Lampris guttatus
| Lampris guttatus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Opah | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Lampriformes |
| Family: | Lampridae |
| Genus: | Lampris |
| Species: | L. guttatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Lampris guttatus Brünnich[1] | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Lampris guttatus (common names opah, cravo, moonfish, kingfish, and Jerusalem haddock) is a large, colorful, deep-bodied pelagic lampriform fish belonging to the family Lampridae, which comprises the genus Lampris, with two extant species. It is a pelagic fish with a worldwide distribution. While it is common to locations such as Hawaii[2] and west Africa, it remains uncommon in others, including the Mediterranean.[3] In the places where L. guttatus is prevalent, it is not a target of fishing, though it does represent an important commercial component of bycatch. In Hawaiian longline fisheries, it is generally caught on deep sets targeting big-eye tuna. In 2005, the fish caught numbered 13,332. In areas where the fish is uncommon, such as the Mediterranean, its prevalence is increasing. Some researchers believe this a result of climate change.[3] Much is still unknown about the distribution, interactions, life histories, and preferred habitats of this fish and other medium to large-sized pelagic fishes. To better implement ecosystem-based, spatially structured fishery management approaches, this must be changed.[4]
Etymology
The genus name Lampris is derived from the Greek word lampros, meaning "brilliant" or "clear", while the Latin species name guttatus means spotted and refers to the spotted body of this fish.
Description

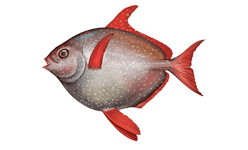
Lampris guttatus is a large discoid and deeply keeled fish with an attractive form and a conspicuous coloration. They usually reach a maximum length of 2 m (6.6 ft) and a maximum weight of 270 kg (600 lb).
The body is a deep steely blue grading to rosy on the belly, with white spots in irregular rows covering the flanks. Both the median and paired fins are a bright vermillion. Jaws are vermillion, too. The large eyes stand out as well, ringed with golden yellow. The body is covered in minute cycloid scales and its silvery, iridescent guanine coating is easily abraded.
They have long falcated pectoral fins inserted (more or less) horizontally. The caudal fins are broadly lunated, forked, and emarginated. Pelvic fins are similar but a little longer than pectoral fins, with about 14–17 rays.
The anterior portion of a dorsal fin (with about 50–55 rays) is greatly elongated, also in a falcate profile similar to the pelvic fins. The anal fin (34–41 rays) is about as high and as long as the shorter portion of the dorsal fin, and both fins have corresponding grooves into which they can be depressed. The snout is pointed and the mouth small, toothless, and terminal. The lateral line forms a high arch over the pectoral fins before sweeping down to the caudal peduncle.
Habitat and distribution
L. guttatus has a worldwide distribution, from the Grand Banks to Argentina in the Western Atlantic, from Norway and Greenland to Senegal and south to Angola (also in the Mediterranean) in the Eastern Atlantic, from the Gulf of Alaska to southern California in the Eastern Pacific, in temperate waters of the Indian Ocean, and rare forays into the Southern Ocean.
This species is presumed to live out their entire lives in the open ocean, at mesopelagic depths of 50–500 m, with possible forays into the bathypelagic zone. Typically, it is found within water at 8 to 22 °C.[2] To better understand the depths L. guttatus inhabited in the tropical and temperate ocean waters, a study was performed, tagging them in the central North Pacific. Their location was found to be related to a temporal scale, inhabiting depths of 50-100 m during the night and 100-400 m during the day. The depths of the vertical habitat varied with local oceanogeographic conditions, though the patterns of deeper depths during the day is universal to the species.[4]
Behavior
The life history and development of L. guttatus still remain rather uncertain.[5] They are apparently solitary, but are known to school with tuna and other scombrids. They propel themselves by a lift-based mode of swimming, that is, by flapping their pectoral fins. This, together with their forked caudal fins and depressible median fins, indicates they swim at constantly high speeds. Squid and krill make up the bulk of their diet; small fish are also taken.
They probably spawn in the spring. Their planktonic larvae lack of dorsal and pelvic fin ornamentation. The slender hatchlings later undergo a marked and rapid transformation from a slender to deep-bodied form; this transformation is complete by 10.6 mm standard length.
Like many other large pelagic visual predators, such as swordfish and big-eye tuna, it exhibits vertical behavior. Its speeds have found to be more than 25 cm/s, and on one occasion one was witnessed to have a burst of speed of 4 m/s.[2]
One of the evolutionary adaptations of L. guttatus is cranial endothermy, the ability to generate and maintain metabolic heat in the cranial and optic regions at 2°C warmer than the rest of the body.[6] This is important for maintaining brain and eye function during the wide range of temperatures it experiences with its vertical movements.[7]
Based on those caught off the Hawaiian coast, the diet of L. guttatus appears to be a squid-based. Those caught along the Patagonia Shelf also showed a narrow range of prey items, the most common of which was the deepwater onychotenhid squid (Morotenthis ingens).[2]
See also
- List of fish families
- List of fish common names
References
- ↑ Fish Base
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Polovina, Jeffrey J.; Hawn, Donald; Abecassis, Melanie (2008). "Vertical movement and habitat of opah (Lampris guttatus) in the central North Pacific recorded with pop-up archival tags". Marine Biology 153 (3): 257–267. doi:10.1007/s00227-007-0801-2. ISSN 0025-3162.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Francour, Patrice; Cottalorda, Jean-Michel; Aubert, Maurice; Bava, Simone; Colombey, Marine; Gilles, Pierre; Kara, Hichem; Lelong, Patrick; Mangialajo, Luisa; Miniconi, Roger; Quignard, Jean-Pierre (2010). "Recent Occurrences of Opah, Lampris guttatus (Actinopterygii, Lampriformes, Lampridae), in the Western Mediterranean Sea". Acta Ichthyologica Et Piscatoria 40 (1): 91–98. doi:10.3750/AIP2010.40.1.15. ISSN 0137-1592.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Richardson, David E.; Llopiz, Joel K.; Guigand, Cedric M.; Cowen, Robert K. (2010). "Larval assemblages of large and medium-sized pelagic species in the Straits of Florida". Progress in Oceanography 86 (1-2): 8–20. doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2010.04.005. ISSN 0079-6611.
- ↑ (Oelschlaeger H. 1976).
- ↑ Bray, Dianne. "Opah, Lampris guttatus". Fishes of Australia. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ↑ Runcie R. 2006. Cranial endothermy in the moonfish (Lampris guttatus)
- Biolib
- Aquatab
- Opah NOAA FishWatch. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- Parin NV and Kukuev EI. 1983. Reestablishment of the validity of lampris immaculata gilchrist and the geographical distribution of lampridae. Voprosy Ikhtiologii.Moscow 23(1):3-14.