.png)
Map of all French possessions and colonies
During the 19th and 20th centuries, the French colonial empire was one of the largest in the world, behind the British Empire, the Russian Empire, and the Spanish Empire; it extended over 12,898,000 km2 (4,980,000 sq mi) of land at its height in the 1920s and 1930s. The French colonial empire was the second largest empire in the 17th century and the second largest empire in 1929 after Spain and Britain respectively. Including metropolitan France, the total amount of land under French sovereignty reached 13,018,575 km² (5,020,000 sq. miles) in 1929, which is 8.7% of the Earth's total land area. Also including Fezzan, captured by Philippe Leclerc de Hauteclocque for Charles de Gaulle during the Second World War, it reached 13,518,575 km2 (5,219,551 sq mi), which is 9% of the Earth's total land area. The French colonial empire's influence made French a widely spoken colonial European language, along with English, Spanish, and Portuguese.
France began to establish colonies in North America, the Caribbean and India, following Spanish and Portuguese successes during the Age of Discovery, in rivalry with Britain for supremacy. A series of wars with Britain during the 18th century and early 19th century, which France lost, ended its colonial ambitions in these regions, and with it what some historians term the "first" French colonial empire. In the 19th century, France established a new empire in Africa and South East Asia. Some of these colonies lasted beyond the invasion and occupation of France by Nazi Germany during World War II. At present, France possesses the second-largest exclusive economic zone in the world, just after the USA; it measures approximately 11,351,000 km2 (4,383,000 sq mi).
Here is a list of all the countries that were part of the French colonial empires in the last 500 years, either entirely or in part, either under French sovereignty or as mandate or protectorate.
In Europe
-en.svg.png)
The 130 French Départements in 1811

Illyrian Provinces
.svg.png)
Flag of French Protectorate of Saar
- Albania
- Principality of Andorra (1806–1814) (the French President is Co-Prince of Andorra)
- Austria
- The French occupied zone in Austria (15.8% of the current country) (1945–1956)
- What is now Belgium (1703–1706) (1745–1748) (1795–1814)
- What is now mostly Croatia and a part of Slovenia
- Illyrian Provinces :
- The eleven French departments of Croatia (1808–1813) (Adelsberg, Bouches-du-Cattaro, Croatie, Dalmatie, Fiume, Gorice, Laybach, Neustdat, Raguse, Trieste, Willach)
- Greece
- Italy (1805–1814)
- Kingdom of Naples
- Town of Venice (1866)
- The fifteen French departments of Italy (26.5% of the current country) (1802–1814) (Doire, Marengo (department), Pô (department), Sésia, Stura, Tanaro, Apennins, Gênes, Montenotte, Méditerranée, Ombrone (department), Taro (department), Tibre, Trasimène)
- Germany
- Town of Kehl (French administration for seven years to prevent possible German attacks after the WWI) (1918–1925??) (1946–1953)
- The Confederation of the Rhine (1806–1813) (Around thirty German German States)
- The French Zone of Occupation in Germany (15.7% of the current country) (1945–1956)
- The French Protectorate of Saar (protectorate) (0.71% of the current country) (1920–1935) (1947–1956)
- Guernsey (1204–1205) (1205–1206) (1338–1340) (1372–1373)
- Jersey (1204–1205) (1205–1206) (1380–1382) (1461–1468) (1781 - Battle of Jersey)
- Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (1792–1793) (1795–1814)
- Malta (1798–1800)
- The rock of Monaco (1793–1814)
- Netherlands (1795–1810)
- Poland
- Portugal (1807–1810)
- Spain (1808–1813)
- Switzerland (1798–1813)
- England (1066), (partly in 1216-1223)
- United Kingdom
- British overseas territories
- Vatican
- The French domains of Vatican (Five churches and their dependence : St Louis des Français, La Trinité des monts, St Nicolas des Lorrains, St Yves des Bretons, St Claude des Francs-comtois de Bourgogne. Then, 13 Residential properties in Rome and one building and about hectares of lands to Lorette)[4]
In the Americas

This map shows the
Louisiana Purchase area, which corresponds approximately with colonial French Louisiana.
- What is now the Dominican Republic (1795–1809)
- Canada
- What is now the United States
- What is now Brazil
- France Équinoxiale (Bay of São Luis) (1610–1615)
- The island of Saint Alexis (1531)
- The Territory of Amapá (1897) (disputed Franco-Brazilian territory resolved in favour of Brazil)[5]
- The city of Viçosa-Ceará (Territory of Ibiapaba) (1590–1604)
- France Antarctique, to Fort Coligny ( Rio de Janeiro Bay) (1555–1567)
- Fernando de Noronha's island (1736-1737)
- Mexico
- Haiti (1627–1804)
- French Guiana (1643- )
- What is now Suriname
- Tapanahony (District of Sipaliwini) (Controversial Franco-Dutch in favour of the Netherlands) (25.8% of the current territory) (1814)
- Guadeloupe (1635- )
- Îles des Saintes (1648- )
- Marie-Galante (1635- )
- la Désirade (1635- )
- Martinique (1635- )
- Clipperton Island (1711- )
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon (1604- )
- Collectivity of Saint Martin (1624- )
- Saint Barthélemy (1648-1784, 1878- )
- Dominica (1625–1663, 1778-1783)
- Nevis (1782–1784)
- Grenada (1650–1762, 1779–1783)
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines (1719-1763, 1779–1783)
- Saint Christopher Island (1628–1690, 1698–1702, 1706, 1782–1783)
- Antigua (briefly in 1666)
- Saint Lucia (1650–1723, 1756–1778, 1784–1803)
- What is now Guyana (1782–1784)
- Tobago (1666–1667, 1781–1793, 1802–1803)
In Africa

Map of French colonies in Africa (in pink)
French East Africa
In Asia
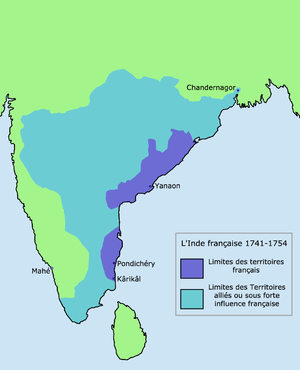
Map Of French Colony in India

Map of French Mandate of Syria
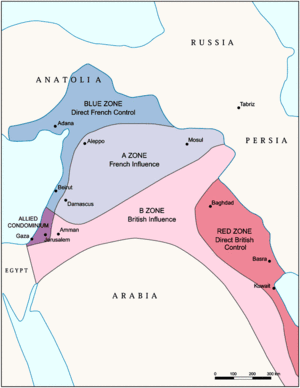
Zones of French and British influence and control established by the Sykes-Picot Agreement
- French Indochina
- French Indochinese Union (1887–1954)
- India and Sri Lanka
- French India
- Arkat (protectorate) (1692–1750)
- Madras (1746–1749)
- French Establishments of India (included 5% of current Indian territory, and the French zone of influence extended to 30% of the territory)
- Pondichéry (1765–1954)
- Karikal (1725–1954)
- Mahé (1721–1954)
- Yanaon (1723–1954)
- Chandernagor (1673–1952)
- Trincomalee (1782–1784)
- Taiwan
- The city/port of Keelung (1884–1885)
- Pescadores Islands (1885)
- Turkey
- The Province of Cilicia (incorporated into the French Mandate of Syria) (1919–1922)
- The Philippines
- China
- Israel
- Lebanon or French Lebanon (1920–1943) (French Mandate of Lebanon)
- Syria (1920–1946) (French Mandate of Syria)
- Yemen
- The peninsula of Cheikh Saïd (1868–1869) (territory in the Cheikh, purchase by a French based company never completed - no official claim to jurisdiction. Yemen's sovereignty was confirmed by France in 1939.)[8]
In Oceania

French flags in Polynesia

Flag of Anglo-French joint Naval
Flag of the Alo/Tu`a chiefdom

Flag of the Sigave chiefdom
Flag of the ʻUvea chiefdom
In Antarctica
See also
Notes and references
- ↑ "Maisons de Victor Hugo". Paris.fr. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ↑ Google Books
- ↑ "domaines français de Sainte-Hélène". Domfrance.helanta.sh. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ↑ "Ambassade de France près le Saint-Siège | Les Pieux Établissements". France-vatican.org. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ↑ http://webtice.ac-guyane.fr/histgeo/IMG/pdf/le_conteste_franco-bresilien-4.pdf
- ↑ http://www.minefe.gouv.fr/fonds_documentaire/notes_bleues/nbb/nbb270/entente_cordiale.pdf
- ↑ "Guerre d'Algérie (1954-1962), prélude à la guerre d'Algérie" by bernard CROCHET and Gérard PIOUFFRE
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Isc - Cfhm - Ihcc". Stratisc.org. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ↑ "Domaines nationaux - Consulat Général de France à Jérusalem". Consulfrance-Jerusalem.org. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ↑ http://expositions.bnf.fr/veo/reperes/index.htm
- ↑ http://www.tahitiheritage.pf/fiche-drapeau-de-rurutu-24163.htm
- ↑ "Consulter le sujet - L'Australie serait-elle française ?!... • [Forums". Francedownunder.com. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ↑ Godard, Philippe; Kerros, Tugdual de; Margot, Odette; Stanbury, Myra; Baxter, Sue; Western Australian Museum; Godard, Phillippe; De Kerros, Tugdual; Margot, Odette; Stanbury, Myra; Baxter, Sue (2008), 1772 : the French annexation of New Holland : the tale of Louis de Saint Aloürn, Western Australian Museum, ISBN 978-1-920843-98-4
- ↑ Philippe Godard, Tugdual de Kerros 2002, "Louis de Saint Aloüarn, un marin breton à la conquête des terres australes", Les Portes du large, Saint-Jacques-de-la-Lande, 331-336
- ↑ "TAAF". Taaf.fr. Retrieved 2012-01-10.
- ↑ "Kerguelen – yves trémarec – james cook – asia – hillsborough – rhodes". Kerguelen-voyages.com.
External links
.png)
-en.svg.png)

.svg.png)

.svg.png)













