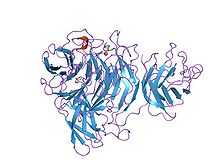
Kelch motif
The Kelch motif is a region of protein sequence found widely in proteins from bacteria and eukaryotes.[2] This sequence motif is composed of about 50 amino acid residues which form a structure of a four stranded beta-sheet "blade". This sequence motif is found in between six and eight copies per protein which fold together to form a larger circular solenoid structure called a beta-propeller domain.
Proteins containing Kelch motifs
The Kelch motif is widely found in eukaryotic and bacterial species. Notably the human genome contains around 100 proteins containing the Kelch motif. Within individual proteins the motif occurs multiple times. For example, the motif appears 6 times in Drosophila egg-chamber regulatory protein. The motif is also found in mouse protein MIPP[3] and in a number of poxviruses. In addition, kelch repeats have been recognised in alpha- and beta-scruin,[4][5] in galactose oxidase from the fungus Dactylium dendroides[6][7] and in the Escherichia coli NanM protein, that is a sialic acid mutarotase.[8]
Structure
The structure of galactose oxidase reveals that the repeated Kelch sequence motif corresponds to a 4-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet motif that forms the repeat unit in a super-barrel structural fold commonly known as a beta propeller.[9]
Function
The known functions of kelch-containing proteins are diverse:
- scruin is an actin cross-linking protein;
- galactose oxidase catalyses the oxidation of the hydroxyl group at the C6 position in D-galactose;
- neuraminidase hydrolyses sialic acid residues from glycoproteins;
- NanM is a sialic acid mutarotase, involved in efficient utilisation of sialic acid by bacteria;
- kelch may have a cytoskeletal function, as it is localised to the actin-rich ring canals that connect the 15 nurse cells to the developing oocyte in Drosophila.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Ito N, Phillips SE, Stevens C et al. (March 1991). "Novel thioether bond revealed by a 1.7 A crystal structure of galactose oxidase". Nature 350 (6313): 87–90. doi:10.1038/350087a0. PMID 2002850.
- ↑ Adams J, Kelso R, Cooley L (January 2000). "The kelch repeat superfamily of proteins: propellers of cell function". Trends Cell Biol. 10 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1016/S0962-8924(99)01673-6. PMID 10603472.
- ↑ Xue F, Cooley L (1993). "kelch encodes a component of intercellular bridges in Drosophila egg chambers". Cell 72 (5): 681–693. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90397-9. PMID 8453663.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Way M, Sanders M, Matsudaira P, Chafel M, Knight A, Tu YH (1995). "beta-Scruin, a homologue of the actin crosslinking protein scruin, is localized to the acrosomal vesicle of Limulus sperm". J. Cell Sci. 108: 3155–3162. PMID 7593276.
- ↑ Way M, Sakai J, Sanders M, Garcia C, Matsudaira P (1995). "Sequence and domain organization of scruin, an actin-cross-linking protein in the acrosomal process of Limulus sperm". J. Cell Biol. 128 (1): 51–60. doi:10.1083/jcb.128.1.51. PMC 2120335. PMID 7822422.
- ↑ Doolittle RF, Bork P (1994). "Drosophila kelch motif is derived from a common enzyme fold". J. Mol. Biol. 236 (5): 1277–1282. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(94)90056-6. PMID 8126718.
- ↑ Keen JN, Ito N, Phillips SE, Stevens C, Ogel ZB, McPherson MJ, Yadav KD, Knowles PF (1991). "Novel thioether bond revealed by a 1.7 A crystal structure of galactose oxidase". Nature 350 (6313): 87–90. doi:10.1038/350087a0. PMID 2002850.
- ↑ Severi E, Müller A, Potts JR, Leech A, Williamson D, Wilson KS, Thomas GH (2008). "Sialic acid mutarotation is catalyzed by the Escherichia coli beta-propeller protein YjhT". J. Biol. Chem. 283 (8): 4841–4849. doi:10.1074/jbc.m707822200. PMID 18063573.
- ↑ Ito N, Phillips SE, Yadav KD, Knowles PF (1994). "Crystal structure of a free radical enzyme, galactose oxidase". J. Mol. Biol. 238 (5): 794–814. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1994.1335. PMID 8182749.
External links
This article incorporates text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR006652
This article incorporates text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR011498