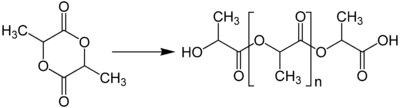
Lactide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Dilactid, (R,R)-3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxan-2,5-dion, (S,S)-3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxan-2,5-dion, (meso)-3,6-Dimethyl-1,4-dioxan-2,5-dion, (R,R)-2,5-Dimethyl-3,6-dioxo-1,4-dioxan, (S,S)-2,5-Dimethyl-3,6-dioxo-1,4-dioxan, (meso)-2,5-Dimethyl-3,6-dioxo-1,4-dioxan | |
| Identifiers | |
| 4511-42-6 [(S,S)-Lactide] 25038-75-9 [(R,R)-Lactide] 13076-19-2 [(R,S)-Lactide = meso-Lactide] 26680-10-4 [mixture of three isomers] | |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C6H8O4 |
| Molar mass | 144.13 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 95 to 97 °C (203 to 207 °F; 368 to 370 K) [(S,S)-Lactide and (R,R)-Lactide][1] |
| Hydrolyses to lactic acid[1] | |
| Solubility | soluble in chloroform, methanol slightly soluble in benzene |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26 S37/39 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Lactide is the cyclic di-ester of lactic acid, i.e., 2-hydroxypropionic acid. Lactic acid cannot form a lactone as other hydroxy acids do because the hydroxy group is too close to the carboxylic group. Instead, lactic acid first forms a dimer, which is similar to a 5-hydroxyacid. The dimer contains a hydroxy group at a convenient distance from the carboxylic group for the formation of a lactone. Indeed, the dimer readily forms a six-membered cyclic diester known as lactide. Lactides may be prepared by heating lactic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst.
In general, a lactide is the cyclic diester, i.e., the di-lactone of two molecules of any 2-hydroxycarboxylic acid.
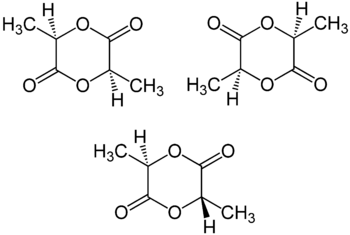
Stereoisomers
Lactic acid is chiral; two enantiomeric forms, (R)-lactic acid and (S)-lactic acid, may exist. Thus, lactide formed from two equivalents of lactic acid consists of two stereocenters. Three different stereoisomers of lactide are known:
Polymerization
Lactide can be polymerized to polylactic acid (polylactide) using suitable catalysts, with either syndiotactic or a heterotactic stereocontrol, to give materials with many useful properties:[2]