Kopp's law

Hermann Kopp
Kopp's law can refer to either of two relationships discovered by the German chemist Hermann Franz Moritz Kopp (1817–1892).
- Kopp found "that the molecular heat capacity of a solid compound is the sum of the atomic heat capacities of the elements composing it; the elements having atomic heat capacities lower than those required by the law of Dulong and Petit retain these lower values in their compounds."[1]
- In studying organic compounds, Kopp found a regular relationship between boiling points and the number of CH2 groups present.[2]
Kopp–Neumann law
Kopp–Neumann law states that the specific heat C per unit mass (in J•kg−1•K−1) for alloys can be calculated from the following equation:
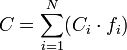
where: i - subsequent numbers from 1 to N, N - total number of alloy constituents, Ci and fi - specific heat and mass fraction of the i-th constituent.
References
- Frederick Seitz, The Modern Theory of Solids, McGraw-Hill, New York, USA, 1940, ASIN: B000OLCK08
- ↑ See page 96 of Millard, Earl Bowman (1921). Physical Chemistry for Colleges. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- ↑ See page 942 of Miller, William Allen (1869). Elements of Chemistry. London: Longmans, Green, Reader, and Dyer.
Further reading
- Thorpe, T. E. (1901). "The Life Work of Hermann Kopp". Memorial lectures delivered before the Chemical Society 25: 774–815.