Krukenberg procedure
Procedure

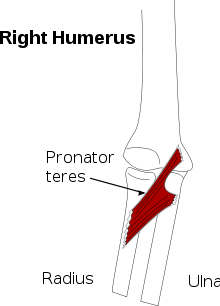
The procedure involves separating the ulna and radius for below-elbow amputations, and in cases of congenital absence of the hand, to provide a pincerlike grasp that is motored by the pronator teres muscle. The prerequisites for the operation are a stump over 10 cm long from the tip of the olecranon, no elbow contracture, and good psychological preparation and acceptance. [4][5][6]
The success of the Krukenberg procedure depends directly on the strength of the pronator teres, the sensibility of the skin surrounding both ulna and radius, elbow mobility, and mobility of the ulna and radius at the proximal radioulnar joint. Individual patient expectations and motivations, although more difficult to assess, probably play a major role in outcomes as well.
Advantages
The procedure is, in this time and age, mostly performed on patients in developing countries who lack the means to obtain expensive prostheses. In the Western world, the Krukenberg procedure is usually reserved for blind patients with bilateral amputations, because it can provide the patient with tactile sensation.[7][8]
While the Krukenberg procedure's poor cosmesis makes it very rare, it does preserve proprioception and stereognosis in the functional stump and so allows for effective maneuvering. Once this procedure is performed, it does not preclude the use of a functional prosthesis giving the patient the option to use either functional strategy.
While the operation is rarely performed in the modern age, patients can prefer it to sophisticated prosthetics, as in one case study of a Dutch woman, reported in 2002.
Initially after traumatic bilateral forearm amputation [the patient] was provided with mechanical prostheses. Eventually she stopped using them because she chose to use her bare stumps as pincers. She explained that being able to feel helped her a lot in her tasks... an excellent functional result was obtained, from both the surgical and the rehabilitation point of view. The patient lives with her family, takes care of the household, and does art and crafts, which she is currently selling, and is very happy with the procedure. A year and a half has gone by and she is still gaining dexterity and strength.[3]The patient in question also requested the procedure be completed on her other arm.[3]
Notable patients
The German physicist Burkhard Heim had two Krukenberg hands as a result of a laboratory accident.
References
- ↑ Krukenberg H. (1917). Uber Plastische Umwertung von Amputationstumpfen. Stuttgart: Ferdinand Enke.
- ↑ Krukenberg H. (1931). Erfahrungen mit der Krukenberg-hand. Arch Klin Chir 165:191 – 201.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Freire J, Schiappacasse C, Heredia A, Martina JD, Geertzen JH. (2005). Functional results after a Krukenberg amputation. Prosthet Orthot Int. 29(1):87-92. PMID 16180381
- ↑ Garst, R.J. (1991). The Krukenberg Hand The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 385(3) PMID 1670433
- ↑ Singh BG, Jain SK, Ravindranath G, Pithawa AK. (2005). Krukenberg Operation: Revisited. IJPMR 16 (1) : 20-23
- ↑ Tubiana R, Stack HG, Hakstian RW. (1966). Restoration of prehension after severe mutilations of the hand. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 48(3):455-73. PMID 5330433
- ↑ Sinaki M, Dobyns JH, Kinnunen JM. (1982). Krukenberg's kineplasty and rehabilitation in a blind, bilateral full-hand amputee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. Sep;(169):163-6. PMID 7105574
- ↑ Swanson AB. (1964). THE Krukenberg procedure in the juvenile amputee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 46:1540-8. PMID 14213413
External links
- Wrist and Forearm Amputations. emedicine
- Digital Amputations. emedicine
- Picture showing the completed procedure