Kurukshetra War
| Kurukshetra War | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Territory-less Pandavas of the Kurus with the support of the mighty Panchala tribe and others. | Kauravas (Kuru tribe) with capital at Hastinapura and their allies | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Overlord Yudhisthira Commanders-in-chief Dhrishtadyumna (day 1-18) † Strategists Krishna |
Overlord Duryodhana † Commanders-in-chief Bhishma (day 1-10) † Drona (day 11-15) † Karna (day 16-17) † Shalya (day 18) † Ashwatthama (night raid) Strategists Shakuni † | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
7 Akshauhinis 153,090 chariots and chariot-riders 153,090 elephants and elephant-riders 459,270 horses and horse-riders 765,450 infantry (total 1,530,900 soldiers) |
11 Akshauhinis 240,570 chariots and chariot-riders 240,570 elephants and elephant-riders 721,710 horses and horse-riders 1,202,850 infantry (total 2,405,700 soldiers) | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Almost total (1,530,900 soldiers), only 8 known survivors - the five Pandavas, Krishna, Satyaki, Yuyutsu. |
Almost total (2,405,700 soldiers), only 4 known survivors - Ashwatthama, Sage Kripa, Kritavarma, Vrishakethu (son of Karna). | ||||||
The Kurukshetra War is a Hindu Historical war described in the Indian epic Mahābhārata as a conflict that arose from a dynastic succession struggle between two groups of cousins of an Indo-Aryan kingdom called Kuru, the Kauravas and Pandavas, for the throne of Hastinapura. It involved a number of ancient kingdoms participating as allies of the rival groups.
The location of the battle is described as having occurred in Kurukshetra in the modern state of Haryana in India. The conflict is believed to form an essential component of an ancient work called Jaya and hence the epic Mahābhārata.
Mahābhārata states that the war started on Kartheeka Bahula Amavasya (the end of the Kartheeka and the start of the Margasira lunar month), moon on Jyesta star, on Tuesday early morning. A solar eclipse also happened on that day and this Muhurtha was kept by Krishna himself. The Bhagavad Gita was told on that early morning, before the war began. The war lasted only eighteen days, during which vast armies from all over the Indian (Bharatha) Subcontinent fought alongside the two rivals. Despite only referring to these eighteen days, the war narrative forms more than a quarter of the book, suggesting its relative importance within the epic, which overall spans decades of the warring families.
The narrative describes individual battles of various heroes of both sides, battle-field deaths of some of the prominent heroes, military formations employed on each day by both armies, war diplomacy, meetings and discussions among the heroes and commanders before commencement of war on each day and the weapons used. The chapters (parvas) dealing with the war (from chapter six to ten) are considered amongst the oldest in the entire Mahābhārat.
The Kurukshetra War is believed to date variously from 6000 BCE to 500 BCE,[1] based on the astronomical and literary information from Mahābhārata. The history of the Kurukshetra War is also traced to the Battle of the Ten Kings mentioned in Rigveda.[2]
Historical context
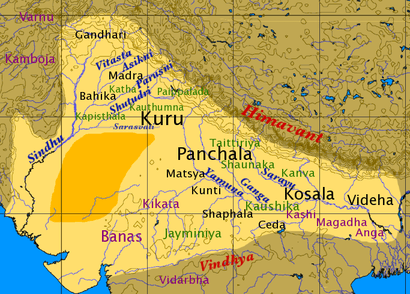

Though the Kurukshetra War is not mentioned in Vedic literature, its prominence in later literature led historians such as A. L. Basham to conclude that, "certainly a great war took place, and succeeding generations looked upon it as marking an end of an epoch".[3] Popular tradition holds that the war marks the transition to Kaliyuga and thus dates it to 3102 BCE;[4] another tradition places the war in 15th century BCE. However historians regard these dates as too early, and inconsistent with the available archaeological and literary evidence. Basham considers the beginning of the 9th century BCE as a more plausible date for the events.[3] Similarly, Michael Witzel concludes that the general setting of the epic has a historical precedent in Iron Age (Vedic) India, where the Kuru kingdom was the center of political power during roughly 1200 to 800 BCE.[5] A dynastic conflict of the period could have been the inspiration for the Jaya, the foundation on which the Mahabharata corpus was built, with a climactic battle eventually coming to be viewed as an epochal event.
Puranic literature presents genealogical lists associated with the Mahabharata narrative. The evidence of the Puranas is of two kinds. Of the first kind, there is the direct statement that there were 1015 (or 1050) years between the birth of Parikshit (Arjun's grandson) and the accession of Mahapadma Nanda, commonly dated to 382 BCE, which would yield an estimate of about 1400 BCE for the Bharata battle.[6] However, this would imply improbably long reigns on average for the kings listed in the genealogies.[7] Of the second kind are analyses of parallel genealogies in the Puranas between the times of Adhisimakrishna (Parikshit's great-grandson) and Mahapadma Nanda. Pargiter accordingly estimated 26 generations by averaging 10 different dynastic lists and, assuming 18 years for the average duration of a reign, arrived at an estimate of 850 BCE for Adhisimakrishna, and thus approximately 950 BCE for the Bharata battle[7]
B. B. Lal used the same approach with a more conservative assumption of the average reign to estimate a date of 836 BCE, and correlated this with archaeological evidence from Painted Grey Ware sites, the association being strong between PGW artifacts and places mentioned in the epic.[8]
There have been a number of theories put forward:[9]
- The most widely accepted date is 10th century BCE or 950 BCE, according to archeological evidence.
- B. N. Achar states a date of 3067 BCE using planetary positions listed in the Mahābhārata.
- S. Balakrishna concluded a date of 2559 BCE using consecutive lunar eclipses.
- P. V. Holey states a date of November 13, 3143 BCE using planetary positions and calendar systems.
- R. N. Iyengar concluded a date of 1478 BCE using double eclipses and Saturn+Jupiter conjunctions.
- P. R. Sarkar estimates a date of 1298 BCE for the war of Kurukshetra.
- P. V. Vartak calculates a date of October 16, 5561 BCE using planetary positions.[10]
- K. Sadananda, based on translation work, states that the Kurukshetra War started on November 22 3067 BCE.[11]
The reconstruction of the history of Vedic India is based on text-internal details. Linguistically, the Vedic texts could be classified in five chronological strata as Rigvedic, Mantra, Samhita, Brahmana, Sutra, and Epic and Pāṇinian. The Mantra language period includes both the mantra and prose language of the Atharvaveda (Paippalada and Shaunakiya), the Rigveda Khilani, the Samaveda Samhita (containing some 75 mantras not in the Rigveda), and the mantras of the Yajurveda. Many of these texts are largely derived from the Rigveda, but have undergone certain changes, both by linguistic change and by reinterpretation. Conspicuous changes include the change of vishva "all" by sarva, and the spread of the kuru- verbal stem (for Rigvedic krno-). This is from the time of the early Iron Age in north-western India, corresponding to the Black and Red Ware (BRW) culture, and the kingdom of the Kurus, dating from ca. the 10th century BCE. The Samhita prose period marks the beginning of the collection and codification of a Vedic canon. An important linguistic change is the complete loss of the injunctive. The Brahmana part ('commentary' on mantras and ritual) of the Black Yajurveda (MS, KS, TS) belongs to this period. Archaeologically, the Painted Grey Ware (PGW) culture from ca. 900 BCE corresponds, and the shift of the political center from the Kurus to the Pancalas on the Ganges.
Background
Mahābhārata, one of the most important Hindu epics, is an account of the life and deeds of several generations of a ruling dynasty called the Kuru clan. Central to the epic is an account of a war that took place between two rival families belonging to this clan. Kurukshetra (literally "field of the Kurus"), was the battleground on which this war, known as the Kurukshetra War, was fought. Kurukshetra was also known as "Dharmakshetra" (the "field of Dharma"), or field of righteousness. Mahābhārata tells that this site was chosen for the war because a sin committed on this land was forgiven on account of the sanctity of this land.
The Kuru territories were divided into two and were ruled by Dhritarashtra (with his capital at Hastinapura) and Yudhishthira of the Pandavas (with his capital at Indraprastha). The immediate dispute between the Kauravas (sons of Dhritarashtra) and the Pandavas arose from a game of dice, which Duryodhana won by deceit, forcing their Pandava cousins to transfer their entire territories to the Kauravas (to Hastinapura) and to "go into exile" for thirteen years. The dispute escalated into a full scale war when Prince Duryodhana, the eldest of the Kauravas, driven by jealousy, refused to restore the Pandavas their territories after the exile as earlier decided, as Duryodhana objected that they were discovered while in exile, and that no return of their kingdom was agreed upon.
Prior to the war, the disinherited Pandavas in the kingdom of Matsya, advised by Krishna, tried to find a diplomatic and peaceful solution to the conflict. Balarama, Krishna's older brother, advised the Pandavas to send an emissary to get the support of the elders of the family like Bhishma, Dhritarashtra, Drona, Kripa etc. with the message "Let us avoid armed conflict as much as possible. Only that which is accrued in peace is worthwhile. Out of war, nothing but wrong can issue".[12] While the emissary was in the Kaurava court, the Pandavas continued with war preparations. They sent messages requesting assistance to a number of neighbouring kingdoms. Their ambassador of peace was insulted and turned away by Duryodhana, who was intent on war, defying the counsel of elders like Bhishma. After several failed attempts on peace, war seemed inevitable. The two sides to the war were the Pandavas and the Kauravas (the official Kuru tribe now ruling both Hastinapura and Indraprastha), both with their allies.
Jaya, the core of Mahābhārata, is structured in the form of a dialogue between Kuru king Dhritarashtra and Sanjaya, his advisor and chariot driver. Sanjaya narrates each incident of the Kurukshetra War, fought in 18 days, as and when it happened. Dhritarāshtra sometimes asks questions and doubts and sometimes laments, knowing about the destruction caused by the war, to his sons, friends and kinsmen. He also feels guilty, due to his own role, that led to this war, destructive to the entire Indian subcontinent.
In the beginning Sanjaya gives a description of the various continents of the Earth, the other planets, and focuses on the Indian Subcontinent and gives an elaborate list of hundreds of kingdoms, tribes, provinces, cities, towns, villages, rivers, mountains, forests etc. of the (ancient) Indian Subcontinent (Bhārata Varsha). He also explains about the 'military formations adopted by each side on each day, the death of each hero and the details of each war-racing. Some 18 chapters of Vyasa's Jaya constitutes the Bhagavad Gita, one of the sacred texts of the Hindus. Thus, this work of Vyasa, called Jaya, deals with diverse subjects like geography, history, warfare, religion and morality. According to Mahabharata itself, the Jaya was recited to the King Janamejaya who is the great-grandson of Arjuna, by Vaisampayana, a disciple of Vyasa (then called the Bharata). The recitation of Vaisampayana to Janamejaya was then recited again by a professional storyteller named Ugrasrava Sauti, many years later, to an assemblage of sages performing the 12-year-long sacrifice for King Saunaka Kulapati in the Naimisha forest(then called the Mahabharata).
Combatants
The Kurus formed a kingdom in the Vedic period of India. They formed the first political center after the Rigvedic period, after their emergence from the Punjab, and it was there that the codification and redaction of the Vedic texts began. Archaeologically, they most likely correspond to the Black and Red Ware Culture of the 12th to 9th centuries BC, at the beginning of the Iron Age in western India. Panchala was the second "urban" center of Vedic civilization, as its focus moved east from the Punjab, after the focus of power had been with the Kurus in the early Iron Age. This period is associated with the Painted Grey Ware culture, arising around 1100 BCE, and declining from 600 BCE, with the end of the Vedic period. The ruling confederacy, the Panchalas, as their name suggests, probably consisted of five clans - the Krivis, the Turvashas, The Keshins, the Srinjayas and the Somakas. Drupada, whose daughter Draupadi was married to the Pandavas belonged to the Somaka clan. However, the Mahabharata and the Puranas consider the ruling clan of the northern Panchala as an offshoot of the Bharata clan and Divodasa, Sudas, Srinjaya, Somaka and Drupada (also called Yajnasena) were the most notable rulers of this clan.
Krishna's peace mission

As a last attempt at peace, Krishna traveled to Hastinapur to persuade the Kauravas to embark upon a peaceful path with him. At Hastinapur, Krishna took his meals and stayed at the house of the minister, Vidura, a religious man and a "devotee" of Krishna. Duryodhana was insulted that Krishna had turned down his invitation to dine with him and stay in his royal palace. Determined to stop the peace mission, Duryodhana plotted to arrest Krishna.
At the formal presentation of the peace proposal by Krishna at the court of Hastinapur, Krishna asked Duryodhana to give back Indraprastha or if not at least five villages, one for each of the pandavas, but Duryodhana said he could not give land even as much as tip of a needle, Krishna's peace proposals were ignored, and Duryodhana publicly ordered his soldiers to arrest Krishna. Krishna laughed and displayed his divine form, radiating intense light. Furious at the insult inflicted upon Him, Lord Krishna cursed Duryodhana that his downfall was certain, to the shock of Dhirtharastra, who tried to pacify the Lord.
His peace mission being rejected by Duryodhana, Krishna returned to Upaplavya to inform the Pandavas that the only course left to uphold the principles of virtue and righteousness was inevitable - war. During the course of his return, Krishna met Karna, Kunti's firstborn (before Yudhisthira), and said to help his brothers, but, being helped by Duryodhana, Karna said to Krishna that he would battle against Pandavas.
War preparations

Krishna had a large force called the Narayani Sena and was himself a great warrior. Duryodhana and Arjuna thus both went to Krishna at Dwarka to ask for his help. Duryodhana arrived first, and found Krishna asleep. Being arrogant and viewing himself as equal to Krishna, Duryodhana chose a seat at Krishna's head and waited for him to rouse. Arjuna arrived later, and being a humble devotee of Krishna, chose to sit and wait at Krishna's feet. When Krishna woke up, He saw Arjuna first and gave him the first right to make his request. Krishna told Arjuna and Duryodhana that he would give the Narayani Sena, to one side, and himself as a non-combatant to the other. Since Arjuna was given the first opportunity to choose, Duryodhana was worried that Arjuna would choose the mighty army of Krishna. When given the choice of either Krishna's army or Krishna Himself on their side, Arjuna on behalf of the Pandavas chose Krishna, unarmed on his own, relieving Duryodhana, who thought Arjuna to be the greatest fool. Later Arjuna requested Krishna to be his charioteer, and Krishna, being an intimate friend of Arjuna, agreed wholeheartedly, and hence received the name Parthasarthy, or 'charioteer of the son of Pritha'. Both Duryodhana and Arjuna returned satisfied.
While camping at a place called Upaplavya, in the territory of Virata, the Pandavas gathered their armies. Contingents arrived from all parts of the country and soon the Pandavas had a large force of seven divisions. The Kauravas managed to raise an even larger army of eleven divisions. Many kingdoms of ancient India such as Dwaraka, Kasi, Kekaya, Magadha, Chedi, Matsya, Pandya, and the Yadus of Mathura were allied with the Pandavas; while the allies of the Kauravas comprised the kings of Pragjyotisha, Kalinga, Anga, Kekaya, Sindhudesa, Avanti in Madhyadesa, Gandharas, Bahlikas,Mahishmati, Kambojas (with the Yavanas, Sakas, Trilinga, Tusharas) and many others.
Pandava army

Seeing that there was now no hope for peace, Yudhisthira, the eldest of the Pandavas, asked his brothers to organize their army. The Pandavas accumulated seven Akshauhinis army with the help of their allies.Each of these divisions were led by Drupada, Virata, Dhristadyumna, Shikhandi, Satyaki, Chekitana and Bhima. After consulting his commanders, the Pandavas appointed Dhristadyumna as the supreme commander of the Pandava army. Mahābhārata says that kingdoms from all over ancient India supplied troops or provided logistic support on the Pandava side. Some of these were: Kekaya, Pandya, Cholas, Magadha, and many more.
Kaurava army
The Kaurava army consisted of 11 Akshauhinis. Duryodhana requested Bhishma to command the Kaurava army. Bhishma accepted on the condition that, while he would fight the battle sincerely, he would not harm the five Pandava brothers. In addition, Bhishma said that Karna would not fight under him as long as he is in the battlefied. It is believed by many that Bhishma pushed Karna into taking this decision due to his affection towards the Pandavas - the Kauravas would be overwhelmingly powerful if both he and Karna appeared in battle simultaneously. However the excuse he used to prevent their simultaneous fighting was that his guru (Parshurama) was insulted by Karna. He also knew that Karna was a Kaunteya(Son of Kunti) from the day he met him in Ranakshetra when Karna offered Arjuna to fight against him and Bhishma wanted to keep Karna out, so that there will be someone to lead the army once he is unable to continue with the war. Regardless, Duryodhana agreed to Bhishma's conditions and made him the supreme commander of the Kaurava army, while Karna was debarred from fighting. But Karna enters the war later when Bhishma is wounded by Arjuna. Apart from the one hundred Kaurava brothers, headed by Duryodhana himself and his brother Dushasana, the second eldest son of Dhritarashtra, the Kauravas were assisted on the battlefield by Drona and his son Ashwathama, the Kaurava's brother-in-law Jayadratha, the brahmin Kripa, Kritavarma, Shalya, Sudakshina, Bhurisravas, Bahlika, Shakuni, and many more who were bound by their loyalty towards either Hastinapura or Dhritarashtra.
Neutral parties
The kingdom of Vidarbha, with its King Rukmi, Vidura, the ex-prime minister of Hastinapur and younger brother to Dhritarashtra, and Balarama were the only neutrals in this war. Rukmi wanted to join the war, but Duryodhana and Arjuna refused to allow him, because he boasted about his war strength and army. Vidura did not want to see the bloodshed of the war, although he was a good battle strategist. The powerful Balarama refused to fight at Kurukshetra, because he was both Bhima and Duryodhana's wrestling coach.[13]
Army divisions and weaponry
Each army consisted of several divisions; the Kauravas had 11 while the Pandavas controlled 7. A division (akshauhini) includes 21,870 chariots and chariot-riders, 21,870 elephants and riders, 65,610 horses and riders, and 109,350 foot-soldiers (in a ratio of 1:1:3:5). The combined number of warriors and soldiers in both armies was approximately 3.94 million.[14] Each Akshauhini was under a commander or a general, apart from the Commander in chief or the generalissimo who was the head of the entire army.
During the Kurukshetra War, the weapons used included: the bow, the weapon of choice for Arjuna, Bhishma, Drona, Karna, Satyaki, Vikarna and Abhimanyu; the mace, chosen by Bhima and Duryodhana, the spear, chosen by Yudhistira and Shalya; the sword chosen by Nakula, Dushasana, Dhristadymna and other Kauravas; and the axe chosen by Sahadeva.
Military formations
At various times during battle, the supreme commander of either army ordered special formations (vyuhas). Each formation had a specific purpose; some were defensive while others were offensive. Each formation had its specific strengths and weaknesses. The Mahābhārata lists the following:
- Krauncha vyuha (heron formation)
- Makara vyuha (crocodile formation)
- Kurma vyuha (tortoise or turtle formation)
- Trishula vyuha (trident formation)
- Chakrvyuha|Chakra vyuha (wheel or discus formation)
- Kamala vyuha or Padma vyuha (lotus formation)
- Garud vyuha (eagle formation)
- Oormi vyuha (ocean formation)
- Mandala vyuha (galaxy formation)
- Vajra vyuha (diamond or thunderbolt formation)
- Shakata vyuha (box or cart formation)
- Asura vyuha (demon formation)
- Deva vyuha (divine formation)
- Soochi vyuha (needle formation)
- Sringataka vyuha (horned formation)
- Chandrakala vyuha (crescent or curved blade formation)
- Mala vyuha (garland formation)
It is not clear what the formations actually indicate. They may be arrangements of bear resemblance to animals, or they may be names given to battle strategies .[15]
Rules of engagement
The two supreme commanders met and framed "rules of ethical conduct", dharmayuddha, for the war. The rules included:
- Fighting must begin no earlier than sunrise and end exactly at sunset.
- More than one warriors may not attack a single warrior.
- Two warriors may "duel", or engage in prolonged personal combat, only if they carry the same weapons and they are on the same type of mount (on foot, on a horse, on an elephant, or in a chariot).
- No warrior may kill or injure a warrior who has surrendered.
- One who surrenders becomes a prisoner of war and will then be subject to the protections of a prisoner of war.
- No warrior may kill or injure an unarmed warrior.
- No warrior may kill or injure an unconscious warrior.
- No warrior may kill or injure a person or animal not taking part in the war.
- No warrior may kill or injure a warrior whose back is turned away.
- No warrior may attack a woman.
- No warrior may strike an animal not considered a direct threat.
- The rules specific to each weapon must be followed. For example, it is prohibited to strike below the waist in mace warfare.
- Warriors may not engage in any unfair warfare.
Course of war
The Kurukshetra War lasted eighteen days. It was fought only during daylight hours; fighting ceased at sunset. Each day the battle was characterised by numerous individual combats, as well as mass raids against entire enemy divisions. The victor or the vanquished on each day was determined not by any territories gained, but by the body count. This was a war to the death. The victor was the survivor. If the text is taken to be chronologically accurate, this was one of the bloodiest wars in the history of mankind. Arjuna, in a fit of extreme anger over the death of his son Abhimanyu, alone killed one akshauhini of Kaurava soldiers in a single day. The war left an extremely large number of widows and orphans and led to an economic depression and the beginning of Kali Yuga.
Before the battle

It has been observed that the year in which the Mahabharata War took place, the year had three solar eclipses on earth in a span of thirty days. Eclipses are considered ill for life on earth according to Hindu astrology.
On the first day of the war, as would be on all the following days, the Kaurava army stood facing west and the Pandava army stood facing east. The Kaurava army was formed such that it faced all sides: elephants formed its body; the kings, its head; and the steeds, its wings. Bhishma, in consultation with his commanders Drona, Bahlika and Kripa, remained in the rear.
The Pandava army was organised by Yudhisthira and Arjuna in the Vajra formation. Because the Pandava army was smaller than the Kaurava's, they decided to employ the tactic of each warrior engaging as many enemies as possible. This involved an element of surprise, with the bowmen showering arrows hiding behind the frontal attackers. The attackers in the front were equipped with short-range weapons like maces, battle-axes, swords and lances.
Ten divisions (Akshauhinis) of the Kaurava army were arranged in a formidable phalanx. The eleventh was put under the immediate command of Bhishma, partly to protect him. The safety of the supreme commander Bhishma was central to Duryodhana's strategy, as he had placed all his hope on the great warrior's abilities. Dushasana, the younger brother of Duryodhana, was the military officer in-charge of Bhishma's protection.
Bhagavad Gita

When the war was declared and the two armies were facing each other, Arjuna realised that he would have to kill his dear great-granduncle (Bhishma), on whose lap he had played as a child, and his respected teacher (Drona), who had held his hand and taught him how to hold the bow and arrow, making him the greatest archer in the world. Arjuna felt weak and sickened at the prospect of killing his entire family, including his 100 cousins, and friends such as Ashwathama. Despondent and confused about what is religious, what is right and what is wrong, Arjuna turned to Krishna for divine advice and teachings. Krishna, who Arjuna chose as his charioteer, advised him of his duty. This conversation forms the Bhagavad Gita, one of the most respected religious and philosophical texts in the Hindu religion. Krishna instructs Arjuna not to yield to degrading impotence and to fight his kin, for that was the only way to righteousness. He also reminded him that this was a war between righteousness and unrighteousness (dharma and adharma), and it was Arjuna's duty to slay anyone who supported the cause of unrighteousness, or sin. Krishna then revealed his divine form and explained that he is born on earth in each aeon when evil raises its head. It also forms one of the foremost treatise on the several aspects of Yoga and mystical knowledge.
Before the battle began, Yudhisthira did something unexpected. He suddenly dropped his weapons, took off his armour and started walking towards the Kaurava army with folded hands in prayer. The Pandava brothers and the Kauravas looked on in disbelief, thinking Yudhisthira was surrendering before the first arrow was shot. Yudhisthira's purpose became clear, however, when he fell on Bhishma's feet to seek his blessing for success in battle. Bhishma, grandfather to both the Pandavas and Kauravas, blessed Yudhisthira. Yudhisthira returned to his chariot and the battle was ready to commence.
Day 1
When the battle was commenced, Bhishma went through the Pandava army wreaking havoc wherever he went but Abhimanyu, Arjuna's son, seeing this went straight at Bhishma, defeated his bodyguards and directly attacked the commander of the Kaurava forces. The Pandavas suffered numerous losses and were defeated at the end of the first day. Virata's sons, Uttara and Sweta, were slain by Shalya and Bhishma. Krishna consoled the distraught Yudhisthira saying that eventually victory would be his.
Day 2
The second day of the war commenced with a confident Kaurava army facing the Pandavas. Arjuna, realising that something needed to be done quickly to reverse the Pandava losses, decided that he must try to kill Bhishma. Krishna skillfully located Bhishma's chariot and steered Arjuna toward him. Arjuna tried to engage Bhishma in a duel, but the Kaurava soldiers placed around Bhishma to protect him attacked Arjuna to try to prevent him from directly engaging Bhishma. Arjuna and Bhishma fought a fierce battle that raged for hours. Drona and Dhristadyumna similarly engaged in a duel during which Drona broke Dhristadyumna's bow numerous times. Bhima intervened and rescued Dhristadyumna. Duryodhana sent the Kalinga forces to attack Bhima and most of them lost their lives at his hands. Bhishma immediately came to relieve the battered Kalinga forces. Satyaki, who was assisting Bhima, shot at Bhishma's charioteer and killed him. Bhishma's horses, with no one to control them, bolted carrying Bhishma away from the battlefield. The Kaurava army had suffered great losses at the end of the second day.
Day 3

On the third day, Bhishma arranged the Kaurava forces in the formation of an eagle with himself leading from the front, while Duryodhana's forces protected the rear. Bhishma wanted to be sure of avoiding any mishap. The Pandavas countered this by using the crescent formation with Bhima and Arjuna at the head of the right and the left horns, respectively. The Kauravas concentrated their attack on Arjuna's position. Arjuna's chariot was soon covered with arrows and javelins. Arjuna, with amazing skill, built a fortification around his chariot with an unending stream of arrows from his bow. Abhimanyu and Satyaki combined to defeat the Gandhara forces of Shakuni. Bhima and his son Ghatotkacha attacked Duryodhana in the rear. Bhima's arrows hit Duryodhana, who swooned in his chariot. His charioteer immediately drove them out of danger. Duryodhana's forces, however, saw their leader fleeing the battlefield and soon scattered. Bhishma soon restored order and Duryodhana returned to lead the army. He was angry at Bhishma, however, at what he saw as leniency towards the five Pandava brothers and spoke harshly at his commander. Bhishma, stung by this unfair charge, fell on the Pandava army with renewed vigor. It was as if there were more than one Bhishma on the field.[16] The Pandava army soon began to retreat in chaos.
Arjuna and Krishna attacked Bhishma trying to restore order. Arjuna and Bhishma again engaged in a fierce duel, however Arjuna's heart was not in the battle as he did not like the idea of attacking his great-uncle. During the battle, Bhishma killed numerous soldiers of Arjuna's armies.
Day 4
The fourth-day of the battle was noted for the valour shown by Bhima. Bhishma commanded the Kaurava army to move on the offensive from the outset. While Abhimanyu was still in his mother's womb, Arjuna had taught Abhimanyu on how to break and enter the chakra vyuha.But, before explaining how to exit the chakra vyuha, Arjuna was interrupted by Krishna (other story: Abhimanyu's mother falls asleep while Arjuna was explaining her). Thus from birth, Abhimanyu only knew how to enter the Chakra vyuha but didn't know how to come out of it. When the Kauravas formed the chakra vyuha, Abhimanyu entered it but was surrounded and attacked by a number of Kaurava princes. Arjuna joined the fray in aid of Abhimanyu. Bhima appeared on the scene with his mace aloft and started attacking the Kauravas. Duryodhana sent a huge force of elephants at Bhima. When Bhima saw the mass of elephants approaching, he got down from his chariot and attacked them single handedly with his iron mace. They scattered and stampeded into the Kaurava forces killing many. Duryodhana ordered an all-out attack on Bhima. Bhima withstood all that was thrown at him and attacked Duryodhana's brothers, killing eight of them. Bhima was soon struck by an arrow on the chest and sat down in his chariot dazed.
Duryodhana was distraught at the loss of his brothers. Duryodhana, overwhelmed by sorrow at the loss of his brothers, went to Bhishma at the end of the fourth day of the battle, and asked his commander how could the Pandavas, facing a superior force against them, still prevail and win. Bhishma replied that the Pandavas had justice on their side and advised Duryodhana to seek peace.
Days 5–9
When the battle resumed on the fifth day, the slaughter continued. The Pandava army again suffered against Bhishma's attacks. Satyaki bore the brunt of Drona's attacks and soon could not withstand them. Bhima drove by and rescued Satyaki. Arjuna fought and killed thousands of soldiers sent by Duryodhana to attack him. The unimaginable carnage continued during the ensuing days of the battle.
The sixth day was marked by a prodigious slaughter. Drona caused immeasurable loss of life on the Pandava side. The formations of both the armies were broken. On day 7 Drona slays Shankya son of Virata. On the eighth day Bhima killed eight of Dhritarashtra's sons.
On the ninth day Krishna, overwhelmed by anger at the apparent inability of Arjuna to defeat Bhishma, rushed towards the Kaurava commander, the wheel of a fallen chariot in his hands. Bhishma lays down his arms and is ready to die at the hands of the Lord, but Arjuna stops Him, reminding of His promise not to wield a weapon. Realizing that the war could not be won as long as Bhishma was standing, Krishna suggested the strategy of placing a eunuch in the field to face him. Some sources however state that it was Yudhistira who visits Bhishma's camp at night asking him for help. To this Bhishma says that he would not fight a eunuch.
Day 10

On the tenth day, the Pandavas, unable to withstand Bhishma's prowess, decided to put Shikhandi, who had been a woman in a prior life in front of Bhishma, as Bhishma has taken a vow not to attack a woman. Shikhandi's arrows fell on Bhishma without hindrance. Arjuna positioned himself behind Shikhandi, protecting himself from Bhishma's attack, and aimed his arrows at the weak points in Bhishma's armour. Soon, with arrows sticking from every part of his body, the great warrior fell from his chariot. His body did not touch the ground as it was held aloft by the arrows protruding from his body.
The Kauravas and Pandavas gathered around Bhishma and, at his request, Arjuna placed three arrows under Bhisma's head to support it. Bhishma had promised his father, King Shantanu, that he would live until Hastinapur were secured from all directions. To keep this promise, Bhishma used the boon of "Ichcha Mrityu" (self wished death) given to him by his father. After the war was over, when Hastinapur had become safe from all sides and after giving lessons on politics and Vishnu Sahasranama to the Pandavas, Bhishma died on the first day of Uttarayana.
Day 11
With Bhishma unable to continue, Karna entered the battlefield, much to Duryodhna's joy. He made Drona the supreme commander of the Kaurava forces. Karna and Duryodhana wanted to capture Yudhisthira alive. Killing Yudhisthira in battle would only enrage the Pandavas more, whereas holding him as hostage would be strategically useful. Drona formulated his battle plans for the eleventh day to this aim. He cut down Yudhisthira's bow and the Pandava army feared that their leader would be taken prisoner. Arjuna rushed to the scene, however, and with a flood of arrows made Drona retreat.
Day 12
With his attempts to capture Yudhisthira thwarted, Drona confided to Duryodhna that it would be difficult as long as Arjuna was around. He summoned King Bhagadatta, the monarch of Pragjyotisha (modern day Assam, India). Bhagadatta had thousands of gigantic elephants in his stable and was considered the strongest warrior on this planet in elephant warfare. Bhagadatta attacked Arjuna with his gigantic elephant named Suprateeka. It was a fierce battle in which Bhagadatta matched Arjuna astra for astra but Arjuna slew him. Drona continued to try and capture Yudhisthira. The Pandavas however fought hard and delivered severe blows to the Kaurava army.
Day 13
The king of Trigartadesa, Susharma along with his 3 brothers and 35 sons who were fighting on the Kaurava side made a pact that they would make sure that Arjuna comes and doesn't break the Chakra Vuyh and kill him or die. They went into the battlefield on the twelfth day and challenged Arjuna. Arjuna gave them a fierce fight in which the brothers fell dead after fighting a brave fight. Drona continued to try and capture Yudhisthira.
On the other side of the battlefield, the remaining four Pandavas and their allies were finding it impossible to break Dronacharya's "Chakra Vyuh" formation. As Arjuna was busy fighting with the Trigartadesa princes and the Prajayogastha monarch on the other side of the battlefield, he could not be summoned to break the Chakra vyuha formation, which could only be broken by entering and exiting the formation. Yudhisthira instructed, Abhimanyu, one of Arjuna's sons to break the Chakra vyuha formation. Abhimanyu knew the secret of entering the Chakra vyuh formation, but did not know how to exit it. Abhimanyu slew tens of thousands of warriors. He also killed Dhuryodhana's son. Dhuryodhana got enraged and ordered Durmashana who was Dushasana's son to attack Abhimanyu but he died under the hands of Abhimanyu. Next he ordered his men to attack Abhimanyu all at once. Abhimanyu fought but was surrounded and killed by many warriors in a combined attack.
Upon learning of the death of his son, Arjuna vowed to kill Jayadratha on the morrow before the battle ended at sunset, otherwise he would throw himself into the fire.
Day 14

While searching for Jayadrath on the battlefield, Arjuna slew an akshauhini (battle formation that consisted of 21,870 chariots (Sanskrit ratha); 21,870 elephants; 65,610 cavalry and 109,350 infantry) of Kaurav soldiers. The Shakatavuyha Kaurav army tightly protected Jayadratha, however, preventing Arjuna from attacking him. Finally, in late afternoon, Arjuna found Jayadrath guarded by the mighty kaurav army. Seeing his friend's plight, Lord Krishna raised his Sudarshan Chakra to cover the sun, faking a sunset. Arjun fought a powerful battle with Jayadrath and finally defeated him. Then, Arjuna shot a powerful arrow decapitating Jayadrath. While Arjuna destroying the rest of the Shakatavuyha, Vikarna, the third eldest Kaurava, challenged Arjuna to an archery fight. Arjuna asks Bhima to decimate Vikarna, but Bhima refused to, because Vikarna defended the Pandavas during the Vastranam. Bhima and Vikarna shower arrows at each other. Later Bhima throws his mace at Vikarna, killing him. The muscular Pandava was devastated and mourned his death saying he was a man of Dharma and it was a pity how he lived his life.

The battle continued past sunset. When the bright moon rose, Ghatotkach, son of Bhima slaughtered numerous warriors, attacking while flying in the air. Karna stood against him and both fought fiercely until Karna released the Shakti, a divine weapon given to him by Indra. Ghatotkach increased his size and fell dead on the Kaurav army killing thousands of them.
Day 15
After King Drupada and King Virata were slain by Drona, Bhima, and Dhristadyumna fought him on the fifteenth day. Because Drona was very powerful and inconquerable having the irresistible brahmadanda, Krishna hinted to Yudhisthira that Drona would give up his arms if his son Ashwathama was dead. Bhima proceeded to kill an elephant named Ashwathama, and loudly proclaimed that Ashwathama was dead. Drona approached Yudhisthira to seek the truth of his son's death. Yudhisthira proclaimed Ashwathama Hatahath, naro va Kunjaro va, implying Ashwathama had died but he was nor sure whether it was a Drona's son or an elephant, The latter part of his proclamation (Naro va Kunjaro va) were drowned out by sound of the conch blown by Krishna intentionally (a different version of the story is that Yudhisthira pronounced the last words so feebly that Drona could not hear the word elephant). Prior to this incident, the chariot of Yudhisthira, proclaimed as Dharma raja (King of righteousness), hovered a few inches off the ground. After the event, the chariot landed on the ground as he lied.
Drona was disheartened, and laid down his weapons. He was then killed by Dhristadyumna to avenge his father's death and satisfy his vow. Later, the Pandava's mother Kunti secretly met her abandoned son Karna and requested him to spare the Pandavas, as they were his younger brothers. Karna promised Kunti that he would spare them except for Arjuna, but also added that he would not fire a same weapon against Arjun twice.
Day 16

On the sixteenth day, Karna was made the supreme commander of the Kuru army. Karna fought valiantly but was surrounded and attacked by Pandava generals, who were unable to prevail upon him. Karna inflicted heavy damage on the Pandava army, which fled. Then Arjuna successfully resisted Karna's weapons with his own, and also inflicted casualties upon the Kaurava army. Nakul kills Satyasena and Sushena sons of Karna, Arjunakills Vrishasena and Dvipata, Bhima kills Banasena, Satyaki kills Prasena and Prativindya kills Shatrunjaya . The sun soon set, and with darkness and dust making the assessment of proceedings difficult, the Kaurava army retreated for the day.[17] On the same day, Bhima swung his mace and shattered Dushasana's chariot. Bhima seized Dushasana, ripped his right hand from shoulder and killed him, tearing open his chest and drinking his blood and carrying some to smear on Draupadi's untied hair, thus fulfilling his vow made when Draupadi was humiliated.
Day 17

On the seventeenth day, Karna defeated the pandava brothers Nakul, Bhima, Sahadeva and Yudhisthira in battle but spared their lives. Later, Karna resumed duelling with Arjuna. During their duel, Karna's chariot wheel got stuck in the mud and Karna asked for a pause. Krishna reminded Arjuna about Karna's ruthlessness unto Abhimanyu while he was similarly left without chariot and weapons. Hearing his son's fate, Arjuna shot his arrow and decapitated Karna. Before the day's battle, Karna's sacred armour ('Kavacha') and earrings ('Kundala') were taken as alms by Lord Indra when asked for, which resulted in his death by Arjuna's arrows.
Day 18

On the 18th day, Shalya took over as the commander-in-chief of the remaining Kaurava forces. Yudhishthira killed king Shalya in a spear combat and Sahadeva killed Shakuni. Realizing that he had been defeated, Duryodhana fled the battlefield and took refuge in the lake, where the Pandavas caught up with him. Under the supervision of the now returned Balarama, a mace battle took place between Bhima and Duryodhana. Bhima flouted the rules (under instructions from Krishna) to strike Duryodhana beneath the waist in which he was mortally wounded.
Ashwatthama, Kripacharya, and Kritavarma met Duryodhana at his deathbed and promised to avenge the actions of Bhima. They attacked the Pandavas' camp later that night and killed all the Pandavas' remaining army including their children. Amongst the dead were Dhristadyumna and Shikhandi. Other than the Pandavas and Krishna, only Satyaki and Yuyutsu survived.
Aftermath


At the end of the 18th day, only twelve warriors survived the war—the five Pandavas, Krishna, Satyaki, Ashwatthama, Kripacharya, Yuyutsu, Vrishakethu (son of Karna) and Kritvarma. Vrishakethu was the only son of Karna who survived the horrific slaughter. He later came under the patronage of the Pandavas. During the campaign that preceded the Ashvamedha –yagna, Vrishakethu accompanied Arjuna and participated in the battles with Sudhava and Babruvahana. During that campaign Vrishakethu married the daughter of king Yavanatha (perhaps a king of the western regions). It is said, Arjuna developed great affection for Vrishakethu, his nephew. Yudhisthira was crowned king of Hastinapur. He renounced the throne after ruling for 36 years, passing on the crown to Arjuna's grandson Parikshit. He then left for the Himalayas with Draupadi and his brothers in what was to be their last journey. Draupadi and four Pandavas—Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—died during the journey. Yudhisthira, the lone survivor and being of pious heart, was invited by Dharma to enter the heavens as a mortal.
Gallery
-

The Battle of Kurukshetra Kashmir c. 1820
References
- ↑ Thomas Block. A Fatal Addiction: War in the Name of God. Algora publishing. p. 93.
- ↑ S.S.N. Murthy (14 November 2003). "The Questionable Historicity of the Mahābhārat" (PDF). Electronic Journal of Vedic Studies 10 (5): 1–15. ISSN 1084-7561.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Basham, A. L. (1986). The wonder that was India (2nd ed.). Rupa. p. 40.
- ↑ Thapar, Romila (2004). Early India: From the Origins to AD 1300. University of California Press. p. 99. ISBN 9780520242258.
- ↑ Michael Witzel (1995). "Early Sanskritization: Origin and Development of the Kuru state" (PDF). EJVS 1 (4).; also in Bernhard Kölver, ed. (1997). Recht, Staat und Verwaltung im klassischen Indien [The state, the law, and administration in classical India] (in German). Munich: R. Oldenbourg. pp. 27–52. ISBN 978-3-486-56193-7.
- ↑ Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan. "14". In Ramesh Chandra Majumdar; A.D. Pusalker. History and culture of the Indian people. 1:The Vedic age. p. 273.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 FE Pargiter. Ancient Indian Historical Tradition. pp. 180–182.. He shows estimates of the average as 47, 50, 31 and 35 for various versions of the lists.
- ↑ B. B. Lal, Mahabharata and Archaeology in Gupta and Ramachandran (1976), p.57-58
- ↑ Among other references, a list of nine pre-1950 papers for the astronomical dating of the War is found in R. C. Majumdar; A. D. Pusalker, eds. (1951). The history and culture of the Indian people. 1: The Vedic age. Bombay: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan. p. 320 (footnote 4).
- ↑ The Scientific Dating of the Mahabharat War
- ↑ Dating of the Mahabharat time period
- ↑ C. Rajagopalachari, Mahābhārata, Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan. 1994
- ↑ "Rukmini". www.mahabharataonline.com. www.mahabharataonline.com. Retrieved 2008-05-27.
- ↑ C. Rajagopalachari, Mahābhārata, Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan. 1994 pp 183
- ↑ C Rajagopalachari, Mahābhārata, 1954
- ↑ C. Rajagopalachar, Mahābhārata, pp 215
- ↑ Sacred-Texts.com
18. pandya dynasty
External links
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
