Lingula (brachiopod)
| Lingula Temporal range: Cretaceous–Recent | |
|---|---|
| | |
| Lingula anatina, shell (top), full habitus (bottom) | |
| | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Brachiopoda |
| Class: | Lingulata |
| Order: | Lingulida |
| Family: | Lingulidae |
| Genus: | Lingula Bruguière, 1791 |
| Type species | |
| Lingula anatina Lamarck, 1801[1][2] | |
| species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Ligula, Ligularius, Lingularius, Pharetra | |
Lingula is a genus of brachiopods within the class Lingulata. Lingula is known as "moule-à-queue" (tailed mussel) in New Caledonia, "bec de cane" (duck bill) along some coasts in the Indian Ocean, and "shamisen-gai" in Japan (for its likeness to the shamisen, a Japanese lute). Lingula is known to have existed possibly since the Cretaceous or at least the Tertiary. Like its relatives, it has two unadorned phosphatic valves and a long fleshy stalk. Lingula lives in burrows in barren sandy coastal seafloor and feeds by filtering detritus from the water. It can be detected by a short row of three openings through which it takes in water (sides) and expels it again (middle). In Thailand, there is limited Lingula anatina fishery, where it is known as hoi pak ped.[3]
Living fossil
Lingula has long been considered an example of a living fossil; in fact, the perceived longevity of this genus led Darwin to coin this concept. This living fossil status is now considered unjustified however. This status is based on the shape of the shell only, and it has been shown that this shape corresponds to a burrowing lifestyle, occurring in different brachiopod lineages, with different and evolving internal structures.[1]
Etymology
Lingula is probably derived from the Latin word for tongue "lingua" and a diminutive suffix -ula, so small tongue. Alternatively it may be derived from the Latin word for spoon (Lingula) directly. The origin of the epithet anatina is not known, but in Latin "anatina" means "belonging to the duck", possibly due to its resemblance to a duck bill. Another possible derivation could be from the French "Anatife" (goose barnacle), for its likeness.[1]
Taxonomy
Reassigned species
The following species, previously assigned to Lingula are now considered better placed in other genera:[4]
- L. albida = Glottidia albida
- L. alveolata = †Dignomia alveolata
- L. attenuata = †Palaeoglossa attenuata
- L. audebarti = Glottidia audebarti [1]
- L. criei = †Tomasina criei
- L. davisii = †Lingulella davisii
- L. imbituvensis = †Langella imbituvensis
- L. lesueuri = †Ectenoglossa lesueuri
- L. nebrascensis = †Trigonoglossa nebrascensis
- L. pinnaformis = †Lingulepis pinnaformis
- L. plumbea = †Monobilina plumbea
- L. polita = †Dicellomus polita
- L. semen = Glottidia semen [1]
- L. subspatulata = †Barroisella campbelli
- L. williamsana = †Lingulipora williamsana
Gallery
-

The sole evidence of the existence of Lingula anatina is a small three-lobed slit on the surface
-

Lingula anatina in tubes in the sand; the upper figure shows a three-lobed iopening on the surface of the sand; the dotted line in the lower figure indicates position in retraction
-
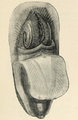
Lingula anatina: animal removed from the shell, mantle reflected, coiled arms separated slightly; a) mouth (marginal setae omitted); ventral aspect, three-quarter face
-
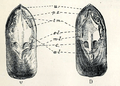
Lingula anatina: interior of the valve showing muscle scars; V. peduncle valve D. brachial valve
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Emig, Christian C. (2008). "On the history of the names Lingula, anatina, and on the confusion of the forms assigned them among the Brachiopoda" (PDF). Carnets de Géologie [Notebooks on Geology] (Article 2008/08).
- ↑ "Lingulidae". Department of Entomology at Texas A&M University.
- ↑ http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/10042857.2013.800376
- ↑ Moore, R.C. (1965). Brachiopoda. Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology. Part H., Volume 1. Boulder, Colorado/Lawrence, Kansas: Geological Society of America/University of Kansas Press. pp. H263. ISBN 0-8137-3015-5.
External links
| External identifiers for Lingula | |
|---|---|
| Encyclopedia of Life | 73305 |
| ITIS | 156762 |
| NCBI | 7571 |
| WoRMS | 235158 |
| Also found in: Wikispecies | |
- Introduction to the Lingulata
 Data related to Lingula at Wikispecies
Data related to Lingula at Wikispecies Media related to Lingula at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lingula at Wikimedia Commons- Brachiopoda world database
- BrachNet