List of U.S. states by date of admission to the Union
This is a list of U.S. states by date of admission to the Union. Although the first 13 states can be considered to have been members of the United States from the date of the Declaration of Independence – July 4, 1776 – or from the date on which they ratified the Articles of Confederation, they are presented here as being "admitted" on the date each ratified the present United States Constitution; most other such lists, including the 50 State Quarters program, do the same.
The admission dates for later states were set by either the act of admission or a later resolution issued under that act, except for Ohio, whose date of admission was determined by act of Congress in 1953 as March 1, 1803, when its legislature first met because of a clerical error of omission—the original act omitted setting a date that the act took effect.[note 1]
This list does not account for the secession of 11 states during the American Civil War to form the Confederate States of America, the subsequent restoration of those states to representation in Congress (sometimes called "readmission") between 1866 and 1870, or the end of Reconstruction in those states. Since their secession was declared illegal by the U.S. Supreme Court in the case of Texas v. White, the federal government does not give legal recognition to their having left the Union. The list also does not account for secessionist governments formed in two other states, as their Unionist governments generally remained in control.
Map

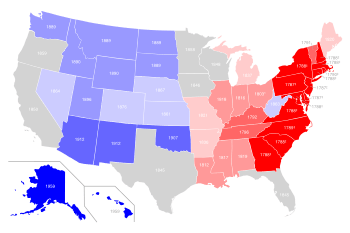
Table
Ratifications of the Constitution by the thirteen original states
The Constitution went into effect upon ratification by nine of the thirteen states. The status of the first eight as members of the federal Union in the form established by the Constitution did not exist until the ninth state, New Hampshire, ratified the Constitution in June 1788. None of the first thirteen states became states upon ratifying the Constitution, since all were already states before that.
| # | State | Date of ratification | Before Statehood | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delaware | December 7, 1787[1] | Lower Counties on Delaware (prior to becoming a sovereign state within the United States of America)[2] | |
| 2 | Pennsylvania | December 12, 1787[3] | Province of Pennsylvania[4] | |
| 3 | New Jersey | December 18, 1787[5] | Province of New Jersey (prior to becoming a sovereign state within the United States of America) | |
| 4 | Georgia | January 2, 1788[6] | Province of Georgia | |
| 5 | Connecticut | January 9, 1788[7] | Connecticut Colony[8] | |
| 6 | Massachusetts | February 6, 1788 | Province of Massachusetts Bay | |
| 7 | Maryland | April 28, 1788 | Province of Maryland | |
| 8 | South Carolina | May 23, 1788 | Province of South Carolina | |
| 9 | New Hampshire | June 21, 1788 | Province of New Hampshire | |
| 10 | Virginia | June 25, 1788 | Virginia Colony | |
| 11 | New York | July 26, 1788 | Province of New York | |
| 12 | North Carolina | November 21, 1789 | Province of North Carolina | |
| 13 | Rhode Island | May 29, 1790 | Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations | |
Admissions of new states beyond the thirteen original states
| # | State | Date of admission | Before Statehood | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | Vermont | March 4, 1791 | Republic of Vermont (formed upon land claimed by both New York and New Hampshire).[note 2] | |
| 15 | Kentucky | June 1, 1792 | Part of Virginia, seceded with approval of the Virginia General Assembly | |
| 16 | Tennessee | June 1, 1796 | Southwest Territory | |
| 17 | Ohio | March 1, 1803[note 1] | Northwest Territory | |
| 18 | Louisiana | April 30, 1812 | Territory of Orleans | |
| 19 | Indiana | December 11, 1816 | Indiana Territory | |
| 20 | Mississippi | December 10, 1817 | Mississippi Territory | |
| 21 | Illinois | December 3, 1818 | Illinois Territory | |
| 22 | Alabama | December 14, 1819 | Alabama Territory | |
| 23 | Maine | March 15, 1820 | Part of Massachusetts, seceded with approval of the Massachusetts General Court) | |
| 24 | Missouri | August 10, 1821 | Missouri Territory (initially organized as the Louisiana Territory) | |
| 25 | Arkansas | June 15, 1836 | Arkansas Territory (initially organized as the Territory of Arkansaw) | |
| 26 | Michigan | January 26, 1837 | Michigan Territory | |
| 27 | Florida | March 3, 1845 | Florida Territory | |
| 28 | Texas | December 29, 1845 | Republic of Texas (granted statehood simultaneously with annexation) | |
| 29 | Iowa | December 28, 1846 | Iowa Territory | |
| 30 | Wisconsin | May 29, 1848 | Wisconsin Territory | |
| 31 | California | September 9, 1850 | California Military District[note 3] | |
| 32 | Minnesota | May 11, 1858 | Minnesota Territory | |
| 33 | Oregon | February 14, 1859 | Oregon Territory | |
| 34 | Kansas | January 29, 1861 | Kansas Territory | |
| 35 | West Virginia | June 20, 1863 | Part of Virginia, seceded with approval of the pro-Union Virginia government, but not the Virginia government in rebellion | |
| 36 | Nevada | October 31, 1864 | Nevada Territory | |
| 37 | Nebraska | March 1, 1867 | Nebraska Territory | |
| 38 | Colorado | August 1, 1876 | Colorado Territory | |
| 39 | North Dakota | November 2, 1889[note 4] | Dakota Territory | |
| 40 | South Dakota | November 2, 1889[note 4] | Dakota Territory | |
| 41 | Montana | November 8, 1889 | Montana Territory | |
| 42 | Washington | November 11, 1889 | Washington Territory | |
| 43 | Idaho | July 3, 1890 | Idaho Territory | |
| 44 | Wyoming | July 10, 1890 | Wyoming Territory | |
| 45 | Utah | January 4, 1896 | Utah Territory | |
| 46 | Oklahoma | November 16, 1907 | Oklahoma Territory and Indian Territory | |
| 47 | New Mexico | January 6, 1912 | New Mexico Territory | |
| 48 | Arizona | February 14, 1912 | Arizona Territory | |
| 49 | Alaska | January 3, 1959 | Territory of Alaska | |
| 50 | Hawaii | August 21, 1959 | Territory of Hawaii | |
- Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Congress recognized the state of Ohio on February 19, 1803 ("An act to provide for the due execution of the laws of the United States, within the state of Ohio", Seventh Congress, Session II, Chapter VII), but no formal date of statehood was set by the act of admission or a later resolution, as occurred with all other new states. On August 7, 1953, Congress passed a law retroactively setting the date of Ohio's statehood at March 1, 1803, the date when Ohio's first legislature convened.
- ↑ Unlike most later instances, this was not really a separate entity. When a state is formed within a territory and encompasses less than the whole territory, then the state is a new entity. When a whole territory becomes a state, the state is a new entity whose constitution, governor, legislature, are distinct from those of the territory that preceded it. However, the state of Vermont simply continued to exist as a state under the same state constitution that it had already, with the same governor and legislators continuing their terms of office. Rather than being a new entity, it was a state whose status changed to one that was admitted to the Union.
- ↑ Although the Republic of California, also known as the Bear Flag Republic, was declared on June 14, 1846 by Anglo-American settlers in Sonoma, that lasted only for 26 days, and never achieved internal or external recognition.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 The actual statehood proclamations for North and South Dakota were intentionally shuffled so it is unknown which state was admitted first. President Benjamin Harrison always refused to tell the order in which he had signed the two statehood bills. However, North Dakota's proclamation was published first in the "Statutes at Large", since it is first in alphabetical order.
See also
- Enabling Act of 1802, for the formation of Ohio from the Northwest Territory
- Enabling Act of 1889, for the formation of North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington
- Texas annexation of 1845 and the subsequent legal status of Texas
- Enabling Act of 1906 for the formation of Oklahoma from Oklahoma Territory and Indian Territory
- Alaska Statehood Act (signed July 7, 1958) and the subsequent legal status of Alaska
- Hawaii Admission Act (enacted March 18, 1959) and the subsequent legal status of Hawaii
- 51st state
- District of Columbia statehood movement
- Puerto Rico (proposed state) and the political status of Puerto Rico
- Territories of the United States
- Territories of the United States on stamps
Footnotes
- ↑ "Dec 7, 1787: Delaware ratifies the Constitution". The History Channel. Retrieved 3 April 2012.
- ↑ "State of Delaware (A brief history)". The State of Delaware. Retrieved 3 April 2012.
- ↑ "Today in History: December 12". The Library of Congress. Retrieved 3 April 2012.
- ↑ "Charter for the Province of Pennsylvania-1681". Yale Law School, Lillian Goldman Law Library. Retrieved 3 April 2012.
- ↑ "New Jersey's Ratification". U.S. Constitution Online. Retrieved 3 April 2012.
- ↑ United States Census Office. "Dates of Statehood for 50 U.S. States". Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ↑ "Connecticut State Quarter". Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ↑ "About Connecticut". Retrieved 19 April 2012.
References
- "50 State Quarter Program". United States Mint. Retrieved January 19, 2006. (including dates of statehood)
- "Dates of statehood". 50states.com. Retrieved January 19, 2006. (includes notes)
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||