that the ultimate meaning of an expression must be consistent with the intention of the person from whom the communication originated (e.g. a work of fiction that is widely received as a blatant allegory must necessarily not be regarded as such if the author intended it not to be so.)[42]
- Ignoratio elenchi (irrelevant conclusion, missing the point) – an argument that may in itself be valid, but does not address the issue in question.[43]
- Kettle logic – using multiple, jointly inconsistent arguments to defend a position.
- Ludic fallacy – the belief that the outcomes of non-regulated random occurrences can be encapsulated by a statistic; a failure to take into account unknown unknowns in determining the probability of events taking place.[44]
- Moral high ground fallacy – in which one assumes a "holier-than-thou" attitude in an attempt to make oneself look good to win an argument.
- Moralistic fallacy – inferring factual conclusions from purely evaluative premises in violation of fact–value distinction. For instance, inferring is from ought is an instance of moralistic fallacy. Moralistic fallacy is the inverse of naturalistic fallacy defined below.
- Moving the goalposts (raising the bar) – argument in which evidence presented in response to a specific claim is dismissed and some other (often greater) evidence is demanded.
- Naturalistic fallacy – inferring evaluative conclusions from purely factual premises[45] in violation of fact–value distinction. For instance, inferring ought from is (sometimes referred to as the is-ought fallacy) is an instance of naturalistic fallacy. Also naturalistic fallacy in a stricter sense as defined in the section "Conditional or questionable fallacies" below is an instance of naturalistic fallacy. Naturalistic fallacy is the inverse of moralistic fallacy.
- Naturalistic fallacy fallacy[46] (anti-naturalistic fallacy[47]) – inferring impossibility to infer any instance of ought from is from the general invalidity of is-ought fallacy mentioned above. For instance, is
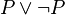 does imply ought
does imply ought 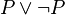 for any proposition
for any proposition 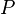 , although the naturalistic fallacy fallacy would falsely declare such an inference invalid. Naturalistic fallacy fallacy is an instance of argument from fallacy.
, although the naturalistic fallacy fallacy would falsely declare such an inference invalid. Naturalistic fallacy fallacy is an instance of argument from fallacy. - Nirvana fallacy (perfect solution fallacy) – when solutions to problems are rejected because they are not perfect.
- Onus probandi – from Latin "onus probandi incumbit ei qui dicit, non ei qui negat" the burden of proof is on the person who makes the claim, not on the person who denies (or questions the claim). It is a particular case of the "argumentum ad ignorantiam" fallacy, here the burden is shifted on the person defending against the assertion.
- Petitio principii – see begging the question.
- Post hoc ergo propter hoc Latin for "after this, therefore because of this" (faulty cause/effect, coincidental correlation, correlation without causation) – X happened, then Y happened; therefore X caused Y. The Loch Ness Monster has been seen in this loch. Something tipped our boat over; it's obviously the Loch Ness Monster.[48]
- Proof by assertion – a proposition is repeatedly restated regardless of contradiction.
- Proof by verbosity (argumentum verbosium, proof by intimidation) – submission of others to an argument too complex and verbose to reasonably deal with in all its intimate details. (See also Gish Gallop and argument from authority.)
- Prosecutor's fallacy – a low probability of false matches does not mean a low probability of some false match being found.
- Proving too much - using a form of argument that, if it were valid, could be used more generally to reach an absurd conclusion.
- Psychologist's fallacy – an observer presupposes the objectivity of his own perspective when analyzing a behavioral event.
- Red herring – a speaker attempts to distract an audience by deviating from the topic at hand by introducing a separate argument the speaker believes is easier to speak to.[49]
- Referential fallacy[50] – assuming all words refer to existing things and that the meaning of words reside within the things they refer to, as opposed to words possibly referring to no real object or that the meaning of words often comes from how we use them.
- Regression fallacy – ascribes cause where none exists. The flaw is failing to account for natural fluctuations. It is frequently a special kind of the post hoc fallacy.
- Reification (hypostatization) – a fallacy of ambiguity, when an abstraction (abstract belief or hypothetical construct) is treated as if it were a concrete, real event or physical entity. In other words, it is the error of treating as a "real thing" something that is not a real thing, but merely an idea.
- Retrospective determinism – the argument that because some event has occurred, its occurrence must have been inevitable beforehand.
- Shotgun argumentation – the arguer offers such a large number of arguments for their position that the opponent can't possibly respond to all of them. (See "Argument by verbosity" and "Gish Gallop", above.)
- Special pleading – where a proponent of a position attempts to cite something as an exemption to a generally accepted rule or principle without justifying the exemption.
- Wrong direction – cause and effect are reversed. The cause is said to be the effect and vice versa.[51]
Faulty generalizations
Faulty generalizations – reach a conclusion from weak premises. Unlike fallacies of relevance, in fallacies of defective induction, the premises are related to the conclusions yet only weakly buttress the conclusions. A faulty generalization is thus produced.
- Accident – an exception to a generalization is ignored.[52]
- No true Scotsman – when a generalization is made true only when a counterexample is ruled out on shaky grounds.[53]
- Cherry picking (suppressed evidence, incomplete evidence) – act of pointing at individual cases or data that seem to confirm a particular position, while ignoring a significant portion of related cases or data that may contradict that position.[54]
- False analogy – an argument by analogy in which the analogy is poorly suited.[55]
- Hasty generalization (fallacy of insufficient statistics, fallacy of insufficient sample, fallacy of the lonely fact, leaping to a conclusion, hasty induction, secundum quid, converse accident) – basing a broad conclusion on a small sample.[56]
- Inductive fallacy – A more general name to some fallacies, such as hasty generalization. It happens when a conclusion is made of premises that lightly support it.
- Misleading vividness – involves describing an occurrence in vivid detail, even if it is an exceptional occurrence, to convince someone that it is a problem.
- Overwhelming exception – an accurate generalization that comes with qualifications that eliminate so many cases that what remains is much less impressive than the initial statement might have led one to assume.[57]
- Thought-terminating cliché – a commonly used phrase, sometimes passing as folk wisdom, used to quell cognitive dissonance, conceal lack of thought-entertainment, move on to other topics etc. but in any case, end the debate with a cliche—not a point.
Red herring fallacies
A red herring fallacy is an error in logic where a proposition is, or is intended to be, misleading in order to make irrelevant or false inferences. In the general case any logical inference based on fake arguments, intended to replace the lack of real arguments or to replace implicitly the subject of the discussion.[58][59][60]
Red herring – argument given in response to another argument, which is irrelevant and draws attention away from the subject of argument. See also irrelevant conclusion.
- Ad hominem – attacking the arguer instead of the argument.
- Poisoning the well – a type of ad hominem where adverse information about a target is presented with the intention of discrediting everything that the target person says.[61]
- Abusive fallacy – a subtype of "ad hominem" when it turns into verbal abuse of the opponent rather than arguing about the originally proposed argument.[62]
- Vacuous truth
- Appeal to authority (argumentum ab auctoritate) – where an assertion is deemed true because of the position or authority of the person asserting it.[63][64]
- Appeal to accomplishment – where an assertion is deemed true or false based on the accomplishments of the proposer.[65]
- Appeal to consequences (argumentum ad consequentiam) – the conclusion is supported by a premise that asserts positive or negative consequences from some course of action in an attempt to distract from the initial discussion.[66]
- Appeal to emotion – where an argument is made due to the manipulation of emotions, rather than the use of valid reasoning. [67]
- Appeal to fear – a specific type of appeal to emotion where an argument is made by increasing fear and prejudice towards the opposing side[68][69]
- Appeal to flattery – a specific type of appeal to emotion where an argument is made due to the use of flattery to gather support.[70]
- Appeal to pity (argumentum ad misericordiam) – an argument attempts to induce pity to sway opponents.[71]
- Appeal to ridicule – an argument is made by presenting the opponent's argument in a way that makes it appear ridiculous.[72][73]
- Appeal to spite – a specific type of appeal to emotion where an argument is made through exploiting people's bitterness or spite towards an opposing party.[74]
- Wishful thinking – a specific type of appeal to emotion where a decision is made according to what might be pleasing to imagine, rather than according to evidence or reason.[75]
- Appeal to equality – where an assertion is deemed true or false based on an assumed pretense of equality.[76]
- Appeal to motive – where a premise is dismissed by calling into question the motives of its proposer.
- Appeal to nature – wherein judgment is based solely on whether the subject of judgment is 'natural' or 'unnatural'.[77]
- Appeal to novelty (argumentum novitatis/antiquitatis) – where a proposal is claimed to be superior or better solely because it is new or modern.[78]
- Appeal to poverty (argumentum ad Lazarum) – supporting a conclusion because the arguer is poor (or refuting because the arguer is wealthy). (Opposite of appeal to wealth.)[79]
- Appeal to tradition (argumentum ad antiquitatem) – a conclusion supported solely because it has long been held to be true.[80]
- Appeal to wealth (argumentum ad crumenam) – supporting a conclusion because the arguer is wealthy (or refuting because the arguer is poor).[81] (Sometimes taken together with the appeal to poverty as a general appeal to the arguer's financial situation.)
- Argument from silence (argumentum ex silentio) – a conclusion based on silence or lack of contrary evidence.
- Argumentum ad baculum (appeal to the stick, appeal to force, appeal to threat) – an argument made through coercion or threats of force to support position.[82]
- Argumentum ad populum (appeal to widespread belief, bandwagon argument, appeal to the majority, appeal to the people) – where a proposition is claimed to be true or good solely because many people believe it to be so.[83]
- Association fallacy (guilt by association) – arguing that because two things share a property they are the same.[84]
- Bulverism (Psychogenetic Fallacy) – inferring why an argument is being used, associating it to some psychological reason, then assuming it is invalid as a result. It is wrong to assume that if the origin of an idea comes from a biased mind, then the idea itself must also be a falsehood.[41]
- Chronological snobbery – where a thesis is deemed incorrect because it was commonly held when something else, clearly false, was also commonly held.[85][86]
- Fallacy of relative privation – dismissing an argument due to the existence of more important, but unrelated, problems in the world.
- Genetic fallacy – where a conclusion is suggested based solely on something or someone's origin rather than its current meaning or context.[87]
- Judgmental language – insulting or pejorative language to influence the recipient's judgment.
- Naturalistic fallacy (is–ought fallacy,[88] naturalistic fallacy[89]) – claims about what ought to be on the basis of statements about what is.
- Reductio ad Hitlerum (playing the Nazi card) – comparing an opponent or their argument to Hitler or Nazism in an attempt to associate a position with one that is universally reviled. (See also – Godwin's law)
- Straw man – an argument based on misrepresentation of an opponent's position.[90]
- Texas sharpshooter fallacy – improperly asserting a cause to explain a cluster of data.[91]
- Tu quoque ("you too", appeal to hypocrisy, I'm rubber and you're glue) – the argument states that a certain position is false or wrong or should be disregarded because its proponent fails to act consistently in accordance with that position.[92]
- Two wrongs make a right – occurs when it is assumed that if one wrong is committed, another wrong will cancel it out.[93]
Conditional or questionable fallacies
- Broken window fallacy – an argument that disregards lost opportunity costs (typically non-obvious, difficult to determine or otherwise hidden) associated with destroying property of others, or other ways of externalizing costs onto others. For example, an argument that states breaking a window generates income for a window fitter, but disregards the fact that the money spent on the new window cannot now be spent on new shoes.[94]
- Definist fallacy – involves the confusion between two notions by defining one in terms of the other.[95]
- Naturalistic fallacy – attempts to prove a claim about ethics by appealing to a definition of the term "good" in terms of either one or more claims about natural properties (sometimes also taken to mean the appeal to nature) or God's will.[77]
- Slippery slope (thin edge of the wedge, camel's nose) – asserting that a relatively small first step inevitably leads to a chain of related events culminating in some significant impact/event that should not happen, thus the first step should not happen. While this fallacy is a popular one, it is, in its essence, an appeal to probability fallacy. (e.g. if person x does y then z would [probably] occur, leading to q, leading to w, leading to e.)[96] This is also related to the Reductio ad absurdum.
See also
- List of common misconceptions
- List of cognitive biases
- List of memory biases
- List of topics related to public relations and propaganda
- Sophistical Refutations, in which Aristotle presented thirteen fallacies
- Straight and Crooked Thinking (book)
- Mathematical fallacy
- List of paradoxes
- Reductio ad absurdum
References
- Notes
- ↑ Bunnin & Yu 2004, "formal fallacy".
- ↑ Leon, Joseph (23 April 2011). "Appeal to Probability". Logical & Critical Thinking. Archived from the original on 27 September 2013.
- ↑ McDonald, Simon (2009). "Appeal to probability". Toolkit For Thinking. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015.
- ↑ Curtis, "Fallacy Fallacy".
- ↑ "Base Rate Fallacy". Psychology Glossary. AlleyDog.com. Retrieved 2011-02-01.
- ↑ Straker, David. "Conjunction Fallacy". ChangingMinds.org. Retrieved 2011-02-01.
- ↑ Curtis, "The Masked Man Fallacy".
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Wilson 1999, p. 316.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Wilson 1999, p. 317.
- ↑ Pirie 2006, pp. 133–136.
- ↑ Wilson 1999, p. 316–317.
- ↑ Bunnin & Yu 2004, "informal fallacy".
- ↑ http://www.jstor.org/discover/10.2307/2709600
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 165.
- ↑ Carroll, Robert T. "The Skeptic's Dictionary". divine fallacy (argument from incredulity). Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- ↑ "Toolkit for Thinking".
- ↑ "Repetition". changingminds.org.
- ↑ http://www.toolkitforthinking.com/critical-thinking/anatomy-of-an-argument/inductive-logic-arguments/ad-nauseam
- ↑ http://www.toolkitforthinking.com/critical-thinking/anatomy-of-an-argument/inductive-logic-arguments/argument-from-silence
- ↑ Bo Bennett. "Argument from Silence". logicallyfallacious.com.
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 150.
- ↑ "Your logical fallacy is begging the question". Thou shalt not commit logical fallacies.
- ↑ "Fallacy: Begging the Question". nizkor.org.
- ↑ Bo Bennett. "Begging the Question". logicallyfallacious.com.
- ↑ "Begging the Question". txstate.edu.
- ↑ Dowden 2010, "Line-Drawing".
- ↑ Pirie 2006, p. 41.
- ↑ Feinberg, Joel (2007). "Psychological Egoism". In Shafer-Landau, Russ. Ethical Theory: An Anthology. Blackwell Philosophy Anthologies. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 193. ISBN 978-1-4051-3320-3.
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 121.
- ↑ Copi & Cohen 1990, p. 206.
- ↑ Fischer 1970, p. 119.
- ↑ Gula 2002, p. 70.
- ↑ Pirie 2006, p. 31.
- ↑ Pirie 2006, p. 53.
- ↑ Gula 2002, p. 97.
- ↑ "Fallacy – False Dilemma". Nizkor. The Nizkor Project. Retrieved 2011-02-01.
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 178.
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 186.
- ↑ Fischer 1970, p. 209.
- ↑ Bunnin & Yu 2004, "Homunculus".
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 "A List Of Fallacious Arguments". Retrieved 6 October 2012.
- ↑ Wimsatt, William K. and Monroe C. Beardsley. "The Intentional Fallacy." Sewanee Review, vol. 54 (1946): 468-488. Revised and republished in The Verbal Icon: Studies in the Meaning of Poetry, U of Kentucky P, 1954: 3-18.
- ↑ Copi & Cohen 1990, p. 105.
- ↑ Taleb, Nassim (2007). The Black Swan. Random House. p. 309. ISBN 1-4000-6351-5.
- ↑ "TheFreeDictionary". Naturalistic fallacy.
- ↑ John Searle, "How to Derive 'Ought' from 'Is'", The Philosophical Review, 73:1 (January 1964), 43-58
- ↑ Alex Walter, "The Anti-naturalistic Fallacy: Evolutionary Moral Psychology and the Insistence of Brute Facts", Evolutionary Psychology, 4 (2006), 33-48
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 180.
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 208.
- ↑ Semiotics Glossary R, Referential fallacy or illusion
- ↑ Gula 2002, p. 135.
- ↑ Pirie 2006, p. 5.
- ↑ Flew 1984, "No-true-Scotsman move".
- ↑ Hurley 2007, p. 155.
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 151.
- ↑ Hurley 2007, p. 134.
- ↑ Fischer 1970, p. 127.
- ↑ Gary Curtis. "Logical Fallacy: Red Herring". fallacyfiles.org.
- ↑ http://logical-critical-thinking.com/logical-fallacy/red-herring-fallacy/
- ↑ "Logical Fallacies". logicalfallacies.info.
- ↑ Walton 2008, p. 187.
- ↑ Bo Bennett. "Ad Hominem (Abusive)". logicallyfallacious.com.
- ↑ Clark & Clark 2005, pp. 13–16.
- ↑ Walton 1997, p. 28.
- ↑ Bo Bennett. "Appeal to Accomplishment". logicallyfallacious.com.
- ↑ Walton 2008, p. 27.
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 111.
- ↑ Bo Bennett. "Appeal to Fear". logicallyfallacious.com.
- ↑ "Appeal to Fear". changingminds.org.
- ↑ Gula 2002, p. 12.
- ↑ Walton 2008, p. 128.
- ↑ "Appeal to Ridicule". changingminds.org.
- ↑ Bo Bennett. "Appeal to Ridicule". logicallyfallacious.com.
- ↑ "Appeal to Spite". changingminds.org.
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 146.
- ↑ Bo Bennett. "B-List Fallacies". logicallyfallacious.com.
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 Gary Curtis. "Logical Fallacy: Appeal to Nature". fallacyfiles.org.
- ↑ Pirie 2006, p. 116.
- ↑ Pirie 2006, p. 104.
- ↑ Pirie 2006, p. 14.
- ↑ Pirie 2006, p. 39.
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 106.
- ↑ "Appeal to Widespread Belief". Retrieved 6 October 2012.
- ↑ Gary Curtis. "Logical Fallacy: Guilt by Association". fallacyfiles.org.
- ↑ http://davidlavery.net/Barfield/Encyclopedia_Barfieldiana/Lexicon/Chronological.html
- ↑ http://www.davidbergan.com/Summa/Chronological_snobbery
- ↑ Damer 2009, p. 93.
- ↑ Dowden 2010, "Is-Ought".
- ↑ Dowden 2010, "Naturalistic".
- ↑ Walton 2008, p. 22.
- ↑ Curtis, "The Texas Sharpshooter Fallacy".
- ↑ Pirie 2006, p. 164.
- ↑ Johnson & Blair 1994, p. 122.
- ↑ Beggs, Jodi. "The Broken Window Fallacy".
- ↑ Frankena, W. K. (October 1939). "The Naturalistic Fallacy". Mind (Oxford University Press) 48 (192): 464–477. JSTOR 2250706.
- ↑ Walton 2008, p. 315.
- Works
- Bunnin, Nicholas; Yu, Jiyuan, eds. (2004). The Blackwell Dictionary of Western Philosophy. Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-0679-5.
- Clark, Jef; Clark, Theo (2005). Humbug! The Skeptic's Field Guide to Spotting Fallacies in Thinking. Nifty Books. ISBN 0-646-44477-8. Also available as an ebook.
- Copi, Irving M.; Cohen, Carl (1990). Introduction to Logic (8th ed.). Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-02-325035-4.
- Curtis, Gary N. Logical Fallacies: The Fallacy Files. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- Damer, T. Edward (2009). Attacking Faulty Reasoning: A Practical Guide to Fallacy-free Arguments (6th ed.). Wadsworth. ISBN 978-0-495-09506-4. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- Dowden, Bradley (December 31, 2010). "Fallacy". The Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. ISSN 2161-0002. Retrieved 2011-04-22.
- Fischer, David Hackett (1970). Historians' Fallacies: Toward a Logic of Historical Thought. HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-06-131545-9.
- Flew, Antony (1984). "A Dictionary of Philosophy: Revised Second Edition". A Dictionary of Philosophy. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-312-20923-0.
- Gula, Robert J. (2002). Nonsense: Red Herrings, Straw Men and Sacred Cows: How We Abuse Logic in Our Everyday Language. Axios Press. ISBN 978-0-9753662-6-4.
- Hurley, Patrick J. (2007). A Concise Introduction to Logic (10th ed.). Cengage. ISBN 978-0-495-50383-5.
- Johnson, Ralph H.; Blair, J. Anthony (1994). Logical Self-Defense. IDEA. ISBN 978-1-932716-18-4.
- Pirie, Madsen (2006). How to Win Every Argument: The Use and Abuse of Logic. Continuum International Publishing Group. ISBN 0-8264-9006-9.
- Wilson, W. Kent (1999). "Formal fallacy". In Audi, Robert. The Cambridge Dictionary of Philosophy (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 316–317. ISBN 978-0-511-07417-2.
- Walton, Douglas (1997). Appeal to Expert Opinion: Arguments from Authority. Pennsylvania State University. ISBN 0-271-01694-9 Paperback ISBN 0-271-01695-7
- Walton, Douglas (2008). Informal Logic: A Pragmatic Approach (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-511-40878-6.
Further reading
The following is a sample of books for further reading, selected for a combination of content, ease of access via the internet, and to provide an indication of published sources that interested readers may review. The titles of some books are self-explanatory. Good books on critical thinking commonly contain sections on fallacies, and some may be listed below.
- Engel, S. Morris (1994). Fallacies and Pitfalls of Language: The Language Trap. Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-28274-0. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- Hughes, William; Lavery, Jonathan (2004). Critical Thinking: An Introduction to the Basic Skills (4th ed.). Broadview Press. ISBN 1-55111-573-5. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- Paul, Richard; Elder, Linda (2006). Thinker's Guide to Fallacies: The Art of Mental Trickery. Foundation for Critical Thinking. ISBN 978-0-944583-27-2. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- Sinnott-Armstrong, Walter; Fogelin, Robert (2010). Understanding Arguments: An Introduction to Informal Logic (8th ed.). Wadsworth Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0-495-60395-5. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- Thouless, Robert H (1953). Straight and Crooked Thinking (PDF). Pan Books. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- Tindale, Christopher W (2007). Fallacies and Argument Appraisal. Critical Reasoning and Argumentation. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-84208-2. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
External links
- Logical Fallacies, Literacy Education Online
- LogicalFallacies.info
- Informal Fallacies, Texas State University page on informal fallacies.
- Stephen's Guide to the Logical Fallacies (mirror)
- The Taxonomy of Logical Fallacies, FallacyFiles.org
- Visualization: Rhetological Fallacies, InformationIsBeautiful.net
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||