Labialized palatal approximant
| Labialized palatal approximant |
|---|
| ɥ |
|---|
| jʷ |
|---|
| IPA number |
171 |
|---|
| Encoding |
|---|
| Entity (decimal) |
ɥ |
|---|
| Unicode (hex) |
U+0265 |
|---|
| X-SAMPA |
H |
|---|
| Kirshenbaum |
j<rnd> |
|---|
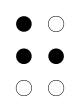
| Braille |
  |
|---|
|
|
| Sound |
|---|
|
source · help |
The labialized palatal approximant, also called the labial–palatal or labio-palatal approximant, is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. It has two constrictions in the vocal tract: with the tongue on the palate, and rounded at the lips. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɥ⟩, a rotated lowercase letter ⟨h⟩, or occasionally ⟨jʷ⟩, since it is a labialized [j].
The labialized palatal approximant is the semivocalic equivalent of the close front rounded vowel [y]. The two are almost identical featurally. They alternate with each other in certain languages, such as French, and in the diphthongs of some languages, ⟨ɥ⟩ and ⟨y̯⟩ with the non-syllabic diacritic are used in different transcription systems to represent the same sound.
Features
Features of the labial-palatal approximant:
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is an oral consonant, which means air is allowed to escape through the mouth only.
- It is a central consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream along the center of the tongue, rather than to the sides.
Occurrence
See also
References
| |
|---|
| | IPA topics |
|---|
| | IPA | |
|---|
| | Phonetics | |
|---|
| | Special topics | |
|---|
| | Encodings | |
|---|
|
| | | |
|---|
|
| — These tables contain phonetic symbols, which may not display correctly in some browsers. [Help] |
| — Where symbols appear in pairs, left–right represent the voiceless–voiced consonants. |
| — Shaded areas denote pulmonic articulations judged to be impossible. |
| — Symbols marked with an asterisk (*) are not defined in the IPA. |
| | | Chart image |
- Pulmonics
- Non-pulmonics
- Affricates
- Co-articulated
|
|---|
|
| | |
|
.svg.png)
