Kostanecki acylation
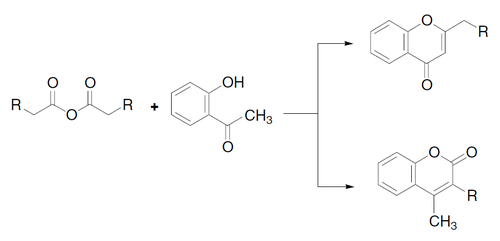
The Kostanecki acylation is a method used in organic synthesis to form chromones or coumarins by acylation of O-hydroxyaryl ketones with aliphatic acid anhydrides, followed by cyclization:[1]
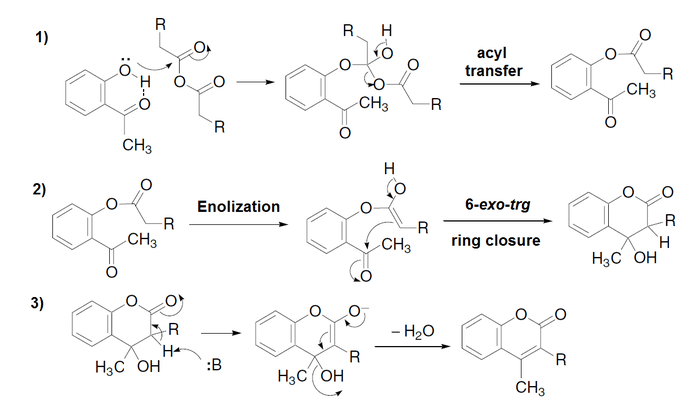
Mechanism
The mechanism consists of three well-differentiated reactions:[2][3]
1) Phenol O-acylation with formation of a tetrahedrical intermediate.
2) Intramolecular aldolic condensation to cyclizate and to form a hydroxydihydrochromone.
3) Elimination of the hydroxyl group to form the chromone (or coumarin).

See also
References
- ↑ v. Kostanecki, St.; Różycki, A. (1901). "Ueber eine Bildungsweise von Chromonderivaten". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 34: 102. doi:10.1002/cber.19010340119.
- ↑ Mamedov, V. A.; Kalinin, A. A.; Gubaidullin, A. T.; Litvinov, I. A. (2003). Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds 39: 96. doi:10.1023/A:1023028927007. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Ellis, G. P. (1977) Chromenes, Chromanones, and Chromones from The Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds, Weissberger, A. and Taylor, E. C., eds.; Wiley & Sons: New York, vol. 31, p. 495.