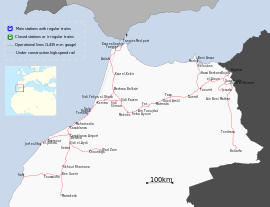
Kenitra–Tangier high-speed rail line
| LGV Tangier-Casablanca | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Status | Under construction |
| Locale | Morocco |
| Termini |
Tangier Kenitra, Casablanca |
| Operation | |
| Opening | 2016 |
| Operator(s) | ONCF |
| Technical | |
| Line length | 350 km (220 mi) |
| No. of tracks | Double track |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge |
| Electrification | 25 kV 50 Hz |
| Operating speed | 320 km/h (200 mph) |
The Casablanca—Tangier high-speed rail line is a high-speed rail line under construction in Morocco.[1] This was decided in November 2007 by the national government after a roadmap performed in 2005[2] by the Morocco's rail company ONCF. ONCF plans to deploy 1500 km of high speed lines in next three decades. The first step of this project is under way between Tangier and Kenitra, to be completed in 2016;[3] until this date a first upgrade (220 km/h) is programmed for the existent line Kenitra–Casablanca. After 2020 the Kenitra–Casablanca (320 km/h) will be performed and Casablanca–Marrakech line will be upgraded in the same time to permit Tangier–Casablanca in 1h30 and Tangier–Marrakech in 2h45. In early 2009, a cooperation contract between Morocco's rail company ONCF and French rail company SNCF was signed to cooperate on the project.[4]
Project details
Sources of finance (20 billion dirhams total):[5]
- The government: 4.8 bn dirhams
- French and European sources: 1.9 bn dirhams,
- Loans: 12.3 bn dirhams.
Expenditure:
- Infrastructure: 10 bn dirhams
- Railway equipment: 5.6 bn dirhams
- Rolling stock: 4.4 bn dirhams
Construction
In February 2010 ONCF signed agreements financing the construction of the 20bn dirham high-speed line between Tangier and Casablanca.[5] Work was expected to start at the end of 2011, with services beginning in December 2015.[6] The foundation stone of the project was laid on 29 September 2011, with the first phase to be operational in 2015.[1]
The line is to be constructed in two sections—a new route from Tangier to Kénitra and an upgrade of the existing route from Kénitra to Casablanca.[1] There will be a top speed of 320 km/h (200 mph) on the new line and 220 km/h (140 mph) on the upgraded line.[1] Upon completion, the travel time between Casablanca and Tangier will be reduced from five hours and 45 minutes to two hours and ten minutes.[1] A potential second phase would see a new track built between Kénitra and Casablanca[1] and upgrade Casablanca - Marrakech to set 1h30 Tangier - Casablanca and 1h05 Casablanca - Marrakech and then link Tangier to Marrakech in less than three hours (10 hours today).[7]
Trains
On 10 December 2010 ONCF signed a contract worth nearly €400M with Alstom for 14 Euroduplex trains each capable of carrying 533 passengers.[8]
Criticism
The project has attracted criticism for being a misguided use of money when there are more serious problems than transport facing Morocco. The country's former finance minister, Mohamed Berrada, said that a better use of the money spent on the rail line would be to address poverty and illiteracy.[9]
Technical information
Signalling and train protection system of the line will be installed by Ansaldo STS and Cofely Ineo. It will be of the type ETCS 1 and 2, and will allow trains to run up to 320 km/h on the line.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "Ceremony launches Tanger – Casablanca high speed project". Railway Gazette International. 29 September 2011.
- ↑ "High Speed Master Plan in Morocco". ONCF.ma. 2006.
- ↑ "Morocco awards Tangier-Kenitra high-speed line contract". railway-technology.com. Kable. 8 April 2013.
- ↑ "Engineers begin work on Moroccan high-speed rail link". Magharebia. 15 April 2009.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "High speed funding package agreed". Railway Gazette International. 2010-02-18.
- ↑ "BIDS FOR MOROCCAN HIGH-SPEED LINE". Railways Africa. 29 November 2010. Retrieved 2010-12-01.
- ↑ "High Speed Master estimated times". ONCF.ma. 2006.
- ↑ "ONCF to buy 14 Duplex high speed trains". Railway Gazette International. 10 December 2010.
- ↑ "Nicolas Sarkozy visits Morocco for TGV rail-link launch". BBC News Online. 29 September 2011. Archived from the original on 13 October 2011. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ↑ "Tanger - Kénitra high speed line signalling contract signed". Railway Gazette International. 4 April 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2013.