Koomey's law
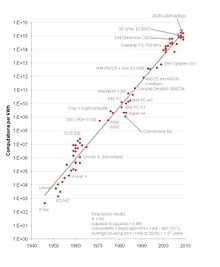
Koomey’s law describes a long-term trend in the history of computing hardware. The number of computations per joule of energy dissipated has been doubling approximately every 1.57 years. This trend has been remarkably stable since the 1950s (R2 of over 98%) and has actually been somewhat faster than Moore’s law. Jonathan Koomey articulated the trend as follows: "at a fixed computing load, the amount of battery you need will fall by a factor of two every year and a half."[1]
Implications
The implications of Koomey’s law are that the amount of battery needed for a fixed computing load will fall by a factor of 100 every decade.[2] As computing devices become smaller and more mobile, this trend may be even more important than improvements in raw processing power for many applications. Furthermore, energy costs are becoming an increasing factor in the economics of data centers, further increasing the importance of Koomey’s law.
History
Koomey was the lead author of the article in IEEE Annals of the History of Computing that first documented the trend.[1] Co-authors were Stephen Berard, Marla Sanchez, and Henry Wong. It was further discussed in MIT’s Technology Review[3] and in a discussed post on the “Economics of Information” blog.[2]
The end of Koomey's law
By the second law of thermodynamics and Landauer's principle, irreversible computing cannot continue to be made more energy efficient forever. As of 2011, computers have a computing efficiency of about 0.00001%.[4] Assuming that the energy efficiency of computing will continue to double every 1.57 years, the Landauer bound will be reached in 2048. Therefore, Koomey's law has the potential to be valid for at most a century.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Koomey, Jonathan; Berard, Stephen; Sanchez, Marla; Wong, Henry; (March 29, 2010). "Implications of Historical Trends in the Electrical Efficiency of Computing]". Annals of the History of Computing, IEEE (Stanford University). Volume: 33 Issue:3: 46−54. doi:10.1109/MAHC.2010.28. ISSN 1058-6180.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 “Is Koomey's Law eclipsing Moore's Law?”, as well as IEEE Spectrum
- ↑ Greene, Kate (September 12, 2011). "A New and Improved Moore's Law: Under ‘Koomey's law,’ it's efficiency, not power, that doubles every year and a half". Technology Review.
- ↑ "Tikalon Blog by Dev Gualtieri". Tikalon.com. Retrieved August 8, 2013.
External links
- The Economist online - Computing power - A deeper law than Moore's? (October 10, 2011)
| ||||||