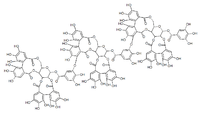
Lambertianin C
 | |
| Properties | |
|---|---|
| C123H80O78 | |
| Molar mass | 2805.81 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Lambertianin C is an ellagitannin.
Natural occurrences
Lambertianin C can be found in Rubus species such as Rubus lambertianus,[1] in cloudberries (Rubus chamaemorus)[2] and in red raspberries (Rubus idaeus).[3]
Chemistry
Lambertianin C is trimer of casuarictin linked by sanguisorbic acid ester groups between glucopyranose moieties.[1]
Health effects
It is a molecule responsible for the antioxidant capacity of raspberries.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tanaka, T.; Tachibana, H.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I.; Hsu, F. L.; Kohda, H.; Tanaka, O. (1993). "Tannins and related compounds. CXXII. New dimeric, trimeric and tetrameric ellagitannins, lambertianins A-D, from Rubus lambertianus Seringe". Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 41 (7): 1214–1220. doi:10.1248/cpb.41.1214. PMID 8374992.
- ↑ Kähkönen, M.; Kylli, P.; Ollilainen, V.; Salminen, J. P.; Heinonen, M. (2012). "Antioxidant Activity of Isolated Ellagitannins from Red Raspberries and Cloudberries". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 60 (5): 1167–1174. doi:10.1021/jf203431g. PMID 22229937.
- ↑ Mullen, W.; Stewart, A. J.; Lean, M. E.; Gardner, P.; Duthie, G. G.; Crozier, A. (2002). "Effect of freezing and storage on the phenolics, ellagitannins, flavonoids, and antioxidant capacity of red raspberries". Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 50 (18): 5197–5201. doi:10.1021/jf020141f. PMID 12188629.
- ↑ Borges, G.; Degeneve, A.; Mullen, W.; Crozier, A. (2010). "Identification of Flavonoid and Phenolic Antioxidants in Black Currants, Blueberries, Raspberries, Red Currants, and Cranberries†". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 58 (7): 3901–3909. doi:10.1021/jf902263n. PMID 20000747.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||