Leadpipe

| Basic trombone anatomy | 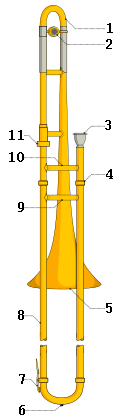 |
|
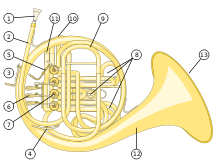
In a brass instrument, a leadpipe is the pipe or tube into which the mouthpiece is placed.
For example, on the illustration of a trombone, the leadpipe would be between #3 and #4, the mouthpiece and the slide lock ring. In the illustration of a French horn, the leadpipe is #2.
Detachable leadpipes
Most leadpipes are permanently fixed in the instrument, though aftermarket changes, usually carried out by a repairer, are quite common.[1] Some instruments have a detachable leadpipe to allow changing key; to permit the player to easily select different playing and tonal characteristics;[2] or simply to act as the instrument's main tuning slide where the shape, or other design issues, make this the best place for it. The use of the leadpipe as the main tuning slide is particularly common in flugelhorns and piccolo trumpets though not unknown in other instruments. For example, in the Selmer piccolo trumpet in the photograph, the leadpipes are used for all three functions: the aftermarket Blackburn pipes shown have different playing characteristics from those of the stock Selmer pipe;[3] the choice of leadpipe determines whether the instrument is in A or B♭; it is also the main tuning slide.
A detachable leadpipe is often held in place with a collar and screw arrangement which locks it at the desired depth into the instrument; however if it is not also a tuning slide it may simply be inserted to its full depth inside a sleeve and sit there without needing securing. Tuning slide leadpipes offer the player the disadvantage that they cannot be adjusted while playing, whereas conventional U-shaped tuning slides can.
See also
References
- ↑ "Najoom Trumpet Leadpipes". Dennis Najoom. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ↑ "Smith-Watkins B-flat Trumpet Leadpipes". Smith-Watkins. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ "Piccolo Leadpipes (Flash page: please click through for the product list)". Blackburn Trumpets. Retrieved 17 December 2012.