Kamchatka Peninsula
Coordinates: 57°N 160°E / 57°N 160°E
.svg.png)
The Kamchatka Peninsula (Russian: полуо́стров Камча́тка, poluostrov Kamchatka) is a 1,250-kilometre-long (780 mi) peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about 270,000 km2 (100,000 sq mi).[1] It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west.[2] Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the 10,500-metre (34,400 ft) deep Kuril–Kamchatka Trench.
The Kamchatka Peninsula, the Commander Islands, and Karaginsky Island constitute the Kamchatka Krai of the Russian Federation. The vast majority of the 322,079 inhabitants are Russians, but there are also about 13,000 Koryaks (2014).[3] More than half of the population lives in Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (179,526 people in 2010) and nearby Yelizovo (38,980).
The Kamchatka peninsula contains the volcanoes of Kamchatka, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Kamchatka receives up to 2,700 mm (110 in) of precipitation per year. The summers are moderately cool, and the winters tend to be rather stormy though rarely producing lightning.
Geography
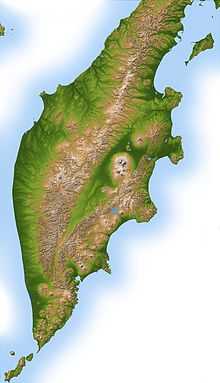


Politically, the peninsula forms part of Kamchatka Krai. The southern tip is called Cape Lopatka. The circular bay to the north of this on the Pacific side is Avacha Bay with the capital, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. North up the Pacific side, the four peninsulas are called Shipunsky Point, Kronotsky Point, Kamchatsky Point and Ozernoy Point. North of Ozernoy is the large Karaginsky Bay, which features Karaginsky Island. Northeast of this (off the displayed map) lies Korfa Bay with the town of Tilichiki. On the opposite side is the Shelikhov Gulf.
The Kamchatka or Central (Sredinny) Range forms the spine of the peninsula. Along the southeast coast runs the Vostochny or Eastern Range. Between these lies the central valley. The Kamchatka River rises northwest of Avacha and flows north down the central valley, turning east near Klyuchi to enter the Pacific south of Kamchatsky Point at Ust-Kamchatsk. In the nineteenth century a trail led west from near Klychi over the mountains to the Tegil river and town which was the main trading post on the west coast. North of Tegil is Koryak Okrug. South of the Tegil is the Icha River. Just south of the headwaters of the Kamchatka, the Bistraya River curves southwest to enter the Sea of Okhotsk at Bolsheretsk, which once served as a port connecting the peninsula to Okhotsk. South of the Bistraya flows the Golygina River.
There is a road from Bolsheretsk to Petropavlovsk and another from this road up the central valley (with a bus service) to Ust-Kamchatsk. The northern end of the road is of poorer quality. Apart from the two roads, transport is by small plane, helicopter, four-wheel drive truck and army truck.
The obvious circular area in the central valley is the Klyuchevskaya Sopka, an isolated volcanic group southeast of the curve of the Kamchatka River. West of Kronotsky Point is the Kronotsky Biosphere Reserve with the Valley of Geysers. At the southern tip is the Southern Kamchatka Wildlife Refuge with Kurile Lake. There are several other protected areas: Palana is located in the Koryak area on the northwest coast.
Climate
Although Kamchatka lies at similar latitudes to Great Britain, cold arctic winds from Siberia combined with the cold Oyashio sea current see the peninsula covered in snow from October to late May. Under the Köppen climate classification Kamchatka generally has a subarctic climate (Dfc) but higher and more northerly areas have a polar climate (ET). Kamchatka is much wetter and milder than eastern Siberia, and is essentially transitional from the hypercontinental climate of Siberia and Manchuria to the rain-drenched subpolar oceanic climate of the Aleutian Islands.

There is considerable variation, however, between the rain-drenched and heavily glaciated east coast and the drier and more continental interior valley. In the heavily glaciated Kronotsky Peninsula, where maritime influences are most pronounced, annual precipitation can reach as high as 2,500 millimetres (98 in), whilst the southeast coast south of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky generally receives around 1,350 millimetres (53 in) of rainfall equivalent per year. Considerable local variations exist: southern parts of the Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky metropolitan area can receive as much as 430 millimetres (17 in) more than the northern part of the city. Temperatures here are very mild, with summer maxima no higher than 15 °C (59 °F) and winter lows around −8 °C (18 °F), whilst diurnal temperature ranges seldom exceed 5˚C (9˚F) due to persistent fog on exposed parts of the coast. South of 57˚N there is no permafrost due to the relatively mild winters and heavy snow cover, whilst northward discontinuous permafrost prevails. The west coastal plain has a similar climate, though rather drier with precipitation ranging from 880 millimetres (35 in) in the south to as little as 430 millimetres (17 in) in the north, where winter temperatures become considerably colder at around −20 °C (−4 °F).
| Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Klyuchi | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The interior valley of the Kamchatka River, represented by Klyuchi, has much lower precipitation (at around 450 to 650 millimetres (18 to 26 in)) and significantly more continental temperatures, reaching 19 °C (66 °F) on a typical summer day and during extreme cold winter spells falling as low as −41 °C (−42 °F). Sporadic permafrost prevails over the lower part of this valley, but it becomes more widespread at higher altitudes and glaciers, and continuous permafrost prevails north of 55˚N.
The summer months, when maximum temperatures range from 15 to 20 °C (59 to 68 °F), are popular with tourists, but a growing trend in winter sports keeps tourism pulsing year-round. The volcanoes and glaciers play a role in forming Kamchatka's climate, and hot springs have kept alive dozens of species decimated during the last ice-age.[6]
Geology, earthquakes and volcanoes

| Volcanoes of Kamchatka | |
|---|---|
| Name as inscribed on the World Heritage List | |
 Koryaksky Volcano rising above Petropavlovsk-Kamchatskiy. | |
| Type | Natural |
| Criteria | vii, viii, ix, x |
| Reference | 765 |
| UNESCO region | Asia |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 1996 (20th Session) |
| Extensions | 2001 |
The Kamchatka River and the surrounding central side valley are flanked by large volcanic belts containing around 160 volcanoes, 29 of them still active. The peninsula has a high density of volcanoes and associated volcanic phenomena, with 19 active volcanoes included in the six UNESCO World Heritage List sites in the Volcanoes of Kamchatka group, most of them on the Kamchatka Peninsula, the most volcanic area of the Eurasian continent, with many active cones. The Kamchatka Peninsula is also known as the "land of fire and ice".[7]
The highest volcano is Klyuchevskaya Sopka (4,750 m or 15,584 ft), the largest active volcano in the Northern Hemisphere,[8] while the most striking is Kronotsky: volcanologists Robert and Barbara Decker regard its perfect cone as a prime candidate for the world's most beautiful volcano. Somewhat more accessible are the three volcanoes visible from Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky: Koryaksky, Avachinsky, and Kozelsky. In the center of Kamchatka is Eurasia's world-famous Geyser Valley which was partly destroyed by a massive mudslide in June 2007.[9]
Owing to the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench, deep-focus seismic events and tsunamis occur fairly commonly. A pair of megathrust earthquakes occurred off the coast on October 16, 1737, and on November 4, 1952, with magnitudes of ~9.3 and 8.2 respectively.[10] A chain of more shallow earthquakes were recorded as recently as April 2006.[11]
These volcanic features are the site of occurrence of certain extremophile micro-organisms that can survive in extremely hot environments.[12]
History and exploration
.jpg)

When Russian explorer Ivan Moskvitin reached the Sea of Okhotsk in 1639, further exploration was impeded by the lack of skills and equipment to build sea-going ships and by the harsh land to the northeast inhabited by the warlike Koryak people. Kamchatka was, consequently, entered from the north. In 1651, after having assisted in the foundation of the Anadyrsk ostrog, explorer Mikhail Stadukhin went south and followed the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk from Penzhina Bay to Okhotsk. From about 1667 there were reports of a Kamchatka River to the south. Some time before 1700 a group of Russians were stranded and died on Kamchatka.
In 1695 explorer Vladimir Atlasov was made commander of Anadyrsk. In 1696 he sent the Cossack Luka Morozko south. Morozko got as far as the Tigil River and returned with reports and some mysterious writings, probably Japanese. In 1697-1699 Atlasov explored nearly the whole of the peninsula. He built an ostrog at Verkhny-Kamchatsk and rescued or captured a Japanese castaway and went to Moscow to report. In 1699 the Russians at Verkhny-Kamchatsk were killed by the Koryaks on their way back to Anadyrsk. The 1700 punitive expedition destroyed a Koryak village and founded Nizhne-Kamchatsk on the lower river. Bolskeretsk was founded in 1703. From about 1705 there was a breakdown of order. There were numerous mutinies and native wars all over the peninsula and north to the Koryak country of the Penzhina River and Olyutorsky Gulf. Several people were sent out to restore order, including Atlasov who was murdered in 1711. Some degree of order was restored by Vasily Merlin in 1733-39. There was no significant resistance after 1756. A major smallpox epidemic that hit in 1768-69 quickly decimated the native population; the roughly 2,500 Itelmens present in 1773 were reduced to 1,900 in 1820, from an original population of 12–25,000. Those who survived adopted Russian customs and there was a great deal of intermarriage so that "Kamchadal", the original Russian name for the Itelmens, came to mean any Russian or part-Russian born on the peninsula.
In 1713 Peter the Great sent shipbuilders to Okhotsk. A fifty-four-foot boat was built and sailed to the Tegil River in June 1716. This one week journey, later shifted to Okhotsk-Bolseretsk, became the standard route to Kamchatka. In 1720 Kamchatka and the Kurils were mapped by Ivan Yevreinov. Danish explorer Vitus Bering left Nezhe-Kamchatsk for his first voyage in 1728 and, as part of his second voyage, he founded Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky in 1740.

Vitus Bering's Second Kamchatka Expedition, in the service of the Russian Navy, began the final "opening" of Kamchatka, helped by the fact that the government began to use the area to exile people, famously the Slovak explorer and rebel the Count de Benyovszky. In 1755, Stepan Krasheninnikov published the first detailed description of the peninsula, An Account of the Land of Kamchatka. The Russian government encouraged the commercial activities of the Russian-American Company by granting land to newcomers on the peninsula. By 1812, the indigenous population had fallen to less than 3,200, while the Russian population had risen to 2,500.
In 1854, the French and British, who were battling Russian forces on the Crimean Peninsula, attacked Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. During the Siege of Petropavlovsk, 988 men with a mere 68 guns managed to defend the outpost against 6 ships with 206 guns and 2,540 French and British soldiers. Despite the heroic defense, Petropavlovsk was abandoned as a strategic liability after the French and British forces withdrew. The next year when a second enemy force came to attack the port, they found it deserted. Frustrated, the ships bombarded the city and withdrew.
The next fifty years were lean ones for Kamchatka. The naval port was moved to Ust-Amur and in 1867 Alaska was sold to the United States, making Petropavlovsk obsolete as a transit point for traders and explorers on their way to the American territories. In 1860, a Primorsky (Maritime) Region was established and Kamchatka was placed under its jurisdiction. In 1875, the Kuril Islands were ceded to Japan in return for Russian sovereignty over Sakhalin island. The Russian population of Kamchatka stayed around 2,500 until the turn of the century, while the native population increased to 5,000. During the 19th century, scientific exploration of the peninsula continued, with Karl von Ditmar making an important journey there in 1851-1854.[13]
World War II hardly affected Kamchatka except for its service as a launch site for the invasion of the Kurils in late 1945. After the war, Kamchatka was declared a military zone. Kamchatka remained closed to Russians until 1989 and to foreigners until 1990.
Terrestrial flora
Kamchatka boasts abundant flora. The variable climate promotes different flora zones where tundra and muskeg are dominant succeeded by grasses, flowering shrubs and forests of pine, birch, alder and willow. The wide variety of plant forms spread throughout the Peninsula promotes just as wide a variation in animal species that feed off them. Although Kamchatka is mostly tundra, deciduous and coniferous trees are abundant and forests can be found throughout the peninsula.
Terrestrial and aquatic fauna


Kamchatka boasts diverse and abundant wildlife. This is due to climates ranging from temperate to subarctic, diverse topography and geography, many free-flowing rivers, proximity to highly productive waters from the northwestern Pacific Ocean and the Bering and Okhotsk Seas, and to the low human density and minimal development. It also boasts the southernmost expanse of Arctic tundra in the world. Commercial exploitation of marine resources and a history of fur trapping has taken its toll on several species.
Kamchatka is famous for the abundance and size of its brown bears. In the Kronotsky Nature Preserve there are estimated to be three to four bears per 100 square kilometres.[14] Other fauna of note include carnivores such as tundra wolf (Canis lupus albus), Arctic fox (Vulpes lagopus) Anadyr fox (Vulpes vulpes beringiana), East Siberian lynx (Lynx lynx wrangeli), wolverine (Gulo gulo), sable (Martes zibellina), Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra), East Siberian stoat (Mustela ermine kaneii) and Siberian least weasel (Mustela nivalis pygmaea). The peninsula hosts habitat for several large ungulates including the Kamchatka snow sheep, reindeer (Rangifer tarandus), and Chukotka moose (Alces alces burulini) one of the largest moose in the world and the largest in Eurasia; and rodents/leporids, including mountain hare (Lepus timidus), marmot, and several species of lemming and squirrel. The peninsula is the breeding ground for Steller's sea eagle,[15] one of the largest eagle species, along with the golden eagle and gyr falcon.
Kamchatka contains probably the world's greatest diversity of salmonid fish, including all six species of anadromous Pacific salmon (chinook, chum, coho, seema, pink, and sockeye). Due to its uniquely suitable environment, biologists estimate that a fifth of all Pacific salmon originates in Kamchatka.[16] Kuril Lake is recognized as the biggest spawning-ground for sockeye in Eurasia.[17] In response to pressure from poaching and to worldwide decreases in salmon stocks, some 24,000 square kilometres (9,300 sq mi) along nine of the more productive salmon rivers are in the process of being set aside as a nature preserve. Stickleback species, particularly Gasterosteus aculeatus and Pungitius pungitius, also occur in many coastal drainages, and are likely present in freshwater as well.
Cetaceans that frequent the highly productive waters of the northwestern Pacific and the Okhotsk Sea include: orcas, Dall's and harbor porpoises, humpback whales, sperm whales and fin whales. Less frequently, gray whales (from the eastern population), the critically endangered North Pacific right whale and bowhead whale, beaked whales and minke whales are encountered. Blue whale are known to feed off of the southeastern shelf in summer. Among pinnipeds, Steller's sea lions, northern fur seals, spotted seals and harbor seals are abundant along much of the peninsula. Further north, walruses and bearded seals can be encountered on the Pacific side, and ribbon seals reproduce on the ice of Karaginsky Bay. Sea otters are concentrated primarily on the southern end of the peninsula.
Seabirds include northern fulmars, thick and thin-billed murres, kittiwakes, tufted and horned puffins, red-faced, pelagic and other cormorants, and many other species. Typical of the northern seas, the marine fauna is likewise rich. Of commercial importance are Kamchatka crab (king crab), scallop, squid, pollock, cod, herring, halibut and several species of flatfish.
See also
References
- ↑ Быкасов В. Е. Ошибка в географии(Russian) // Известия Всесоюзного Географического Общества. — 1991. — № 6. (in Russian)
- ↑ "Kamchatka Peninsula". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- ↑ "Kamchatka Peninsula". Government of Kamchatskiy Kray. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ↑ Погода и климат
- ↑ Sistema de Clasificación Bioclimática Mundial
- ↑ "Climate of Kamchatka peninsula". Retrieved March 2011.
- ↑ World Heritage (1996). "Volcanoes of Kamchatka". UNESCO. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- ↑ Press Releases - Public Affairs Office - The University of Nottingham
- ↑ The World Wildlife Fund (2007). "Natural Wonder of the World Transformed within Hours, says World Wildlife Fund". earthtimes.org. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- ↑ "The 4 November 1952 Kamchatka Earthquake and Tsunami". Australian Government Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- ↑ Earthquake Hazards Program (2006). "Magnitude 7.6 - Koryakia, Russia". US Geological Survey. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- ↑ C.Michael Hogan. 2010. Extremophile. eds. E.Monosson and C.Cleveland. Encyclopedia of Earth. National Council for Science and the Environment, Washington DC
- ↑ "Cambridge Journals Online - Polar Record - Abstract - Carl von Ditmar, 1822-192:a geologist in Kamchatka". Polar Record. Cambridge University Press. Retrieved 6 July 2013.
- ↑ "Кроноцкий государственный биосферный заповедник, Долина Гейзеров. Туры по Камчатке с камчатской туристической компанией". www.kamchatkatravel.net. Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- ↑ "Haliaeetus pelagicus — Detailed documentation". The World Conservation Union Red List. Archived from the original on 2007-12-10. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- ↑ Dronova, Natalia; Spiridonov, Vassily (2008). "Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated Pacific Salmon Fishing in Kamchatka". WWF Russia, IUCN. Retrieved 2012-08-14.
- ↑ "Discovering Kamchatka: Terrestrial and aquatic fauna". The Royal Geographical Society. 2008. Retrieved 2012-08-14.
Further reading
- Gleadhill, Diana (2007), Kamchatka: A Journal & Guide to Russia's Land of Ice and Fire, Hong Kong: Odyssey Books, ISBN 978-962-217-780-2.
External links
-
 Kamchatka travel guide from Wikivoyage
Kamchatka travel guide from Wikivoyage - UNESCO World Heritage Site profile
- Information about Kamchatka peninsula and traveling there