List of HVDC projects
This is a list of notable high-voltage direct-current power transmission projects.
HVDC projects for long-distance transmission have two (or rarely, more) converter stations and a transmission line interconnecting them. Generally overhead lines are used for interconnection, but an important class of HVDC projects use submarine power cables. A back-to-back station has no transmission line and connects two AC grids at different frequencies or phase counts. Historical HVDC systems used the Thury system of motor-generators but these have all been made obsolete by later developments such as mercury-arc valves, thyristors, and IGBT power transistors.
Legend
Line type:
- Thury = Series-connected generators as designed by René Thury
- Merc = Mercury-arc valve rectifier and inverter
- Thyr = Thyristor rectifier and inverter
- IGBT = Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors
Line status:
Transmission lines
Africa
| Name |
Converter station 1 |
Converter station 2 |
Total Length (Cable/Pole) (km) |
Volt (kV) |
Power (MW) |
Year |
Type |
Remarks |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cahora Bassa | Mozambique - Songo 15°36′41″S 32°44′59″E / 15.61139°S 32.74972°E | South Africa - Apollo 25°55′11″S 28°16′34″E / 25.91972°S 28.27611°E | 1420 (0/1420) | 533 | 1920 | 1979 | Thyr | First HVDC with voltage above 500 kV ABB refurb 2013-2014 |
[1][2][3] |
| Inga-Shaba | Democratic Republic of Congo - Kolwezi 10°39′27″S 25°27′08″E / 10.65750°S 25.45222°E | Democratic Republic of Congo - Inga 05°31′27″S 13°36′39″E / 5.52417°S 13.61083°E | 1700 (0/1700) | 500 | 560 | 1982 | Thyr | Upgraded in 2014 Supplier: ABB, GE | [1][4][5][6] |
| Caprivi Link | Namibia - Gerus 20°18′53″S 16°27′9″E / 20.31472°S 16.45250°E | Namibia - Zambezi 17°30′6″S 24°13′20″E / 17.50167°S 24.22222°E | 950 (950/0) | 350 | 300 | 2010 | IGBT | Supplier: ABB | [1][7] |
Australia and Oceania
| Name |
Converter station 1 |
Converter station 2 |
Total Length (Cable/Pole) (km) |
Volt (kV) |
Power (MW) |
Year |
Type |
Remarks |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HVDC Inter-Island 1 | New Zealand - Benmore 44°33′55″S 170°11′24″E / 44.56528°S 170.19000°E | New Zealand - Haywards 41°9′1″S 174°58′52″E / 41.15028°S 174.98111°E | 611 (40/571) | 270 | 600 | 1965 | Merc | Built as 250 kV 600 MW link Paralleled to operate at 270 kV as positive pole with HVDC Inter-Island 2 in 1992. Partially decommissioned in 2007, fully decommissioned in August 2012. Supplier: ABB |
[1] |
| HVDC Inter-Island 2 | New Zealand - Benmore 44°33′55″S 170°11′24″E / 44.56528°S 170.19000°E | New Zealand - Haywards 41°9′1″S 174°58′52″E / 41.15028°S 174.98111°E | 611 (40/571) | 350 | 700 | 1992 | Thyr | Negative pole, operates in bipole configuration with HVDC Inter-Island 3 (previously HVDC Inter-Island 1) Restricted to 500 MW due to cable rating. Supplier: ABB | [1] |
| HVDC Inter-Island 3 | New Zealand - Benmore 44°33′55″S 170°11′24″E / 44.56528°S 170.19000°E | New Zealand - Haywards 41°9′1″S 174°58′52″E / 41.15028°S 174.98111°E | 611 (40/571) | 350 | 735 | 2013 | Thyr | Positive pole, operates in bipole configuration with HVDC Inter-Island 2 Supplier: Siemens | [8] |
| Terranora interconnector (Directlink) | Australia - Mullumbimby 28°34′15″S 153°27′8″E / 28.57083°S 153.45222°E | Australia - Bungalora 28°15′20″S 153°28′20″E / 28.25556°S 153.47222°E | 59 (59/0) | 80 | 180 | 2000 | IGBT | Land cable Supplier: ABB | [1] |
| Murraylink | Australia - Red Cliffs 34°17′31″S 142°14′19″E / 34.29194°S 142.23861°E | Australia - Berri 34°14′17″S 140°36′01″E / 34.23806°S 140.60028°E | 176 (176/0) | 150 | 200 | 2002 | IGBT | Underground XLPE cable Supplier: ABB | [1] |
| Basslink | Australia - LoyYang, Vic 38°15′45″S 146°36′29″E / 38.26250°S 146.60806°E | Australia - GeorgeTown, Tas 41°6′53″S 146°53′31″E / 41.11472°S 146.89194°E | 370 (298/72) | 400 | 500 | 2006 | Thyr | One of the longest HVDC cable in operation Supplier: Siemens | [1][9][10] |
Asia
| Name | Converter station 1 |
Converter station 2 |
Total Length (Cable/Pole) (km) |
Volt (kV) |
Power (MW) |
Year |
Type |
Remarks |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hokkaido - Honshu | Japan - Hakodate 41°55′55″N 140°39′47″E / 41.93194°N 140.66306°E | Japan - Kamikita 40°48′06″N 141°11′52″E / 40.80167°N 141.19778°E | 193 (44/149) | 250 | 300 | 1979 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB, Hitachi, Toshiba | [1] |
| Zhou Shan | China - Ningbo 29°55′25″N 121°46′51″E / 29.92361°N 121.78083°E | China - Gao Tongge 30°02′13″N 122°04′03″E / 30.03694°N 122.06750°E | 54 (12/42) | 100 | 50 | 1982 | Thyr | [1] | |
| Gezhouba - Shanghai | China - Gezhouba 30°43′44″N 111°14′39″E / 30.72889°N 111.24417°E | China - Nan Qiao 30°57′22″N 121°24′48″E / 30.95611°N 121.41333°E | 1046 (0/1046) | 500 | 1200 | 1989 | Thyr | Power line shares pylons of HVDC Hubei - Shanghai in most part of its track
Supplier: ABB,Siemens |
[11] |
| Sileru-Barsoor | India - Sileru 17°52′01″N 81°39′21″E / 17.86694°N 81.65583°E | India - Barsoor 19°8′20″N 81°23′47″E / 19.13889°N 81.39639°E | 196 (0/196) | 200 | 100 | 1989 | Thyr | Supplier: BHEL | [1] |
| Ekibastuz–Tambov | Kazakhstan - Ekibastuz 51°52′53″N 75°13′3″E / 51.88139°N 75.21750°E | Russia - Tambov 52°46′25″N 41°19′17″E / 52.77361°N 41.32139°E | 2414 (0/2414) | 750 | 6000 | (1990) | Thyr | Abandoned around 1990 owing to collapse of Soviet Union | |
| Rihand-Delhi | India - Rihand 24°01′13″N 82°47′21″E / 24.02028°N 82.78917°E | India - Dadri 28°35′36″N 77°36′16″E / 28.59333°N 77.60444°E | 814 (0/814) | 500 | 1500 | 1990 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB, BHEL | [12] |
| Haenam-Cheju | South Korea - Haenam 34°22′03″N 126°35′34″E / 34.36750°N 126.59278°E | South Korea - Jeju 33°32′06″N 126°35′44″E / 33.53500°N 126.59556°E | 101 (101/0) | 180 | 300 | 1996 | Thyr | Supplier: Alstom | [1] |
| Chandrapur-Padghe | India - Chandrapur 20°0′36″N 79°17′06″E / 20.01000°N 79.28500°E | India - Padghe 19°21′26″N 73°11′18″E / 19.35722°N 73.18833°E | 752 (0/752) | 500 | 1500 | 1999 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [13] |
| Leyte - Luzon | Philippines - Ormoc, Leyte 11°5′19″N 124°38′21″E / 11.08861°N 124.63917°E | Philippines - Naga, Camarines Sur 13°36′40″N 123°14′19″E / 13.61111°N 123.23861°E | 451 (21/430) | 350 | 440 | 1998 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB, Marubeni | [1] |
| Kii Channel | Japan - Anan 33°49′40″N 134°38′14″E / 33.82778°N 134.63722°E | Japan - Kihoku 34°12′50″N 135°30′07″E / 34.21389°N 135.50194°E | 100 (50/50) | 250 | 1400 | 2000 | Thyr | Supplier: Hitachi, Toshiba, Mitsubishi | [1] |
| Tian-Guang | China - Tianshengqiao 24°54′56″N 105°05′47″E / 24.91556°N 105.09639°E | China - Beijiao 23°18′58″N 113°15′05″E / 23.31611°N 113.25139°E | 960 (0/960) | 500 | 1800 | 2001 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [1] |
| Talcher-Kolar | India - Talcher, Orissa 21°06′01″N 85°03′49″E / 21.10028°N 85.06361°E | India - Kolar, Karnataka 13°10′39″N 78°7′0″E / 13.17750°N 78.11667°E | 1450 (0/1450) | 500 | 2000 | 2003 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [1] |
| Thailand-Malaysia | Thailand - Khlong Ngae 6°42′56″N 100°27′8″E / 6.71556°N 100.45222°E | Malaysia - Gurun 5°48′45″N 100°32′6″E / 5.81250°N 100.53500°E | 110 (0/110) | 300 | 300 | 2001 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [1] |
| Three Gorges - Changzhou | China - Longquan 30°47′6″N 111°31′48″E / 30.78500°N 111.53000°E | China - Zhengping 31°36′42″N 119°59′27″E / 31.61167°N 119.99083°E | 890 (0/890) | 500 | 3000 | 2003 | Thyr | From north bank of Three Gorges to Zhengping, 200 km from Shanghai in the East grid Supplier: ABB, Siemens. Sharing of grounding electrode at Chujiahu with HVDC Hubei-Shanghai | [1][14][15] |
| Three Gorges - Guangdong | China - Jingzhou 30°27′26″N 112°08′18″E / 30.45722°N 112.13833°E | China - Huizhou 23°16′15″N 114°12′5″E / 23.27083°N 114.20139°E | 940 (0/940) | 500 | 3000 | 2004 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [1][16] |
| Three Gorges - Shanghai | China - Yidu 30°31′45″N 111°22′35″E / 30.52917°N 111.37639°E | China - Shanghai 31°14′13″N 121°11′13″E / 31.23694°N 121.18694°E | 1060 (0/1060) | 500 | 3000 | 2006 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [1][17] |
| Guizhou - Guangdong I | China - Anshun, Guizhou 26°16′23″N 105°48′21″E / 26.27306°N 105.80583°E | China - Zhaoqing, Guangdong 22°54′57″N 112°29′11″E / 22.91583°N 112.48639°E | 980 (0/980) | 500 | 3000 | 2004 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [1] |
| Guizhou - Guangdong II | China - Xingren 25°27′56″N 105°15′14″E / 25.46556°N 105.25389°E | China - Shenzhen 22°45′1″N 113°59′28″E / 22.75028°N 113.99111°E | 1200 (0/1200) | 500 | 3000 | 2007 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens, Sharing of grounding electrode at Linwu with HVDC Yunnan - Guangdong | [1] |
| Ballia - Bhiwadi | India - Ballia 26°04′16″N 83°42′48″E / 26.07111°N 83.71333°E | India - Bhiwadi 28°11′0″N 76°48′58″E / 28.18333°N 76.81611°E | 800 (0/800) | 500 | 2500 | 2010 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [1] |
| Xiangjiaba-Shanghai | China - Fulong 28°32′47″N 104°25′04″E / 28.54639°N 104.41778°E | China - Fengxia 30°55′32″N 121°46′16″E / 30.92556°N 121.77111°E |
1980 (0/1980) | 800 | 6400 | 2010 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [1][18] |
| Yunnan - Guangdong | China - Yunnan province | China - Zengcheng 23°15′19″N 113°40′44″E / 23.25528°N 113.67889°E | 1418 (0/1418) | 800 | 5000 | 2010 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens, Sharing of grounding electrode at Linwu with HVDC Guizhou - Guangdong II | [1] |
| Qinghai - Tibet | China - Geermu 36°21′20″N 95°11′05″E / 36.35556°N 95.18472°E | China - Lhasa 29°52′39″N 91°11′44″E / 29.87750°N 91.19556°E | 1038 (0/1038) | 400 | 1500 | Scheduled 2012 | Thyr | Powerline reaches altitudes up to 5300 m above sea level Supplier: CET, SGCC | [1] |
| Ningdong - Shangdong | China - Yinchuan 38°06′56″N 106°30′55″E / 38.11556°N 106.51528°E | China - Qingdao 36°18′41″N 119°52′53″E / 36.31139°N 119.88139°E | 1335 (0/1335) | 660 | 4000 | 2011 | Thyr | Supplier: Alstom | [1] |
| Ningxia - Tianjing | China - Ningxia | China - Tianjing | 3000 | 2010 | Thyr | ??? | |||
| Baoji - Denyang | China - Baoji | China - Denyang 31°19′22″N 104°34′51″E / 31.32278°N 104.58083°E | 500 | 3000 | 2010 | Thyr | ??? | ||
| Hulunbeir - Liaoning | China - Hulunbeir 48°31′04″N 119°43′30″E / 48.51778°N 119.72500°E | China - Shenyang 41°07′25″N 122°46′44″E / 41.12361°N 122.77889°E | 920 (0/920) | 500 | 3000 | 2010 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [1][19] |
| North Shaanxi - Shandong | China | China | 3000 | 2011 | Thyr | ??? | |||
| Hubei - Shanghai | China - Jingmen 30°49′21″N 112°07′15″E / 30.82250°N 112.12083°E | China - Fenjing 30°52′00″N 121°00′58″E / 30.86667°N 121.01611°E | 970 (0/970) | 500 | 3000 | 2011 | Thyr | Power line shares pylons of HVDC Gezhouba - Shanghai in most part of its track, sharing of grounding electrode at Chujiahu with HVDC Shanghai-Changzhou | ??? |
| Sumatera - Java | Indonesia - Java | Indonesia - Sumatera | 700 (700/0) | 500 | 3000 | Under construction 2013 | Thyr | [1] | |
| Jindo - Jeju | Korea- Jeju | Korea - Jindo | 105 (105/0) | 250 | 400 | 2011 | Thyr | Supplier: Alstom | [1] |
| Nanhui Wind Farm Integration | China | China | 8.4 (8.4/0) | 30 | 18 | 2011 | IGBT | [20] | |
| Jinping - Sunan | China-Jinping | China-Suzhou | 2090 (0/2090) | 800 | 7200 | 2013 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [21] |
| Mundra - Haryana | India - Mundra 22°49′46″N 69°33′22″E / 22.82944°N 69.55611°E | India - Mohindergarh 28°21′40″N 76°12′56″E / 28.36111°N 76.21556°E | 960 (0/960) | 500 | 2500 | Under construction 2012 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [1] |
| Xiluodo - Guangdong | China - Zhaotong | China - Conghua | 1286 (0/1286) | 500 | 6400 | 2013 | Thyr | ??? | |
| Jinhong - Thailand | China | Thailand | 3000 | 2013 | Thyr | ??? | |||
| Dalian City Infeed | China - Dalian North | China - Dalian South | 43 (43/0) | 320 | 1000 | 2013? | Thy | [22] | |
| Xiluodo - West Zhejiang | China-Xiluodu | China-Jinghua | 1680 | 800 | 8000 | 2014 | Thyr | ??? | |
| North-East Agra | India - Agra 27°05′01″N 78°04′22″E / 27.08361°N 78.07278°E | India - Biswanath | 1728 (0/1728) | 800 | 6000 | Planned commissioning 2016 | Thyr | Will supply electricity to serve 90 million people Bipole Ultra high voltage, multiterminal (intermediate converter station at Alipurdauar) Suplier: ABB | [23] |
| Naoao Multi-terminal VSC HVDC | China | China | 32 (10/32) | +/-160 | 200/100/50 | 2013 | IEGT/IGBT | SEPRI (Electric Power Research Institute, China Southern Power Grid) is technically responsible for the entire project. Multiple suppliers are involved: three different VSC HVDC valve suppliers, two different HVDC land/sea cable suppliers and three different control & protection system/equipment suppliers. | [24] |
| Zhoushan Multi-terminal DC Interconnection | China | China | 134 (134/0) | 200 | 400 | ? | IGBT | [26] | |
| Humeng - Shandong | China | China | 800 | 6400 | 2015 | Thyr | ??? | ||
| Xiluodo - Hanzhou | China | China | 800 | 6400 | 2015 | Thyr | ??? | ||
| Irkutsk - Beijing | Russia - Irkutsk | China - Beijing | 800 | 6400 | 2015 | Thyr | ??? | ||
| Nuozhadu - Guangdong | China | China | 1413 | 800 | 6400 | 2013 | Thyr | ??? | |
| Jinsha River II - East China | China | China | 800 | 6400 | 2016 | Thyr | ??? | ||
| Goupitan - Guangdong | China | China | 3000 | 2016 | Thyr | ??? | |||
| Humeng - Liaoning | China | China | 800 | 6400 | 2018 | Thyr | ??? | ||
| Hami - Central China | China-Hami | China-Zhengzhou | 2192 | 800 | 6400 | 2014 | Thyr | ??? | |
| Jinsha River II - Fujian | China | China | 800 | 6400 | 2018 | Thyr | ??? | ||
| Humeng - Liaoning | China | China | 800 | 6400 | 2018 | Thyr | ??? | ||
| Bakun HVDC | Malaysia - Similajau | Malaysia - Bentong | 1700 (670/1030) | 500 | ? | ? | Thyr | Unfinished | ??? |
| Shanghai - Shensi | Shanghai – China | Shensi – China | 123 (63/60) | 50 | ? | ? | Thyr | ??? |
Europe
| Name |
Converter station 1 |
Converter station 2 |
Total Length (Cable/Pole) (km) |
Volt (kV) |
Power (MW) |
Year |
Type |
Remarks |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miesbach-Munich Power Transmission | Germany - Miesbach | Germany - Munich | 58 (0/58) | 2 | 0.0025 | 1882 | Single machine | Demonstration facility
Dismantled |
|
| Gorzente River - Genoa DC transmission scheme | Italy - Gorzente River | Italy - Genoa | ? | 6 | ? | 1889 | Thury | Upgraded later to a voltage of 14 kV, power of 2.5 MW and a length of 120 km
Dismantled |
|
| La Chaux-de-Fonds DC transmission scheme | Switzerland - ? | Switzerland - ? | ? | 14 | ? | 1897 | Thury | Dismantled | |
| St. Maurice - Lausanne DC transmission scheme | Switzerland - St. Maurice | Switzerland - Lausanne | ? | 22 | 3.7 | 1899 | Thury | Dismantled | |
| Lyon-Moutiers DC transmission scheme | France - Lyon | France - Moutiers | 200 (10/190) | 75 | 30 | 1906 | Thury | Dismantled in 1936 | |
| Wilesden-Ironbridge DC transmission scheme | UK - Wilesden | UK - Ironbridge | ? | 100 | ? | 1910 | Thury | Dismantled | |
| Chambéry DC transmission scheme | France - ? | France - ? | ? | 150 | ? | 1925 | Thury | Dismantled in 1937 | |
| HVDC Zurich-Wettingen | Switzerland - Wettingen 47°27′25″N 8°19′15″E / 47.45694°N 8.32083°E | Switzerland - Zurich | 20 (0/20) | 50 | 0.5 | 1939 | Merc | Experimental facility built by BBC
Dismantled |
|
| HVDC Charlottenburg-Moabit | Germany - Berlin-Moabit | Germany - Berlin-Charlottenburg | 4.6 (0/4.6) | 100 | 14 | 1942 | Merc | Experimental facility built by Siemens
Dismantled in 1945 |
|
| Lehrte-Misburg HVDC | Germany - Lehrte 52°22′54″N 9°55′03″E / 52.38167°N 9.91750°E | Germany - Hannover/Misburg | ? | 80 | 16 | 1944 | Merc | Experimental facility
Dismantled |
|
| Elbe-Project | Germany, Vockerode 51°50′40″N 12°21′50″E / 51.84444°N 12.36389°E | Germany - Berlin, Marienfelde 52°25′49″N 13°22′42″E / 52.43028°N 13.37833°E | 115 (115/0) | 200 | 60 | 1945 | Merc | Never placed in service
Dismantled |
|
| HVDC Trollhattan-Merud | Sweden - Trollhattan | Sweden - Merud | 50 (0/50) | 45 | 6.5 | 1946 | Merc | Experimental facility built by ASEA
Dismantled |
|
| Moscow–Kashira | Russia - Moscow 55°39′32″N 37°38′16″E / 55.65889°N 37.63778°E | Russia - Kashira | 100 (100/0) | 200 | 30 | 1951 | Merc | Built of parts of HVDC Elbe-Project
Shut down |
[1] |
| Gotland 1 | Sweden - Västervik 57°43′41″N 16°38′51″E / 57.72806°N 16.64750°E | Sweden - Yigne 57°35′13″N 18°11′44″E / 57.58694°N 18.19556°E | 98 (98/0) | 200 | 20 | 1954 | Merc | World's first commercial HVDC link. Expanded by ABBin 1970, decommissioned in 1986 | [1][27] |
| Cross-Channel | France - Echingen 50°41′48″N 1°38′21″E / 50.69667°N 1.63917°E | UK - Lydd 50°54′54″N 0°56′50″E / 50.91500°N 0.94722°E | 64 (64/0) | 100 | 160 | 1961 | Merc | Shut down in 1984 | [1] |
| Volgograd-Donbass | Russia - Volzhskaya 48°49′34″N 44°40′20″E / 48.82611°N 44.67222°E | Ukraine - Mikhailovskaya 48°39′13″N 38°33′56″E / 48.65361°N 38.56556°E | 475 (0/475) | 400 | 750 | 1965 | Merc/Thyr | Shut down in 2014 | [1] |
| Konti-Skan 1 | Denmark - Vester Hassing 57°3′46″N 10°5′24″E / 57.06278°N 10.09000°E | Sweden - Stenkullen 57°48′15″N 12°19′13″E / 57.80417°N 12.32028°E | 176 (87/89) | 250 | 250 | 1965 | Merc | Replaced in August 2006 by modern converters using thyristors | [1] |
| SACOI 1 | Italy - Suvereto 43°3′10″N 10°41′42″E / 43.05278°N 10.69500°E ( before 1992: Italy - San Dalmazio 43°15′43″N 10°55′05″E / 43.26194°N 10.91806°E) | France- Lucciana 42°31′40″N 9°26′59″E / 42.52778°N 9.44972°E ; Codrongianos, Italy 40°39′7″N 8°42′48″E / 40.65194°N 8.71333°E | 483 (365/118) | 200 | 200 | 1965 | Merc | Replaced in 1986 by Thyr, multiterminal scheme | [1] |
| Kingsnorth | UK - Kingsnorth 51°25′11″N 0°35′46″E / 51.41972°N 0.59611°E | UK - London-Beddington 51°22′23″N 0°7′38″W / 51.37306°N 0.12722°W | 85 (85/0) | 266 | 320 | 1975 | Merc | Bipolar scheme
Supplier: English Electric Shut down in 1987 |
[28] |
| Kingsnorth | UK - Kingsnorth | UK - London-Willesden 51°32′03″N 0°15′29″W / 51.53417°N 0.25806°W | 111 (111/0) | 266 | 320 | 1975 | Merc | Opposite pole of Kingsnorth - Beddington. Cable wholly underground except for Thames crossing - crossed on upstream side of Putney District line railway bridge | |
| Skagerrak 1 + 2 | Denmark - Tjele 56°28′44″N 9°34′1″E / 56.47889°N 9.56694°E | Norway - Kristiansand 58°15′36″N 7°53′55″E / 58.26000°N 7.89861°E | 230 (130/100) | 250 | 500 | 1977 | Thyr | Supplier: STK(Nexans) Control system upgrade by ABB in 2007 | [29][30][31] |
| Gotland 2 | Sweden - Västervik 57°43′41″N 16°38′51″E / 57.72806°N 16.64750°E | Sweden - Yigne 57°35′13″N 18°11′44″E / 57.58694°N 18.19556°E | 99.5 (92.9/6.6) | 150 | 130 | 1983 | Thyr | ||
| Cross-Channel (new) | France - Les Mandarins 50°54′11″N 1°47′5″E / 50.90306°N 1.78472°E | UK - Sellindge 51°6′21″N 0°58′32″E / 51.10583°N 0.97556°E | 72 (72/0) | 270 | 2000 | 1986 | Thyr | 2 bipolar systems
Supplier: Alstom |
[1] |
| Gotland 3 | Sweden - Västervik 57°43′41″N 16°38′51″E / 57.72806°N 16.64750°E | Sweden - Yigne 57°35′13″N 18°11′44″E / 57.58694°N 18.19556°E | 98 (98/0) | 150 | 130 | 1987 | Thyr | ||
| Konti-Skan 2 | Denmark - Vester, Hassing 57°3′46″N 10°5′24″E / 57.06278°N 10.09000°E | Sweden - Lindome 57°36′24″N 12°6′40″E / 57.60667°N 12.11111°E | 147 (87/60) | 285 | 300 | 1988 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | |
| Fenno-Skan | Finland - Rauma 61°09′07″N 21°37′32″E / 61.15194°N 21.62556°E | Sweden - Dannebo 60°24′14″N 18°08′10″E / 60.40389°N 18.13611°E | 233 (200/33) | 400 | 500 | 1989 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | |
| SACOI 2 | Italy - Suvereto 43°3′10″N 10°41′42″E / 43.05278°N 10.69500°E ( before 1992: Italy - San Dalmazio 43°15′43″N 10°55′05″E / 43.26194°N 10.91806°E) | France- Lucciana 42°31′40″N 9°26′59″E / 42.52778°N 9.44972°E ; Codrongianos, Italy 40°39′7″N 8°42′48″E / 40.65194°N 8.71333°E | 422 (118/304) | 200 | 300 | 1992 | Thyr | Multiterminal scheme
Supplier: Alstom |
|
| Skagerrak 3 | Denmark - Tjele 56°28′44″N 9°34′1″E / 56.47889°N 9.56694°E | Norway - Kristiansand 58°15′36″N 7°53′55″E / 58.26000°N 7.89861°E | 230 (130/100) | 350 | 440 | 1993 | Thyr | Supplier: Nexans ABB | [29] |
| Baltic Cable | Germany - Lübeck- Herrenwyk 53°53′46″N 10°48′9″E / 53.89611°N 10.80250°E | Sweden - Kruseberg 55°30′1″N 13°8′45″E / 55.50028°N 13.14583°E | 262 (250/12) | 450 | 600 | 1994 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | |
| Kontek | Denmark - Bjæverskov 55°27′1″N 12°0′27″E / 55.45028°N 12.00750°E | Germany - Bentwisch 54°6′3″N 12°13′1″E / 54.10083°N 12.21694°E | 170 (170/0) | 400 | 600 | 1996 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | |
| Hellsjön-Grängesberg | Sweden - Hellsjön 60°02′50″N 15°08′52″E / 60.04722°N 15.14778°E | Sweden - Grängesberg 60°03′53″N 14°59′39″E / 60.06472°N 14.99417°E | 10 (0/10) | 180 | 3 | 1997 | IGBT | Experimental HVDC
Supplier: ABB |
|
| Visby-Nas | Sweden - Nas 57°05′58″N 18°14′27″E / 57.09944°N 18.24083°E | Sweden - Visby 57°37′29″N 18°21′18″E / 57.62472°N 18.35500°E | 70 (70/0) | 80 | 50 | 1999 | Thyr | ||
| SwePol | Poland - Wierzbięcin 54°30′8″N 16°53′28″E / 54.50222°N 16.89111°E | Sweden - Stärnö 56°9′11″N 14°50′29″E / 56.15306°N 14.84139°E | 245 (245/0) | 450 | 600 | 2000 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [32] |
| Tjæreborg | Denmark - Tjæreborg/Enge 55°26′52″N 8°35′34″E / 55.44778°N 8.59278°E | Denmark - Tjæreborg/Substation 55°28′07″N 8°33′36″E / 55.46861°N 8.56000°E | 4.3 (4.3/0) | 9 | 7 | 2000 | IGBT | Interconnection to wind power generating stations | |
| Italy-Greece | Greece - Arachthos 39°11′00″N 20°57′48″E / 39.18333°N 20.96333°E | Italy - Galatina 40°9′53″N 18°7′49″E / 40.16472°N 18.13028°E | 310 (200/110) | 400 | 500 | 2001 | Thyr | ||
| Moyle | UK - Auchencrosh 55°04′10″N 4°58′50″W / 55.06944°N 4.98056°W | UK - N. Ireland- Ballycronan More 54°50′34″N 5°46′11″W / 54.84278°N 5.76972°W | 63.5 (63.5/0) | 250 | 250 | 2001 | Thyr | Supplier: Nexans Siemens | |
| HVDC Troll | Norway - Kollsnes 60°33′01″N 4°50′26″E / 60.55028°N 4.84056°E | Norway - Offshore platform Troll A 60°40′00″N 3°40′00″E / 60.66667°N 3.66667°E | 70 (70/0) | 60 | 80 | 2004 | IGBT | Power supply for offshore gas compressor
Supplier: ABB |
[33] |
| Estlink | Estonia - Harku 59°23′5″N 24°33′37″E / 59.38472°N 24.56028°E | Finland - Espoo 60°12′14″N 24°33′06″E / 60.20389°N 24.55167°E | 105 (105/0) | 150 | 350 | 2006 | IGBT | Supplier: ABB | [33] |
| NorNed | Netherlands - Eemshaven 53°26′4″N 6°51′57″E / 53.43444°N 6.86583°E | Norway - Feda 58°16′58″N 6°51′55″E / 58.28278°N 6.86528°E | 580 (580/0) | 450 | 700 | 2008 | Thyr | Supplier:Nexans ABB | [33] |
| NordE.ON 1 | Germany - Diele 53°7′31″N 7°18′33″E / 53.12528°N 7.30917°E | Germany - Borkum 2 platform 54°21′15″N 6°01′30″E / 54.35417°N 6.02500°E | 203 (203/0) | 150 | 400 | 2009 | IGBT | Supplier: ABB | [34] |
| HVDC Valhall | Norway - Lista 58°04′37″N 6°46′29″E / 58.07694°N 6.77472°E | Norway - Valhall, Offshore platform | 292 (292/0) | 150 | 78 | 2009 | IGBT | Supplier: Nexans | |
| BritNed | UK - Grain 51°26′24″N 0°43′0″E / 51.44000°N 0.71667°E | Netherlands - Maasvlakte 51°57′27″N 4°01′17″E / 51.95750°N 4.02139°E | 245 (245/0) | 450 | 1000 | 2010* | Thyr | Operational since April 2011. Supplier: Siemens | [33][35] |
| StoreBælt | Denmark - Fraugde 55°22′01″N 10°30′25″E / 55.36694°N 10.50694°E | Denmark - Herslev 55°31′53″N 11°19′01″E / 55.53139°N 11.31694°E | 56 (56/0) | 400 | 600 | 2010* | Thyr | Operational since August 2010. Supplier: Siemens | [33] |
| Cometa | Spain - Morvedre 39°38′28″N 0°14′7″W / 39.64111°N 0.23528°W | Spain - Santa Ponsa 39°32′2″N 2°30′21″E / 39.53389°N 2.50583°E | 247 (247/0) | 250 | 400 | 2011* | Thyr | Expected completion 2011
Supplier: Siemens (PRYSMIAN/NEXANS) |
[33] |
| SAPEI | Italy - Latina 41°25′47″N 12°48′25″E / 41.42972°N 12.80694°E | Italy - Fiume Santo 40°50′29″N 8°18′21″E / 40.84139°N 8.30583°E | 435 (435/0) | 500 | 1000 | 2011 | Thyr | The largest HVDC link in the Mediterranean Sea. Supplier: ABB | [33][36][37] |
| Fenno-Skan 2 | Finland - Rauma 61°09′07″N 21°37′32″E / 61.15194°N 21.62556°E | Sweden - Finnbole 60°25′30″N 17°3′42″E / 60.42500°N 17.06167°E | 303 (200/103) | 500 | 800 | 2011 | Thyr | ||
| BorWin1 | Germany - Diele | Germany - BorWin Alpha platform | 200 (200/0) | ±150 | 400 | 2012 | IGBT | Supplier: ABB | [38][39][40] |
| BorWin2 | Germany - Diele 53°7′30″N 7°18′29″E / 53.12500°N 7.30806°E | Germany - BorWin Beta platform 54°21′18″N 6°01′30″E / 54.35500°N 6.02500°E | 200 (200/0) | ±300 | 800 | 2015 | IGBT | Supplier: Siemens | [41] |
| East West Interconnector | Ireland - Woodland 53°28′16″N 6°34′3″W / 53.47111°N 6.56750°W | UK - Shotton, Wales 53°13′38″N 3°4′22″W / 53.22722°N 3.07278°W | 130 (130/0) | ±200 | 500 | 2012 | IGBT | Planned completion 2012. 2 alternative plans under consideration. | |
| DolWin1 | Germany - Heede 52°58′57″N 7°15′26″E / 52.98250°N 7.25722°E | Germany - DolWin Alpha platform 53°59′42″N 6°25′16″E / 53.99500°N 6.42111°E | 165 (165/0) | ±320 | 800 | 2015 | IGBT | Supplier:ABB | [42] |
| HelWin1 | Germany - Büttel 53°55′01″N 9°13′55″E / 53.91694°N 9.23194°E | Germany - HelWin Alpha platform 54°27′07″N 7°44′20″E / 54.45194°N 7.73889°E | 130 (130/0) | ±250 | 576 | 2015 | IGBT | Supplier: Siemens | [43] |
| Fenno-Skan 1 Upgrade | Sweden - Finnböle | Finland - Rauma | 233 (200/33) | 400 | 500 | 2013 | Thyr | Upgrade
Supplier:ABB |
[44][45][46] |
| SylWin1 | Germany - Büttel 53°55′01″N 9°13′55″E / 53.91694°N 9.23194°E | Germany - SylWin Alpha platform 55°03′47″N 7°14′28″E / 55.06306°N 7.24111°E | 205 (205/0) | ±320 | 864 | 2015 | IGBT | [47] | |
| Estlink 2 | Estonia - Püssi 59°22′13″N 27°04′05″E / 59.37028°N 27.06806°E | Finland - Anttila 60°22′36″N 25°22′01″E / 60.37667°N 25.36694°E | 171 (157/14) | 450 | 650 | 2014 | Thyr | Supplier: Nexans | |
| INELFE | France - Baixas 42°43′56″N 2°48′14″E / 42.73222°N 2.80389°E | Spain - Santa Llogaia 42°13′59″N 2°56′39″E / 42.23306°N 2.94417°E | 64 (64/0) | ±320 | 2000 | 2014 | IGBT | Supplier: Siemens | [48] |
| Skagerrak 4 | Norway - Kristiansand | Denmark - Tjele | 244 (244/0) | 500 | 700 | 2014 | IGBT |
Supplier: Nexans | |
| SydVästlänken | Norway–Hallsberg | Sweden - Barkeryd ; Sweden - Hurva | 260 (197/63) | ±300 | 2x720 | 2013- 2015 | IGBT | Supplier: Alstom | |
| LitPol Link | Lithuania - Alytus | Poland - Elk | 160 (0/160) | 70 | 500 | 2015 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [49][50][51][52] |
| Åland - Finland | Åland - Ytterby | Finland - Nådendal | 158 (158/0) | 80 | 100 | 2015 | IGBT | Supplier: ABB | [53][54] |
| Troll A 3&4 | Norway - Kollsnes | Norway - Troll A 3&4 platform | 70 (70/0) | 66 | 100 | 2015 | IGBT | Supplier: ABB | [55][56][57][58][59][60] |
| Western HVDC Link | UK - Hunterston | UK - Flintshire Bridge | 422 (422/0) | 600 | 2200 | ~2016 | Thyr | Supplier: Prysmian Group, Siemens First subsea 600kV link | [61] |
| HVDC NordBalt | Sweden - Nybro 56°46′1″N 15°51′35″E / 56.76694°N 15.85972°E | Lithuania - Klapeida 55°40′54″N 21°15′29″E / 55.68167°N 21.25806°E | 450 (450/0) | 300 | 700 | 2015 | IGBT | Supplier: ABB | [62] |
| DolWin2 | Germany - Heede 52°58′52″N 7°15′26″E / 52.98111°N 7.25722°E | Germany - DolWin Beta platform 53°58′41″N 6°55′23″E / 53.97806°N 6.92306°E | 135 (135/0) | ±320 | 900 | 2015 | IGBT | Supplier: ABB | [63] |
| HelWin2 | Germany - Büttel 53°55′01″N 9°13′55″E / 53.91694°N 9.23194°E | Germany - HelWin Beta platform 54°27′11″N 7°44′20″E / 54.45306°N 7.73889°E | 130 (130/0) | ±320 | 690 | 2015 | IGBT | Supplier: Siemens | |
| DolWin3 | Germany - DolWin Gamma platform | 160 (160/0) | ±320 | 900 | 2017 | IGBT | Supplier: Alstom | [64] | |
| BorWin3 | Germany - Diele | Germany - BorWin Gamma platform | 200 (200/0) | ±320 | 900 | 2019 | IGBT | Supplier: Siemens | |
| HVDC Finland - Åland | Finland - Ytterby | Finland - Nådendal 60°27′49″N 22°03′49″E / 60.46361°N 22.06361°E | 158 (158/0) | 80 | 100 | 2015 | IGBT | ||
| Shetland HVDC Connection | UK - Upper Kergord Valley | UK - Blackhillock | 345 (345/0) | ? | 550 | 2016 | Thyr | ||
| HVDC Italy-Croatia | Italy - Candia | Croatia - Konjsko | ? | 2017 | Thyr | ||||
| NSN | Norway - Kvilldal | UK - Blyth | 700 | 500 | 1400 | ~2020 | [65][66] | ||
North America
| Name |
Converter station 1 |
Converter station 2 |
Total Length (Cable/Pole) (km) |
Volt (kV) |
Power (MW) |
Year |
Type |
Remarks |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HVDC Mechanicville–Schenectady | USA - Mechanicville,NY 42°54′45″N 73°40′49″W / 42.91250°N 73.68028°W | USA - Schenectady, NY | 37 (0/37) | 12 | 5 | 1932 | Merc | Experimental, frequency conversion 40 to 60 Hz
Dismantled after WW II |
[67] |
| Vancouver Island 1 | Canada - Delta, BC 49°5′31″N 123°2′31″W / 49.09194°N 123.04194°W | Canada - North Cowichan, BC 48°49′39″N 123°42′55″W / 48.82750°N 123.71528°W | 75 (42/33) | 260 | 312 | 1968 | Merc | Supplier: ASEA | [1] |
| Vancouver Island 2 | Canada - Delta, BC 49°5′31″N 123°2′31″W / 49.09194°N 123.04194°W | Canada - North Cowichan, BC 48°49′39″N 123°42′55″W / 48.82750°N 123.71528°W | 75 (33/42) | 280 | 370 | 1977 | Thyr | Supplier: GE | [1] |
| Pacific DC Intertie | USA - Celilo, OR 45°35′39″N 121°6′51″W / 45.59417°N 121.11417°W | USA - Sylmar, CA 34°18′39″N 118°29′21″W / 34.31083°N 118.48917°W, 34°18′42″N 118°28′53″W / 34.31167°N 118.48139°W | 1362 (0/1362) | 500 | 3100 | 1970 | Thyr | Transmission voltage 400 kV until 1984 Maximum transmission power 1440 MW until 1982 From 1982 to 1984 1600 MW From 1984 to 1989 2000 MW Merc replaced by Thyr in 2004 Original supplier: ASEA, GE In 1989 upgraded by ABB In 2004 upgraded by ABB and Siemens | [1][1][68][69] |
| Nelson River Bipole 1 | Canada - Gillam, Manitoba 56°21′41″N 94°36′48″W / 56.36139°N 94.61333°W | Canada - Rosser, Manitoba 49°59′34″N 97°25′42″W / 49.99278°N 97.42833°W | 1835 (940/895) | 500 | 1000 | 1971 | Thyr | Used the largest mercury arc rectifiers ever built Poles converted to Thyr in 1993 Original supplier: English Electric, Alstom In 1993 upgraded by Alstom In 2004 upgraded by Siemens | [1][70] |
| Nelson River Bipole 2 | Canada - Sundance, Manitoba 56°30′14″N 94°8′24″W / 56.50389°N 94.14000°W | Canada - Rosser, Manitoba 49°59′34″N 97°25′42″W / 49.99278°N 97.42833°W | 940 (0/940) | 500 | 2000 | 1985 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [1][70] |
| Square Butte | USA - Center, ND (Young) 47°4′18″N 101°11′45″W / 47.07167°N 101.19583°W | USA - Adolph, MN (Arrowhead) 46°46′25″N 92°17′39″W / 46.77361°N 92.29417°W | 749 (0/749) | 250 | 500 | 1977 | Thyr | Supplier: GE In 2004 Control system upgrade by ABB | [1][71][72] |
| CU | USA - Underwood, ND (Coal Creek) 47°22′24″N 101°9′23″W / 47.37333°N 101.15639°W | USA - Rockford, MN (Dickinson) 45°6′40″N 93°48′36″W / 45.11111°N 93.81000°W | 687 (0/687) | 400 | 1000 | 1979 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB In 2004, control system upgrade by ABB | [1][73] |
| Path 27 | USA - Intermountain, UT 39°30′2″N 112°34′51″W / 39.50056°N 112.58083°W | USA - Adelanto, CA 34°33′4″N 117°26′14″W / 34.55111°N 117.43722°W | 785 (0/785) | 500 | 1920 | 1986 | Thyr | ||
| Quebec - New England Transmission | Canada - Radisson, QC 53°43′33″N 77°44′17″W / 53.72583°N 77.73806°W | Canada - Nicolet, QC 46°04′47″N 72°14′58″W / 46.07972°N 72.24944°W; USA - Ayer, MA 42°34′13″N 71°31′27″W / 42.57028°N 71.52417°W | 1105 (5/1100) | 450 | 2250 | 1991 | Thyr | 3 terminals Converter stations near Windsor, QC and Monroe, NH were decommissioned in 2007. Supplier: ABB |
[1] |
| Cross Sound Cable | USA - New Haven, CT 41°17′12″N 72°54′8″W / 41.28667°N 72.90222°W | USA - Shoreham, Long Island, NY 40°57′33″N 72°52′3″W / 40.95917°N 72.86750°W | 40 (40/0) | 150 | 330 | 2002 | IGBT | Buried underwater cable Supplier: ABB |
[74] |
| Neptune Cable | USA - Long Island (Hicksville) NY 40°45′38″N 73°33′4″W / 40.76056°N 73.55111°W | USA -Sayreville, NJ 40°28′25.38″N 74°21′11.1″W / 40.4737167°N 74.353083°W | 105 (105/0) | 500 | 660 | 2007 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [75] |
| Trans Bay Cable | USA - Pittsburg, CA 38°01′51″N 121°53′48″W / 38.03083°N 121.89667°W | USA - San Francisco, CA 37°45′17″N 122°23′09″W / 37.75472°N 122.38583°W | 85 (85/0) | 200 | 400 | 2010 | IGBT | First HVDC system using Modular Multi-Level Converter
Supplier: Siemens, Pirelli |
[76][77][78] |
| Western Alberta Transmission Line | Canada – Genesee, AB 53°21′13″N 114°18′33″W / 53.35361°N 114.30917°W | Canada – Langdon, AB 50°57′37″N 113°43′11″W / 50.96028°N 113.71972°W | 350 (0/350) | 500 | 1000 | 2015 | [79][80] | ||
| Eastern Alberta Transmission Line | Canada – Newell, AB 50°30′41″N 112°01′02″W / 50.51139°N 112.01722°W | Canada – Heathfield, AB 53°51′28″N 113°13′52″W / 53.85778°N 113.23111°W | 485 (0/485) | 500 | 1000 | 2014 | Completion due December 2014 | [79] | |
| Labrador-Island Link | Canada - Muskrat Falls, NL | Canada - Soldiers Pond, NL | 1135 (35/1100) | 350 | 900 | ~2017 | Thyr | Drilling for cable landfall began in 2014. Supplier: Alstom Grid | [81][82] |
| Maritime Link | Canada - Bottom Brook, NL 48°31′52″N 58°15′39″W / 48.53111°N 58.26083°W | Canada - Woodbine, NS 45°59′30″N 60°16′26″W / 45.99167°N 60.27389°W | 360 (170/190) | 200 | 500 | ~2017 | IGBT | Right-of-way clearing began in 2014. Supplier: ABB | [83][84][85][86] |
| TransWest Express | USA – Sinclair, WY | USA – Boulder City, NV | 1165 (0/1165) | 600 | 3000 | Final EIS expected in April 2015. | [87][88] | ||
| Rock Island Clean Line | USA - O'Brien County, IA | USA - Grundy County, IL | 805 (0/805) | 600 | 3500 | ~2017 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [89] |
| Plains & Eastern Clean Line | USA - Texas County, OK | USA - Shelby County, TN | 1207 (0/1207) | 600 | 3500 | ~2018 | Thyr | [90] | |
| New England Clean Power Line | USA - Alburgh, VT | USA - Ludlow, VT | 248 (248/0) | 320 | 1000 | ~2019 | [91][92] |
South America
| Name |
Converter station 1 |
Converter station 2 |
Total Length (Cable/Pole) (km) |
Volt (kV) |
Power (MW) |
Year |
Type |
Remarks |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Itaipu 1 | Brazil - Foz do Iguaçu, Paraná 25°27′58″S 54°32′33″W / 25.46611°S 54.54250°W | Brazil - São Roque, São Paulo 23°40′2″S 47°6′19″W / 23.66722°S 47.10528°W | 785 (0/785) | 600 | 3150 | 1984 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [1] |
| Itaipu 2 | Brazil - Foz do Iguaçu, Paraná 25°27′58″S 54°32′33″W / 25.46611°S 54.54250°W | Brazil - São Roque, São Paulo 23°40′2″S 47°6′19″W / 23.66722°S 47.10528°W | 805 (0/805) | 600 | 3150 | 1987 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB | [1] |
| Rio Madeira | Brazil, Porto Velho 08°54′53″S 63°57′27″W / 8.91472°S 63.95750°W | Brazil, Araraquara 21°49′59″S 48°20′52″W / 21.83306°S 48.34778°W | 2375 (0/2375) | 600 | 7100 | 2013 | Thyr | The longest transmission link in the world Suppliers: ABB, Alstom |
[93] |
Back to back
| Name |
Location |
Volt (kV) |
Power (MW) |
Year |
Type |
Remarks |
Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carnegie Steel Company B2B | USA - Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania | ? | ? | ? | Merc | built for an interconnection between 60 Hz-utility system and a 25 Hz System, dismantled | [94] | |
| Sakuma B2B | Japan - Sakuma 35°04′57″N 137°47′56″E / 35.08250°N 137.79889°E | 125 | 300 | 1965 | Merc | replaced in 1993 by new converter using light-triggered thyristors | ||
| Eel River B2B | Canada - Eel River, NB 48°01′05″N 66°26′39″W / 48.01806°N 66.44417°W | 80 | 320 | 1972 | Thyr | life extension project 2014 | [95][96] | |
| Shin Shinano B2B | Japan - Shin Shinano 36°08′14″N 137°52′58″E / 36.13722°N 137.88278°E | 125 | 600 | 1977 | Thyr | Supplier: Toshiba, Hitachi | ||
| Acaray B2B | Paraguay - Ciudad de Este 25°27′26″S 54°37′26″W / 25.45722°S 54.62389°W | 25.6 | 50 | 1981 | Thyr | |||
| Vyborg B2B | Russia - Vyborg 60°40′49″N 28°55′7″E / 60.68028°N 28.91861°E | 85 | 1065 | 1982 | Thyr | |||
| Dürnrohr B2B | Austria - Dürnrohr 48°19′46″N 15°52′48″E / 48.32944°N 15.88000°E | 145 | 550 | 1983 | Thyr | shut down in October 1996, dismantled in 2007 | ||
| Artesia, New Mexico (Eddy County HVDC B2B) B2B | USA - Artesia, NM 32°48′51.7″N 104°14′29.6″W / 32.814361°N 104.241556°W | 82 | 200 | 1983 | Thyr | |||
| Chateauguay B2B | Canada – Châteauguay, QC 45°15′11″N 73°52′11″W / 45.25306°N 73.86972°W | 140 | 1000 | 1984 | Thyr | Control system upgrade by ABB in 2009 | [97][98] | |
| Oklaunion B2B | USA - Oklaunion, TX 34°5′6″N 99°11′1″W / 34.08500°N 99.18361°W | 82 | 200 | 1984 | Thyr | ABB replacement in 2014 | [99][100]
| |
| Blackwater, New Mexico B2B | USA - Blackwater, NM 34°18′3″N 103°10′27″W / 34.30083°N 103.17417°W | 57 | 200 | 1984 | Thyr | Valve cooling and control systems upgrade by ABB in 2009 | [101][102] | |
| Madawaska, Quebec B2B | Canada - Dégelis, QC 47°30′31″N 68°31′25″W / 47.50861°N 68.52361°W | 140 | 350 | 1985 | Thyr | |||
| Miles City, Montana B2B | USA - Miles City, MT 46°24′31″N 105°47′36″W / 46.40861°N 105.79333°W | 82 | 200 | 1985 | Thyr | |||
| Highgate, VT B2B | USA - Highgate, VT 44°56′17″N 73°3′15″W / 44.93806°N 73.05417°W | 56 | 200 | 1985 | Thyr | Refurbishment by ABB in 2012, | [103] | |
| Uruguaiana B2B | Brazil - Uruguaiana 29°48′22″S 57°0′17″W / 29.80611°S 57.00472°W | 17.9 | 53.9 | 1986 | Thyr | |||
| Broken Hill B2B | Australia - Broken Hill 31°59′10″S 141°25′9″E / 31.98611°S 141.41917°E | 8.33 | 40 | 1986 | Thyr | |||
| Virginia Smith B2B | USA - Sidney, NE 41°9′51″N 102°59′15″W / 41.16417°N 102.98750°W | 50 | 200 | 1988 | Thyr | [104] | ||
| Vindhyachal B2B | India - Vindhyachal 24°05′38″N 82°40′44″E / 24.09389°N 82.67889°E | 176 | 500 | 1989 | Thyr | |||
| McNeill B2B | Canada - Mc Neill, AB 50°35′56″N 110°01′25″W / 50.59889°N 110.02361°W | 42 | 150 | 1989 | Thyr | Supplier: Alstom | ||
| Wolmirstedt B2B | Germany - Wolmirstedt 52°16′21″N 11°38′10″E / 52.27250°N 11.63611°E | 160 | 600 | (1992) | Thyr | construction work was stopped after reunification, static inverter hall is today part of a recycling yard | ||
| Etzenricht B2B | Germany - Etzenricht 49°37′52″N 12°6′56″E / 49.63111°N 12.11556°E | 160 | 600 | 1993 | Thyr | shut down in October 1995, dismantled in 2009 | ||
| Vienna-Southeast B2B | Austria - Vienna 48°7′22″N 16°25′6″E / 48.12278°N 16.41833°E | 142 | 600 | 1993 | Thyr | shut down in October 1996, dismantled in 2007 | ||
| Chandrapur B2B | India - Chandrapur 20°5′21″N 79°8′36″E / 20.08917°N 79.14333°E | 205 | 2x500 | 1998 | Thyr | Supplier: Alstom | ||
| Welsh HVDC Converter Station B2B | USA - Titus County, TX 33°03′30.3″N 94°50′36.54″W / 33.058417°N 94.8434833°W | 162 | 600 | 1998 | Thyr | |||
| Garabi HVDC | Brazil - Garabi 28°15′19″S 55°40′18″W / 28.25528°S 55.67167°W | ±70 | 2200 | 1999 | Thyr | Brazil-Argentina Interconnection. Supplier: ABB In 2002, the second phase 'Garabi 2' was supplied by ABB . | [105] | |
| Vizag 1 | India - Visakhapatnam Gazuwaka 17°38′33″N 83°7′57″E / 17.64250°N 83.13250°E | 205 | 500 | 1999 | Thyr | Supplier: Alstom | ||
| Minami-Fukumitsu B2B | Japan - Minami - Fukumitsu 36°29′46″N 136°54′57″E / 36.49611°N 136.91583°E | 125 | 300 | 1999 | Thyr | |||
| Rivera B2B | Uruguay - Rivera 30°56′29″S 55°33′34″W / 30.94139°S 55.55944°W | 22 | 70 | 2000 | Thyr | Supplier: Alstom | ||
| Eagle Pass, Texas B2B | USA - Eagle Pass, TX 28°42′58.8″N 100°29′26.88″W / 28.716333°N 100.4908000°W | 15.9 | 36 | 2000 | IGBT | |||
| Sasaram B2B | India - Sasaram 25°07′42″N 83°42′29″E / 25.12833°N 83.70806°E | 205 | 500 | 2003 | Thyr | Supplier: Alstom | ||
| Rapid City DC Tie B2B | USA - Rapid City, SD 44°00′37″N 103°9′54″W / 44.01028°N 103.16500°W | 13 | 200 | 2003 | Thyr | [106][107] | ||
| Vizag 2 | India - Visakhapatnam 17°38′26″N 83°8′10″E / 17.64056°N 83.13611°E | 176 | 500 | 2005 | Thyr | Installed at Gazuwaka. Supplier:ABB. This is similar in specs to Vizag I and connects the Eastern and Southern grids. | [108] | |
| Lingbao B2B | China - Lingbao 34°32′56″N 110°50′49″E / 34.54889°N 110.84694°E | 168 | 360 | 2005 | Thyr | Supplier: NR(Protection&Control), Extension project 2010: Supplier: ABB | [109][110] | |
| Lamar Co., Colorado B2B | USA - Lamar, CO 38°12′25.08″N 102°31′43.92″W / 38.2069667°N 102.5288667°W | 63.6 | 210 | 2005 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens; Combination of B2B HVDC & Grid Power Flow Controller (GPFC) | [111] | |
| Higashi-Shimuzu B2B | Japan - Shimuzu 35°03′24″N 138°29′58″E / 35.05667°N 138.49944°E | 125 | 300 | 2006 | Thyr | |||
| Sharyland B2B | USA - Mission, TX 26°10′01″N 98°19′25″W / 26.16694°N 98.32361°W | 21 | 150 | 2007 | Thyr | |||
| Al Fadhili B2B | Saudi Arabia - Al Fadhili 26°54′3″N 49°21′3″E / 26.90083°N 49.35083°E | 222 | 3x600 | 2008 | Thyr | Used mainly for Dynamic Reserve Power Sharing rather than economic energy transfer. Supplier: Alstom | [112] | |
| Outaouais B2B | Canada - Buckingham, QC 45°36′01″N 75°26′47″W / 45.60028°N 75.44639°W | 315 | 625 (2x) | 2009 | Thyr | Expected completion 2009. Supplier:ABB | [33] | |
| Heihe B2B | China - Heihe 50°15′19″N 127°25′37″E / 50.25528°N 127.42694°E | 125 | 750 | 2008 | Thyr | Supplier: NR(Protection&Control) [113] | ||
| Gaoling B2B | China - Gaoling 40°10′49″N 120°00′22″E / 40.18028°N 120.00611°E | 1500 | 2008? | Thyr | ||||
| Shandong - East B2B | China | 1200 | 2011 | Thyr | ||||
| Melo B2B | Uruguay - Melo 32°25′02″S 54°05′34″W / 32.41722°S 54.09278°W | ? | 500 | 2011 | Thyr | Supplier:Alstom | ||
| North - Central B2B | China | 1000 | 2012 | Thyr | ||||
| Rio Madeira B2B | Brazil – Porto Velho 8°54′46″S 63°57′27″W / 8.91278°S 63.95750°W | 100 | 800 | 2013 | Thyr | Supplier: ABB[114] | [115][116][117][118] | |
| Ridgefield B2B ( Hudson Project) | USA - Ridgefield, NJ 40°49′56″N 74°00′44″W / 40.83222°N 74.01222°W | 185 | 660 | 2013 | Thyr | |||
| Bheramara B2B | Bangladesh – Bheramara 24°04′03″N 89°0′04″E / 24.06750°N 89.00111°E | 158 | 500 | 2013 | Thyr | |||
| Akhaltsikhe B2B | Georgia - Akhaltsikhe 41°38′58″N 42°59′13″E / 41.64944°N 42.98694°E | 96 | 700 | 2013 | Thyr | Supplier: Siemens | [119] | |
| Mackinac B2B | USA - Saint Ignace, MI ~45°51′31″N 84°44′09″W / 45.85861°N 84.73583°W | 70 | 200 | 2014 | IGBT | Supplier: ABB | [120] | |
| Railroad DC Tie | USA - Mission, TX 26°10′01″N 98°19′25″W / 26.16694°N 98.32361°W | 21 | 150 | 2014 | Thyr | |||
| Mogocha B2B | Russia - Mogocha 53°43′30″N 119°47′22″E / 53.72500°N 119.78944°E | ? | ? | 2014 | Thyr | [121] | ||
| Alytus B2B | Lithuania - Alytus 54°26′19″N 23°58′02″E / 54.43861°N 23.96722°E | ? | 500 | 2015 | ? | |||
| Tres Amigas SuperStation | USA - Clovis, NM | ? | 5000 | ? | IGBT |
Maps
Europe
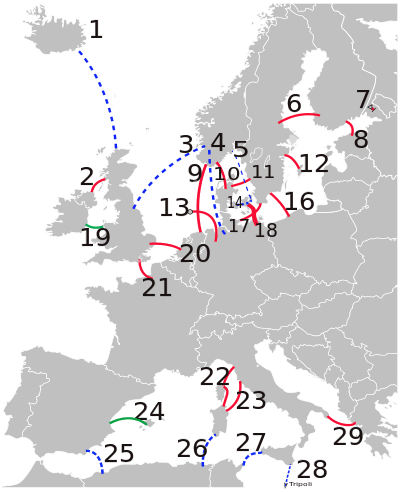
- Iceland – UK (option), 1.1 GW
- Moyle: Auchencrosh, UK – Ballycronan More, Northern Ireland, UK
- Norway – UK (option), 1.4 GW
- Viking cable (option): Germany – Norway, 600 MW
- Kattegat (option): Norway – Zealand, Denmark; or Norway – southern Sweden
- Fenno-Skan: Rauma, Finland – Dannebo, Sweden
- Vyborg
- Estlink: Harku, Estonia – Espoo, Finland
- NorNed: Feda, Norway – Eemshaven, Netherlands
- Cross-Skagerrak 1, 2, and 3: Tjele, Denmark – Kristiansand, Norway
- Konti-Skan 1 and 2: VesterHassing, Denmark – Stenkullen, Sweden
- Gotland: Västervik, Sweden – Ygne, Sweden
- NordE.ON 1: Diele, Germany – Borkum 2 platform, Germany
- StoreBælt: Fyn, Denmark – Zealand, Denmark
- (purposely left blank)
- SwePol: Stärnö, Sweden – Wierzbięcin (Słupsk), Poland
- Baltic Cable: Lübeck- Herrenwyk, Germany – Kruseberg, Sweden
- Kontek: Bjæverskov, Denmark – Bentwisch, Germany
- East West Interconnector: Leinster, Ireland – Anglesey, Wales, UK
- BritNed: UK – Netherlands. Operational since April 2011.
- HVDC Cross-Channel: Les Mandarins, France – Sellindge, UK
- HVDC Italy–Corsica–Sardinia: "SACOI" – Codrongianos, Sardinia, Italy – Lucciana, Corsica, France – Suvereto, Italy (mainland)
- Sapei, Sardinia – Italian mainland
- Cometa: Valencia, Spain – Mallorca, Spain
- 25 — 28 EuroMed options:
- Algeria – Spain
- Algeria – Sardinia
- Tunis – Sicily
- Tripoli – Sicily
- HVDC Italy-Greece: Arachthos, Greece – Galatina, Italy
See also
- Electrode line
- European super grid
- High-voltage direct current
- Lyon-Moutiers DC transmission scheme
- Scotland-Norway interconnector
- HVDC converter station
- Submarine power cable
- Transmission tower
- Uno Lamm
- Valve hall
- List of high voltage underground and submarine cables
- Desertec
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 1.25 1.26 1.27 1.28 1.29 1.30 1.31 1.32 1.33 1.34 1.35 1.36 1.37 1.38 1.39 1.40 1.41 1.42 1.43 1.44 1.45 1.46 1.47 1.48 HVDC Projects List, March 2012 - Existing or Under Construction (PDF), accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Cahora Bassa, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ ABB wins $50 million HVDC order in Mozambique, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Inga-Kolwezi – One of the world's longest electric power transmissions, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ ABB wins $107 million power order in Africa, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Report on Congo DRC – SOCIETE NATIONALE D'ELECTRICITE, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ "ABB commissions Caprivi link". 1 January 2011. Retrieved February 2014.
- ↑ "HVDC Inter-Island Link Project - Transpower". Transpower New Zealand. Retrieved February 2014.
- ↑ Basslink Homepage, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Joerg Dorn; Dietmar Retzmann; Cristen Schimpf; Dag Soerangr (2007-11-06). "HVDC Solutions for System Interconnection and Advanced Grid Access" (PDF). EPRI HVDC conference 2007-09-13 to 14 (Siemens): 44. Retrieved February 2014.
- ↑ Gezhouba - Shanghai, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Rihand - Delhi, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Chandrapur - Padghe – The first HVDC transmission to Mumbai., accessed in February 2014
- ↑ "ROLE OF THREE GORGES - CHANGZHOU HVDC IN INTERCONNECTING CENTRAL AND EAST CHINA" (PDF). ABB Asea Brown Boveri. Retrieved 2014-02-10.
- ↑ Three Gorges - Changzhou, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Three Gorges - Guangdong, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Three Gorges - Shanghai, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Xiangjiaba - Shanghai, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Hulunbeir - Liaoning, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Nanhui Wind Farm Integration, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Jinping - Sunan: The most powerful transmission line in the world, accessed in January 2015
- ↑ Dalian City Infeed, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ North-East Agra, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ world’s first multi-terminal VSC HVDC transmission project , accessed in February 2014
- ↑ world’s first multi-terminal VSC HVDC transmission project , accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Zhoushan Multi-terminal DC Interconnection, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ "The Gotland HVDC link". abb.com.
- ↑ Kingsnorth Power Station brochure on the DC system (Kingsnorth to London HVDC power reinforcement scheme - dated 1975)
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Skagerrak". abb.com.
- ↑ "New lease on life for northern European power link". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB wins $180 million order for Norway-Denmark power transmission link". abb.com.
- ↑ "SwePol Link". abb.com.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 33.3 33.4 33.5 33.6 33.7 Working Group on HVDC and FACTS Bibliography and Records (2008-07-07). "HVDC PROJECTS LISTING" (PDF). IEEE Transmission and Distribution Committee. Retrieved 2008-12-19.
- ↑ "NordE.ON 1". ABB. Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ↑ "BritNed cable live today" (Press release). BritNed. 2011-04-01. Retrieved 2011-04-01.
- ↑ "SAPEI". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB wins $180 million order for undersea power link in Italy". abb.com.
- ↑ "BorWin1". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB wins power order worth more than $400 million for world’s largest offshore wind farm". abb.com.
- ↑ BorWin1 - Transmission project. YouTube. 7 July 2010.
- ↑ "Wir bringen die Windenergie vom Meer an Land - TenneT TSO GmbH". tennettso.de.
- ↑ "DolWin1". abb.com.
- ↑ http://www.tennettso.de/pages/tennettso_en/Press/Press_releases/News/Pressemitteilung.htm?id=1441603
- ↑ "ABB Fenno-Skan - ABB HVDC Reference Projects in Europe (HVDC References)". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB to upgrade transmission control for Scandinavian power interconnector". abb.com.
- ↑ http://search-ext.abb.com/library/Download.aspx?DocumentID=9AKK105713A1113&LanguageCode=en&DocumentPartId=&Action=Launch New Fenno-Skan 2 HVDC pole with an upgrade of the existing Fenno-Skan 1 pole
- ↑ "Wir bringen die Windenergie vom Meer an Land - TenneT TSO GmbH". tennettso.de.
- ↑ "2014 INELFE, France-Spain" (PDF) (Press release). Siemens. 2011-01-12. Retrieved 2012-05-13.
- ↑ "LITPOL Link". litpol-link.com.
- ↑ "LITPOL Link". litpol-link.com.
- ↑ "ABB wins $110 million power order to interconnect Lithuania and Poland". abb.com.
- ↑ "LitPol Link". abb.com.
- ↑ "Åland". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB wins $130-million HVDC order for subsea power transmission link in Finland". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB wins $270 million order from Statoil for world’s largest offshore gas platform". abb.com.
- ↑ "Inauguration event of ABB technologies at the Troll A platform in Norway". abb.com.
- ↑ "The Troll area". statoil.com.
- ↑ "ABB signs US$ 230 million in contracts with Statoil". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB HVDC Light - Electrical/Integrated Project Solutions (Offshore Production)". abb.com.
- ↑ "Very high voltage synchronous motors". abb.com.
- ↑ "Q&A". Western HVDC. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- ↑ "NordBalt". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ↑ "DolWin2". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ↑ "Offshore wind energy: TenneT awards “DolWin3”project to Alstom, marking next step in Germany’s energy turnaround". alstom.com.
- ↑ "Heading for British clarification of interconnector framework conditions". Retrieved 12 January 2015.
- ↑ "Cable to the UK". Statnett. 2014. Retrieved 2014-11-20.
- ↑ James A. Besha, The historic Mechanicville Hydroelectric Station part 2, IEEE INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS MAGAZINE Mar/Apr 2007, page 8
- ↑ ABB Rededicates Sylmar Converter Station, 24 March 2005
- ↑ "Pacific Intertie". abb.com.
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 Siemens HVDC Reference List, accessed in February 2014.
- ↑ http://new.abb.com/systems/hvdc/references/square-butte Square Butte | References | ABB
- ↑ http://www.minnkota.com/Documents/AnnualReports/2004%20SBAR.pdf Square Butte annual report 2004
- ↑ CU HVDC Project, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Fairley, Peter (April 2005). "TransÉnergie: Playing Two Power Games". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 2014-08-05.
- ↑ "What is Neptune RTS?". Retrieved 2008-12-19.
- ↑ Westerweller T., Friedrich, K., Armonies, U., Orini, A., Parquet, D., Wehn, S., Trans Bay cable – world's first HVDC system using multilevel voltage-sourced converter, CIGRÉ session, Paris, 2010, paper reference B4-101
- ↑ "IEEE PES; HVDC Systems and Trans-Bay Cable" (PDF). 16 March 2005. Retrieved 16 September 2009.
- ↑ "HDVC Plus Technology provided by Siemens". 2012. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 "AESO 2013 Long-term Transmission Plan" (PDF). Alberta Electric System Operator. January 2014. pp. 77–78.
- ↑ Bachusky, Johnnie (2015-01-27). "Billion dollar transmission line is complete". Mountain View Gazette (Olds, AB). Retrieved 2015-02-02.
- ↑ Roberts, Stephen (July 7, 2014). "Muskrat Falls work well underway in Forteau". Northern Pen (St. Anthony: Transcontinental Media G.P.). Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "Awarded Contracts: Muskrat Falls Generation and Labrador-Island Link". Nalcor Energy. Retrieved 2014-07-26.
CD0501 Supply and Install Converter Stations and Transition Compounds 19-Jun-2014
- ↑ "ABB awarded $400 million order for Maritime Link power project in Canada" (Press release). Zurich, Switzerland: ABB. July 9, 2014. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "Maritime Link Infrastructure". Emera Newfoundland and Labrador. 2014. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "4.1.3". Maritime Link Environmental Assessment Report (PDF) (Report). Emera Newfoundland and Labrador. January 10, 2013. Retrieved 2014-07-25.
- ↑ "Maritime Link construction underway in western Newfoundland". CBC News. 2014-11-27. Retrieved 2014-11-27.
- ↑ "BLM/Western publish fifth EIS update newsletter" (Press release). Transwest Express LLC. 2014-11-26. Retrieved 2014-12-30.
- ↑ "Delivering Wyoming wind energy to the West". TransWest Express Transmission Project. TransWest Express LLC. 2014. Retrieved 2014-08-05.
- ↑ Rock Island Clean Line Homepage, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ Plains & Eastern Clean Line Homepage, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ "TDI New England Files State Permit Application for the New England Clean Power Link". Transmission & Distribution World (New York, NY: Penton). 2014-12-20. Retrieved 2014-12-30.
- ↑ "NECPL Submarine Cable Installation" (PDF). New England Clean Power Link: Project Development Portal. TDI New England. 2014-10-09. Retrieved 2014-12-30.
- ↑ Rio Madeira – The longest transmission link in the world - 2,375 kilometers, accessed in February 2014
- ↑ http://www.ieee.org/organizations/pes/public/2005/may/peshistory.html
- ↑ "Eel River". abb.com.
- ↑ http://www.nbpower.com/html/en/about/media/media_release/pdfs/2013/EN_PR_QCInterconnectUpgrade.pdf
- ↑ "Châteauguay". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB to upgrade transmission control for vital North American power interconnector". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB Oklaunion - ABB HVDC Reference Projects in North America (HVDC References)". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB awarded $60 million HVDC order to support grid reliability in Texas". abb.com.
- ↑ "Blackwater". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB to upgrade control and valve cooling system for HVDC station in New Mexico". abb.com.
- ↑ "Highgate". abb.com.
- ↑ "HVDC Transformers- details". Siemens. Retrieved 2008-12-19.
- ↑ "Brazil-Argentina HVDC Interconnection". abb.com.
- ↑ http://www.abb.com/cawp/gad02181/c1256d71001e0037c1256b830034ab10.aspx
- ↑ Archived 27 June 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "THE SECOND 1 x 500 MW HVDC BACK-TO-BACK INTERCONNECTION AT VIZAG" (PDF). 2005-09-29. Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ↑ "Lingbao II". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB wins orders worth $8-million to upgrade HVDC station in China". abb.com.
- ↑ "APPLICATION OF THE GRID POWER FLOW CONTROLLER (GPFC) IN A BACK TO BACK PROJECT- details" (PDF). Siemens. Retrieved 2009-09-29.
- ↑ http://85.91.240.105/netprint/PDFfinal/areva/44883_Systems-L5-GCCIA-1839-V1-EN_loRes.pdf
- ↑ http://www.nari-relays.com/en/files/HVDC%20Control%20and%20Protection%20Solutions.pdf
- ↑ "Rio Madeira". abb.com.
- ↑ "ABB wins $540-million order in Brazil for world's longest power transmission link". abb.com.
- ↑ "Designing Madeira Transmission System - Transmission content from TDWorld". tdworld.com.
- ↑ A remarkable journey - Transportation of the world's largest HVDC transformers. YouTube. 20 June 2012.
- ↑ The Rio Madeira HVDC System – Design aspects of Bipole 1 and the connector to Acre-Rondônia
- ↑ http://www.energy.siemens.com/us/pool/hq/power-transmission/HVDC/HVDC-Classic/pm-pdf/EPT201008116e.pdf
- ↑ "Mackinac". abb.com.
- ↑ "HVDC Advances in the Russia - Substations content from TDWorld". tdworld.com.
Sources
- Vijay K. Sood. HVDC and FACTS Controllers: Applications Of Static Converters In Power Systems. Springer-Verlag. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-4020-7890-3.