Kengtung State
| Kengtung ကျိုင်းတုံ / | |||||
| State of the Shan States | |||||
| |||||
 | |||||
| History | |||||
| - | Dynasty established by a delegate of King Mangrai | c. 1243 | |||
| - | Abdication of the last Saopha | 1959 | |||
| Area | |||||
| - | 1901 | 31,079 km2 (12,000 sq mi) | |||
| Population | |||||
| - | 1901 | 190,698 | |||
| Density | 6.1 /km2 (15.9 /sq mi) | ||||




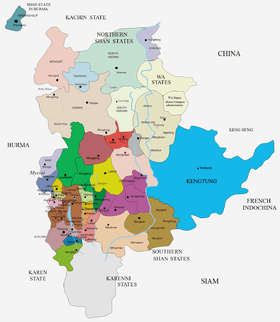
Kengtung (Burmese: ကျိုင်းတုံ; Thai: Chiang Tung) was a Shan state in what is today Burma. The capital and the residence of the ruler was Kengtung in the centre of the state. It was the only urban area in this mountainous state whose landscape is dominated by the Daen Lao Range.
Kengtung was the largest of the states in present-day Shan State and ranked first in the order of precedence at the time of the invasion of the Shan States by the British Empire. It was also the easternmost of the Southern Shan States, lying almost entirely east of the Salween and stretching eastwards to the Mekong. It was separated from the northern Shan state of Manglon by the Hka River.
Most of the early history of Kengtung is made up of myths and legends. At the time of British rule in Burma the Tai Yai people were the majority of the population in Kengtung state with other groups such as Akha and Lahu, forming sizeable communities. In the distant past the territory had belonged to the Wa people who were displaced around 1229 and were later defeated by King Mangrai. The Wa now form a minority of only about 10% in Kengtung State despite having been the original inhabitants.[2]
History
According to local tradition Khemarattha, the predecessor state, was founded in an unknown date in the distant past. It was ruled by the Tai Khün of Tai Yai (Shan) ethnic background. The current dynasty has its origins in the kingdom founded around 1243 by a prince named Mang Kun, said to be a delegate of King Mangrai.[3][4] Despite the ethnic affinity of the ruling Tai with the Siamese to the south,[5] Kengtung was led by Saopha princes who historically preferred to pay tribute to the Burmese kings to the west. The King of Mandalay restricted himself to exacting a yearly tribute, often in the form of offerings of ritual gold flowers, leaving the Kengtung rulers largely alone. The Salween river also acted as a protective natural border in the West hampering communication with Upper Burma. On the other hand, the kingdoms of Lanna and Ayutthaya, as well as the Chinese to the northeast, were closer, more bellicose and had easier access to the territory.
In 1760, following conflicting claims of political influence over Kengtung State, there was a war between the Qianlong Emperor of the Qing Dynasty and the King of Burma, Hsinbyushin. In 1802 Kengtung came under the rule of Chiang Mai, but with the help of the Burmese the former ruling dynasty was reinstated in 1814 and Mongyawng (Möngnawng) state was annexed.[6]
Kengtung was historically located at the crossroads of the trade between China and Siam and 19th century sources talk about caravans crossing Kengtung on their way to Chiang Mai totaling yearly 8,000 mules loaded with goods from China.[2] During British rule in Burma the eastern border was demarcated by the colonial powers and the western part of Kengcheng was merged with Kengtung.[7] Historically Kengtung also included the substates of Hsenyawt, Hsenmawng, Monghsat and Mongpu.[6][8]
On 27 May 1942, during World War II, Kengtung State was invaded and its capital captured by the Thai Phayap Army.[9] Following a previous agreement between Thai Prime Minister Plaek Phibunsongkhram and the Japanese Empire, in December the same year the Thai administration occupied Kengtung and Möngpan. The annexation by Thailand as Saharat Thai Doem northern province was formalised on 1 August 1943.[10] Thailand left the territory in 1945, but officially relinquished its claim over Kengtung State only in 1946 as part of the condition for admission to the United Nations and the withdrawal of all wartime sanctions for having sided with the Axis powers.[11]
The last ruler of Kengtung abdicated in 1959. The state became then part of Shan State and, despite the independence struggle of the latter, eventually part of Burma. After the 1962 military coup by General Ne Win all the privileges of the saophas were abolished.[12]
Rulers
The rulers of Kengtung bore the title of Saopha; their ritual style was Khemadhipati Rajadhiraja.[13]
The Kengtung Yazawin, also known as 'Padaeng Chronicle' and 'Jengtung State Chronicle', is a history of the rulers of Kengtung written in the 19th century in Burmese language. It was translated into English by Sao Saimong Mangrai.
Saophas
- 1243 - 1247 Man Kun (1st Saopha) (b. .... - d.1247)
- .... - .... Sao Awk (28th Saopha)
- .... - 1730 Sao Möng Lek (b. 1646 - d. 1730)
- 1730 - c.1735 Sao Maung Hkawn (1st time) (b. 1706 - d.17..)
- c.1735 - 1739 Vacant
- 1739 - 1742 Sao Maung Hkawn (2nd time) (s.a.)
- 1742 - 1786 Sao Möng Hsam (b. 1744 - d. 1786)
- 1787 - 1802 Sao Kawng Tai I (1st time) (b. 1769 - d. 1813)
- 1814 - 1815 Sao Kawng Tai I (2nd time) (s.a.)
- 1815 - 1857 Sao Maha Hkanan (b. 1781 - d. 1857)
- 1857 - 1876 Sao Maha Pawn (b. 1814 - d. 1876)
- 1877 - 1881 Sao Hseng (b. 1818 - d. 1881)
- 1881 - 1885 Sao Kawng Tai II (b. 1829 - d. 1885)
- 1886 - 1895 Sao Kawn Kham Hpu (b. 1874 - d. 1895)
- 7 May 1895 - 21 Jul 1935 Sao Kawng Kiao Intaleng (b. 1874 - d. 1935) (administrator to 9 Feb 1897)
- 21 Jul 1935 - Aug 1935 Sao Kaung Tai (b. 1899 - d. 1935)
- 1935 - 1942 British administration
- 1942 - 1945 annexed by Thailand
- 1945 - 1962 Sao Sai Long (b. 1927 - d. 1997)
Thai Military governor
Following the Thai occupation, a military governor was appointed for the administration of the annexed territories of Kengtung and Möngpan by Thailand.
- Dec 1942 - 1945 Phin Choonhavan (b. 1891 - d. 1973)
See also
- Burmese–Siamese War (1765–67)
- Kengtung Yazawin
- Mi Mi Khaing
- Saharat Thai Doem
- Sao Kawng Kiao Intaleng
- Sao Saimong
- Sino-Burmese War (1765–69)
References
- ↑ Mi Mi Khaing, Kanbawsa - A Modern Review
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Donald M. Seekins, Historical Dictionary of Burma (Myanmar), p. 251
- ↑ Keng Tung Royal
- ↑ Kengtung (Kyaington) (Shan State)
- ↑ The Migration and History of Tai Yai
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 15, p. 200.
- ↑ The Tai Of The Shan State
- ↑ Sir Charles Crosthwaite "The pacification of Burma"
- ↑ Thailand and the Second World War at the Wayback Machine (archived October 27, 2009)
- ↑ Shan and Karenni States of Burma
- ↑ David Porter Chandler & David Joel Steinberg eds. In Search of Southeast Asia: A Modern History. p. 388
- ↑ "WHKMLA : History of the Shan States". 18 May 2010. Retrieved 21 December 2010.
- ↑ Ben Cahoon (2000). "World Statesmen.org: Shan and Karenni States of Burma". Retrieved 7 July 2014.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
