Lövheim cube of emotion
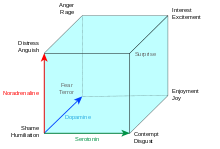
Lövheim Cube of emotion[1][2] is a proposed theoretical model aiming at explaining the relationship between the monoamine neurotransmitters and the emotions. The model was proposed in a paper of 2012 by Hugo Lövheim.[3] In the model, the three monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine and noradrenaline form the axes of a coordinate system, and the eight basic emotions, labeled according to the affect theory of Silvan Tomkins, are placed in the eight corners. The origin corresponds to a situation where all three signal substance are low. The eight corners of the cube corresponds to the eight possible combinations of low or high level of the three monoamines as shown in the table below. The model hence proposes a direct relation between specific combinations of the levels of the signal substances and certain basic emotions,[4] and merges a categorical and a dimensional view of emotions.[5]
| Basic emotion | Serotonin | Dopamine | Noradrenaline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shame/humiliation | Low | Low | Low |
| Distress/anguish | Low | Low | High |
| Fear/terror | Low | High | Low |
| Anger/rage | Low | High | High |
| Contempt/disgust | High | Low | Low |
| Surprise | High | Low | High |
| Enjoyment/Joy | High | High | Low |
| Interest/excitement | High | High | High |
Anger is for example, according to the model, produced by the combination of low serotonin, high dopamine and high noradrenaline.
Due to the direct relation to the monoamine neurotransmitters, the model might have an advantage compared to previous models of basic emotions such as, for example, Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions or the PAD emotional state model. Symptoms of depression might be interpreted as an emotional palette restricted to the low-serotonergic side of the Lövheim cube, where only the basic emotions shame/humiliation, distress/anguish, fear/terror and anger/rage are within reach. The core depressive symptoms of sadness and lack of interest can be interpreted as the inability to reach the basic emotions of joy and interest located on the high-serotonergic side.
"While the validity of the model remains unverified ... if valid it would allow direct extraction of emotions from given combinations of the monoamines (and possibly vice versa)." [6]
Lövheim's autonomic nervous system theory

Lövheim also proposed that the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system might be viewed as orthogonal axes, instead of viewing them as antagonists. The sympathetic axis were thought to represent arousal and the parasympathetic axis to represent secretion and possible positive versus negative valence.[7] This model corresponds, in a way, to the cube model of emotions (the sympathetic axis appears to be similar to the noradrenergic axis, and the parasympathetic axis to the serotonergic axis in the CNS).
In culture
In 2012, a dance performance based on the model was set up in Miami, USA.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ Lövheim H. A new three-dimensional model for emotions and monoamine neurotransmitters. (2012). Med Hypotheses, 78, 341-348. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2011.11.016 PMID 22153577
- ↑ Larue O. The emergence of (artificial) emotions from cognitive and neurological processes. Biologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures. In Press, Available online 1 February 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bica.2013.01.001
- ↑ Lövheim H. A new three-dimensional model for emotions and monoamine neurotransmitters. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22153577
- ↑ Lövheim H. A new three-dimensional model for emotions and monoamine neurotransmitters. (2012). Med Hypotheses, 78, 341-348. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2011.11.016 PMID 22153577
- ↑ Guo, B., Riboni, D., & Hu, P. (2014). Creating Personal, Social, and Urban Awareness through Pervasive Computing (pp. 1-440). Hershey, PA: IGI Global. doi:10.4018/978-1-4666-4695-7
- ↑ von Haugwitz R. Modulating Reinforcement- Learning Parameters Using Agent Emotions. (2012). Chalmers University of Technology, Master’s Thesis. http://publications.lib.chalmers.se/records/fulltext/173825/173825.pdf
- ↑ Lövheim H. A new perspective on the autonomic nervous system. (2013) Med Hypotheses, 81, 356. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2013.05.005 Epub 2013 Jun 2 PMID 23735561
- ↑ http://pioneerwinter.org/gallery/lovheim-cube-a-movement-study/