Line Islands
Coordinates: 2°00′S 156°30′W / 2°S 156.5°W
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands, is a chain of eleven atolls and low coral islands in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands, that stretches for 2,350 km in a northwest-southeast direction, making it one of the longest island chains of the world. Eight of the islands form part of Kiribati, while the remaining three are United States territories grouped with the United States Minor Outlying Islands.
Those that are part of Kiribati are in the world's farthest forward time zone, UTC+14:00. The time of day is the same as in the U.S. state of Hawaiʻi, but the date is one day ahead. The time is 26 hours ahead of some other islands in Oceania like Baker Island which uses UTC−12:00.
The United States previously claimed all the Line Islands under the Guano Islands Act. This claim was relinquished under the Treaty of Tarawa, which recognised Kiribati's sovereignty over the majority of the chain.
The group is geographically divided into three subgroups; The Northern, Central, and Southern Line Islands. The Central Line Islands are sometimes grouped with the Southern Line Islands. The table below lists the islands from North to South.
* The lagoon areas marked with an asterisk are contained within the island areas of the previous column because they are, unlike in the case of a typical atoll, inland waters completely sealed off from the sea.
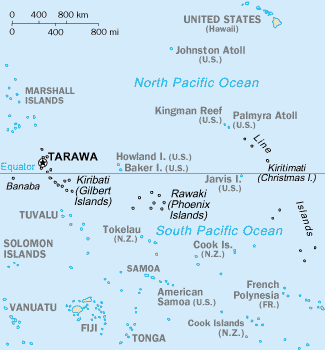
Kiritimati is the largest atoll in the world in terms of land area. The islands were annexed by Britain in 1888 with a view to laying the Pacific cable, with Tabuaeran (then Fanning Island) as a relay station. The cable was laid and was operational between 1902 and 1963 except for a short period in 1914.
Copra and "Petfish" are the main export products (with seaweed).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Australia-Oceania :: United States Pacific Island Wildlife Refuges". CIA - The World Factbook. US CIA. Retrieved 2012-09-16.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 "Kiribati 2005 Census of Population and Housing: Provisional Tables" (PDF). Kiribati National Statistics Office. Retrieved 2012-09-16.
- ↑ "CIA - The World Factbook -- Kiribati". The World Factbook. US CIA. Retrieved 2012-09-16.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Line Islands. |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
