Kaliningrad Oblast
| Kaliningrad Oblast Калининградская область (Russian) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| — Oblast — | |||
| |||
|
| |||
| |||
|
| |||
| Political status | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Federal district | Northwestern[2] | ||
| Economic region | Kaliningrad[3] | ||
| Established | April 7, 1946[4] | ||
| Administrative center | Kaliningrad[5][6] | ||
| Government (as of February 2015) | |||
| - Governor[7] | Nikolay Tsukanov[8] | ||
| - Legislature | Oblast Duma[9] | ||
| Statistics | |||
| Area (as of the 2002 Census)[10] | |||
| - Total | 15,100 km2 (5,800 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 76th | ||
| Population (2010 Census)[11] | |||
| - Total | 941,873 | ||
| - Rank | 56th | ||
| - Density[12] | 62.38/km2 (161.6/sq mi) | ||
| - Urban | 77.6% | ||
| - Rural | 22.4% | ||
| Population (January 2014 est.) | |||
| - Total | 963,128[13] | ||
| Time zone(s) | USZ1 (UTC+02:00)[14] | ||
| ISO 3166-2 | RU-KGD | ||
| License plates | 39, 91 | ||
| Official languages | Russian[15] | ||
| Official website | |||
Kaliningrad Oblast (Russian: Калинингра́дская о́бласть, Kaliningradskaya oblast) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It is an exclave, with no land connection to the rest of Russia, on the Baltic coast. As of the 2010 Census, it had a population of 941,873.[11]
The territory of the oblast is that of the northern part of historical East Prussia (German: Nord-Ostpreußen). It was once inhabited by the Sambians (speakers of the old Baltic language). They became extinct around 17th century, after they were conquered by the Teutonic Knights and exposed to assimilation and Germanization. Then it was a part of the Prussian state and of Germany until 1945. That year, it was conquered by the Soviet Union and annexed into it under border changes promulgated in the Potsdam Agreement, when it was attached to the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. Most of its German population were killed or fled westward to what would become West and East Germany during the last months of the war. Others were expelled between 1944 and 1950. Russian settlers inhabited the land, and have been the majority ethnic group since.
The oblast forms the westernmost part of Russia. Surrounded by Poland to the south, Lithuania to the east and north, and the Baltic Sea to the west, Kaliningrad Oblast has no land connection to the rest of Russia. Since its creation after World War II, it has been a Russian exclave, first of the Russian SFSR and then of the Russian Federation. The fall of the Soviet Union, and Poland and Lithuania's subsequent joining the European Union and NATO as well as their entering the Schengen Zone has left Kaliningrad increasingly isolated from the rest of Russia. Visa-free travel to the main part of Russia is only possible by sea or air.
The oblast's largest city and administrative center is Kaliningrad (formerly Königsberg), which has historical significance as both a major city of the historical state of Prussia and the capital of the former German province of East Prussia. After World War II, East Prussia was divided between the USSR and Poland, and Königsberg was renamed after the Soviet head of state Mikhail Kalinin.
Currently, Kaliningrad Oblast is one of Russia's best performing regional economies, bolstered by a low manufacturing tax rate as set by its "Special Economic Zone" (SEZ) status, which was issued by Moscow. As of 2006, one in three televisions in Russia are made in Kaliningrad. The territory's population is one of the few in Russia that is expected to show strong growth during the early 21st century.[16]
Geography


Kaliningrad Oblast is an exclave of Russia surrounded by Poland, Lithuania and the Baltic Sea. Its largest river is the Pregolya. It starts as a confluence of the Instruch and the Angrapa and drains into the Baltic Sea through Vistula Lagoon. Its length under the name of Pregolya is 123 km (76 mi), 292 km (181 mi), including the Angrapa.
Notable geographical features include:
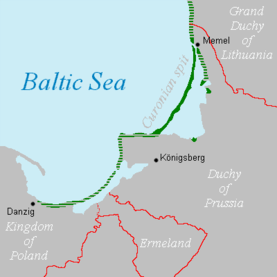
- Curonian Lagoon (shared with Lithuania)
- Vistula Lagoon (shared with Poland)
Major cities and towns:
| Russian | German † | Lithuanian † | Polish † | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baltiysk | Балтийск | Pillau | Piliava | Piława |
| Chernyakhovsk | Черняховск | Insterburg | Įsrutis | Wystruć |
| Gusev | Гусев | Gumbinnen | Gumbinė | Gąbin |
| Kaliningrad | Калининград | Königsberg | Karaliaučius | Królewiec |
| Sovetsk | Советск | Tilsit | Tilžė | Tylża |
† Pre-1946 (the German-language names were also used in English in this period)
Politics
The current governor (since 2010) of Kaliningrad Oblast is Nikolay Tsukanov, who succeeded Georgy Boos. The election for the fifth term of the Kaliningrad Oblast Duma was held on March 13, 2011.
History
Beginnings
The territory of what is now Kaliningrad Oblast was inhabited during the Middle Ages by tribes of Old Prussians (Sambians) in the western part and Lithuanians in the eastern part, divided by the Pregolya and Alna Rivers. The Teutonic Knights conquered the region and established a monastic state. On the foundations of a destroyed Prussian settlement known as Tvanksta, the Order founded the major city of Königsberg (modern Kaliningrad).
East Prussia
  History of Brandenburg and Prussia | |||
| Northern March pre–12th century |
Old Prussians pre–13th century | ||
| Margraviate of Brandenburg 1157–1618 (1806) |
Teutonic Order 1224–1525 | ||
| Duchy of Prussia 1525–1618 |
Royal (Polish) Prussia 1466–1772 | ||
| Brandenburg-Prussia 1618–1701 | |||
| Kingdom in Prussia 1701–1772 | |||
| Kingdom of Prussia 1772–1918 | |||
| Free State of Prussia 1918–1947 |
Klaipėda Region (Lithuania) 1920–1939 / 1945–present | ||
| Brandenburg (Germany) 1947–1952 / 1990–present |
Recovered Territories (Poland) 1918/1945–present |
Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia) 1945–present | |
Germans resettled the territory and assimilated the indigenous Old Prussians. The Lithuanian-inhabited areas became known as Lithuania Minor. In 1525, Grand Master Albert of Brandenburg secularized the Prussian branch of the Teutonic Order and established himself as the sovereign of the Duchy of Prussia, a Polish fief, later inherited by the Margravate of Brandenburg. Through the periods of Germanization and colonization over the following centuries, German culture became dominant and native Sambians became extinct in the 17th century.
Königsberg was the original capital of Prussia from 1525 until 1701, but as Prussia grew westward, the position of the capital became too peripheral and Berlin became the new Prussian capital city. During the Seven Years' War it was occupied by the Russian Empire. The region was reorganized into the Province of East Prussia within the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773.
German culture and Germanization
East Prussia was an important center of German culture. Many important figures, such as Immanuel Kant and E. T. A. Hoffmann, came from this region. The cities of Kaliningrad Oblast, despite being heavily damaged during World War II and thereafter, still contain some typical German architecture, in styles such as the Jugendstil, showcasing the rich German history and cultural importance of the area. The Lithuanian-speaking community in East Prussia declined due to organic Germanization and cultural assimilation. By the early 20th century Lithuanians made up a majority only in rural parts of the far northeast corner of East Prussia (Memelland and Lithuania Minor). A similar fate befell the Latvian-speaking Kursenieki who had settled the coast of East Prussia between Gdańsk and Klaipėda. The rest of the area, with the exception of the Slavic Masurians in southern Prussia, was overwhelmingly German-speaking.
The Memel Territory (Klaipėda region), formerly part of northeastern East Prussia as well as Lithuania Minor, was annexed by Lithuania in 1923. In 1938, Nazi Germany radically altered about a third of the place names of this area, replacing names of Old Prussian or Lithuanian origin with newly invented German names. Slavic and Jewish populations under Nazi Germany were classified as subhuman and were the target of a campaign of genocide by the German state, with the eventual goal of their extermination.
-

Historical Lithuania Minor comprises a sizeable part of Prussia that is now the Kaliningrad Oblast.
-
In 1649 settlement of the Latvian-speaking Kursenieki spanned from Klaipėda to Gdańsk. Much of this population was Germanized by the onset of World War II.
-

The former East Prussian town of Cranz as it looked ca. 1900. It is now the resort town of Zelenogradsk. Before 1945, it was a famous destination for German artists and intelligentsia.
Soviet Union
Entry of the Red Army
On August 29, 1944, during World War II, Soviet troops reached the border of East Prussia. In January 1945, the Red Army overran all of East Prussia except for the area around Königsberg. Many inhabitants fled west at this time. During the last days of the war, over two million of them were evacuated by sea. The remaining population of some 300,000 Germans was condemned to forced labor.
Potsdam
At the end of the War in 1945, the city became part of the Soviet Union pending the final determination of territorial questions at the peace settlement (as part of the Russian SFSR) as agreed upon by the Allies at the Potsdam Conference:
VI. CITY OF KÖNIGSBERG AND THE ADJACENT AREA
The Conference examined a proposal by the Soviet Government that pending the final determination of territorial questions at the peace settlement the section of the western frontier of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics which is adjacent to the Baltic Sea should pass from a point on the eastern shore of the Bay of Danzig to the east, north of Braunsberg and Goldap, to the meeting point of the frontiers of Lithuania, the Polish Republic and East Prussia.The Conference has agreed in principle to the proposal of the Soviet Government concerning the ultimate transfer to the Soviet Union of the city of Koenigsberg and the area adjacent to it as described above, subject to expert examination of the actual frontier.
The President of the United States and the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom have declared that they will support the proposal of the Conference at the forthcoming peace settlement.[17]
Kaliningrad

Königsberg was renamed Kaliningrad in 1946 after the death of Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR Mikhail Kalinin, one of the original Bolsheviks. The survivors of the German population were expelled, and the city was repopulated with Soviet citizens, mostly Russians but to a lesser extent by Ukrainians and Belarusians. The German language was replaced with the Russian language.
About 200,000 survivors of the Prussian population were deported to Germany at the end of 1947 and the beginning of 1948. In 1950, there were 1,165,000 inhabitants, which was only half the number of the pre-war population.
The city was rebuilt, and during the Cold War the Kaliningrad Oblast, as the westernmost territory of the Soviet Union, became a strategically important area. The Soviet Baltic Fleet had its headquarters in Kaliningrad during the 1950s. Because of its strategic importance, the city was closed to foreign visitors.
In 1957, an agreement was signed and later came into force which delimited the border between Poland and the Soviet Union.[18][19]
Incorporation into the Russian SFSR
According to some accounts from the 1950s and 1960s, immediately after the Second World War the Soviet government had planned to make the rest of the area a part of the Lithuanian SSR, as a substantial portion of the oblast consists of Lithuania Minor. The area was administered by the planning committee of the LSSR, although it had its own Communist Party committee. However, the leadership of the Lithuanian SSR (especially Antanas Sniečkus) refused to take the territory, mainly because of its devastation during the war. Some modern nationalistic Lithuanian authors say that the reason for the refusal was the Lithuanians' concern that there might be as many Russians as Lithuanians within the Lithuanian SSR. Instead, the region was added as an exclave to the Russian SFSR and since 1946 it has been known as the Kaliningrad Oblast. According to some historians, Stalin created it as an oblast separate from the LSSR because it further separated the Baltic states from the West.[20] Names of the cities, towns, rivers and other geographical features were changed to newly created Russian names.
Russian Federation
Isolation


Kaliningrad Oblast is an exclave, geographically separated from the rest of Russia. This isolation was enhanced by the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 when Lithuania became an independent country and even more when both Poland and Lithuania became members of NATO and subsequently the European Union in 2004. Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the independence of the Baltic states, Kaliningrad Oblast has been separated from the rest of Russia by other countries instead of by other Soviet republics. Neighboring nations imposed strict border controls when they joined the European Union. All military and civilian land links between the region and the rest of Russia have to pass through members of NATO and the EU. Russian proposals for visa-free travel between the EU and Kaliningrad have so far been rejected by the EU. Travel arrangements, based on the Facilitated Transit Document (FTD) and Facilitated Rail Transit Document (FRTD).[21][22] have been made.[21][22]
The territory's economic situation was badly affected by its geographic isolation and the significant reduction in the size of the Russian military garrison, which had previously been one of the major employers and helped the local economy.
Ethnic rebirth
After 1991, some ethnic Germans began to return to the area, such as Volga Germans from other parts of Russia and Kazakhstan, especially after Germany raised the requirements for people from the former Soviet Union to be accepted as ethnic Germans and have a "right of return." A similar migration by Poles from the lands of the former Soviet Union to the Kaliningrad Oblast occurred at this time as well.
Recently, the situation has begun to change, albeit slowly. Germany, Lithuania, and Poland have renewed contact with Kaliningrad Oblast, through town twinning and other projects. This has helped to promote interest in the history and culture of the East Prussian and Lietuvininkai communities.
21st century
In July 2005, the 750-year jubilee of the city was widely celebrated.
Kaliningrad is the only Russian Baltic Sea port that is ice-free all year round and hence plays an important role in maintenance of the Baltic Fleet.
In July 2007, Russian First Deputy Prime Minister Sergei Ivanov declared that if US-controlled missile defense systems were deployed in Poland, then nuclear weapons might be deployed in Kaliningrad. On November 5, 2008, Russian leader Dmitry Medvedev said that installing missiles in Kaliningrad was almost a certainty.[23] These plans were suspended, however, in January 2009.[24] However, during late 2011, a long range Voronezh-DM radar Voronezh radar was commissioned to monitor missile launches within about 6,000 km. It is situated in the settlement of Pionersky (formerly German Neukuhren) in Kaliningrad Oblast.[25]
Administrative divisions
Demographics
Population
According to the 2010 Census, the oblast population was 941,873;[11] down from 955,281 recorded in the 2002 Census.[26] The 1989 Census recorded 871,283 inhabitants.[27] Kaliningrad Oblast was the fourth most densely populated federal subject in Russia, with 62.5 persons/km2 (162 persons/sq mi).
Population-wise, the oblast is thoroughly Russian and Russophone in character, with almost none of the pre–World War II German, Lithuanian (Lietuvininks), Latvian speaking Kursenieki, or Polish population remaining in today's Kaliningrad Oblast. However, after 1991, some ethnic Germans and Poles began to return to the area, from Kazakhstan, Russia, and other sites in the former Soviet Union.
Ethnic groups
According to the 2010 Census, the ethnic composition of the oblast was as follows:[11]
- 772,534 Russians (86.4%)
- 32,771 Ukrainians (3.7%)
- 32,497 Belarusians (3.6%)
- 9,769 Lithuanians (1.1%)
- 9,226 Armenians (1%)
- 7,349 Germans (0.8%)
- 4,534 Tatars (0.5%)
- 3,282 Azeris (0.4%)
- 2,788 Poles (0.3%)
- 2,245 Uzbeks (0.3%)
- 16,857 others (1.9%)
- 48,021 people were registered from administrative databases and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.[28]
| census[29] | 1959 | 1970 | 1979 | 1989 | 2002 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russians | 473,861 (77.6%) | 564,469 (77.1%) | 632,717 (78.3%) | 683,563 (78.5%) | 786,885 (82.4%) | 772,534 (86.4%) |
| Ukrainians | 35,717 (5.8%) | 48 044 (6.6%) | 54,656 (6.8%) | 62,750 (7.2%) | 47,229 (4.9%) | 32,771 (3.7%) |
| Belarusians | 57,178 (9.4%) | 68,808 (9.4%) | 72,465 (9.0%) | 73,926 (8.5%) | 50,748 (5.3%) | 32,497 (3.6%) |
| Lithuanians | 21,262 (3.5%) | 23,376 (3.2%) | 19,647 (2.4%) | 18,116 (2.1%) | 13,937 (1.5%) | 9,769 (1.1%) |
Total fertility rate [30]
| Year | Rate |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 1.11 |
| 2005 | 1.16 |
| 2010 | 1.46 |
| 2013 | 1.64 |
| 2014 | 1.67 (e) |
Religion
According to a 2012 official survey[31] 34% of the population of Kaliningrad Oblast declare themselves to be "spiritual but not religious", 30.9% adhere to the Russian Orthodox Church, 22% are atheist and 11.1% follow other religions or did not give an answer to the question, 1% are unaffiliated generic Christians and 1% adhere to the Catholic Church.[31]
Until 1945, the region was overwhelmingly Lutheran, with a small number of Catholics and Jews.
Military
For some years after the fall of the Soviet Union, Kaliningrad Oblast was one of the most militarized areas of the Russian Federation and the density of military installations was the highest in Europe, as much of the Soviet equipment pulled out of Eastern Europe was left there. As of 2009, there were 11,600 Russian ground troops based in the oblast, plus additional naval and air force personnel.[33] Thus military troops amount to less than 2% of the oblast's population. Kaliningrad is the headquarters of the Russian Baltic Fleet together with Chernyakhovsk (air base), Donskoye (air base) and Kaliningrad Chkalovsk (naval air base).
The Washington Times claimed on January 3, 2001, citing anonymous intelligence reports, that Russia had transferred tactical nuclear weapons into a military base in Kaliningrad for the first time since the end of the Cold War. Russian top-level military leaders denied those claims.[34] A Pentagon spokesperson said that such deployment would violate the Russian pledge to remove nuclear weapons from the Baltics. Russia and the United States announced in 1991 and 1992 a non-binding agreement to reduce arsenals of tactical nuclear weapons. On the eve of the reunification of Germany, Helmut Kohl promised Mikhail Gorbachev that NATO's military infrastructures would not move eastward into the territory of East Germany, a fact since confirmed by the former U.S. Ambassador to Moscow Jack Matlock.
On November 5, 2008, Russian President Dimitry Medvedev said that Russia would deploy Iskander missiles in the oblast as a response to U.S. plans for basing missile defense missiles in Poland.[35] Equipment to electronically hamper the operation of future U.S. missile facilities in Poland and the Czech Republic would also be deployed, he said.
However, on January 28, 2009, a Russian defense official stated that the deployment of short-range missiles in Kaliningrad Oblast would cease, due to perceived changes in the attitude of the United States government towards the Russian Federation, following the election of United States President Barack Obama.[36] In September 2009, Russia fully scrapped plans to send short-range missiles into the Kaliningrad Oblast in response to Obama's decision to cancel the missile defense system.
In November 2011, Dmitry Medvedev issued another stern warning that Russia would deploy new missiles aimed at U.S. missile defense sites in Europe if Washington went ahead with the planned shield.[37] Then in 2012, Russia chose Kaliningrad as the second region (after Moscow) to deploy the S-400 (SAM) missile system.[38][39] Subsequently Russian newspaper Izvestia reported in Dec 2013 that the short range Iskander-M 9K720 operational-tactical missile systems had been commissioned by the Western Military District's missile and artillery forces at about the same time.[40]
Economy
Kaliningrad Oblast's economy is positively influenced by several factors, such as ice-free ports, the world's largest amber deposits and proximity to European countries. The region also has a developed tourist infrastructure, unique museums and monuments, and tourist attractions. One of these is the famous Curonian Spit.[41]
To combat the oblast's economic problems such as high unemployment, in 1996 the Russian authorities granted Kaliningrad special economic status and tax advantages intended to attract investors. The oblast's economy has since benefited substantially and in recent years experienced a boom. A US$45 million airport terminal has been opened and the European Commission provides funds for business projects under its special program for the region. The oblast has begun to see increasing trade with the countries of the EU as well as increasing economic growth and rising industrial output.[42]
According to official statistics, the Gross Regional Product in 2006 was 115 billion roubles.[43] GRP per capita in 2007 was 155,669 roubles.[44]
Industry
Car and truck assembly (GM, BMW, Kia, Yuejin), and production of auto parts, are major industries in Kaliningrad Oblast. There are shipbuilding facilities in Kaliningrad and Sovetsk. Food processing is a mature industry in the region. OKB Fakel, a world leader in the field of Hall thruster development, as well as a leading Russian developer and manufacturer of electric propulsion systems, is based in Neman. The company employs 960 people.[45][46] General Satellite (GS) is the biggest employer in Gusev city producing satellite receivers, cardboard packaging, nanomaterials etc.
Natural resources
Kaliningrad Oblast possesses more than 90% of the world's amber deposits.[47] Most of the mined amber is processed outside the region, in Russia and in other countries.
There are small oil reservoirs beneath the Baltic Sea not far from Kaliningrad's shore. Small-scale offshore exploration started in 2004 and some Baltic countries (Poland and Lithuania), as well as local NGOs, voiced concerns regarding possible environmental impact.
Fishing
Fishing is an important regional industry, with big fishing ports in Kaliningrad and Pionersky (formerly Neukuhren) and smaller ones in Svetly and Rybachy.
Power generation
Average yearly power consumption in the Kaliningrad Oblast was 3.5 terawatt-hours in 2004 with local power generation providing just 0.235 terawatt-hours. The balance of energy needs was imported from neighboring countries. A new Kaliningrad power station was built in 2005, covering 50% of the oblast's energy needs. A second power station was scheduled to enter service in 2010, making the oblast independent from electricity imports.
As of 2014, there are plans to build two nuclear power reactors in the eastern part of the region.
See also
- Kaliningrad Oblast election, 2011
- Baltic Republican Party
- List of rural localities in Kaliningrad Oblast
- Kaliningrad Special Region
References
Notes
- ↑ Article 5 of the Charter of Kaliningrad Oblast states that the oblast may have an anthem, providing a law is adopted to that effect. As of 2015, no such law is in place.
- ↑ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", №20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
- ↑ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ↑ Charter of Kaliningrad Oblast, Article 3
- ↑ Law #463
- ↑ "Kaliningrad Oblast in Russia | By Russia Channel". Russia-channel.com. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- ↑ Charter of Kaliningrad Oblast, Article 28
- ↑ Official website of the Government of Kaliningrad Oblast. Nikolay Nikolayevich Tsukanov, Governor of Kaliningrad Oblast (Russian)
- ↑ Charter of Kaliningrad Oblast, Article 17
- ↑ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)". Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2011-11-01.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). "Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1" [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года (2010 All-Russia Population Census) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ↑ The density value was calculated by dividing the population reported by the 2010 Census by the area shown in the "Area" field. Please note that this value may not be accurate as the area specified in the infobox is not necessarily reported for the same year as the population.
- ↑ Kaliningrad Oblast Territorial Branch of the Federal State Statistics Service. Оценка численности населения Калининградской области по состоянию на 1 января 2014 года (Russian)
- ↑ Правительство Российской Федерации. Федеральный закон №107-ФЗ от 3 июня 2011 г. «Об исчислении времени», в ред. Федерального закона №248-ФЗ от 21 июля 2014 г. «О внесении изменений в Федеральный закон "Об исчислении времени"». Вступил в силу по истечении шестидесяти дней после дня официального опубликования (6 августа 2011 г.). Опубликован: "Российская газета", №120, 6 июня 2011 г. (Government of the Russian Federation. Federal Law #107-FZ of June 31, 2011 On Calculating Time, as amended by the Federal Law #248-FZ of July 21, 2014 On Amending Federal Law "On Calculating Time". Effective as of after sixty days following the day of the official publication.).
- ↑ Official on the whole territory of Russia according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- ↑ Sheeter, Laura (2006-10-16). "Kaliningrad erases stains of past". BBC News. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
- ↑ "THE POTSDAM DECLARATION". Retrieved 2009-04-02.
- ↑ "Russia (USSR) / Poland Treaty (with annexed maps) concerning the Demarcation of the Existing Soviet-Polish State Frontier in the Sector Adjoining the Baltic Sea 5 March 1957" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-04-02.
- ↑ For other issues of the frontier delimitation see "Maritime boundary delimitation agreements and other material". Retrieved 2009-04-02.
- ↑ Weinberg, Gerhard L. (2005). Visions of Victory: The hopes of eight World War II leaders. Cambridge University Press. p. 114. ISBN 978-0-521-85254-8.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Transit from/to Kaliningrad Region, www.euro.lt
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Council Regulation (EC) No 693/2003, eur-lex.europa.eu
- ↑ "Medvedev Says Russia to Deploy Missiles Near Poland" Associated Press via Yahoo News
- ↑ "Russia scraps plans to deploy nuclear-capable missiles in Kaliningrad" The Guardian
- ↑ "Russia's new radar to monitor all Europe including Britain" Pravda 28.11.2011
- ↑ Russian Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек" [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian). Retrieved August 9, 2014.
- ↑ Demoscope Weekly (1989). "Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров" [All Union Population Census of 1989: Present Population of Union and Autonomous Republics, Autonomous Oblasts and Okrugs, Krais, Oblasts, Districts, Urban Settlements, and Villages Serving as District Administrative Centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года[All-Union Population Census of 1989] (in Russian). Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета: Высшая школа экономики [Institute of Demography at the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. Retrieved August 9, 2014.
- ↑ http://www.perepis-2010.ru/news/detail.php?ID=6936
- ↑ Переписи населения Российской Империи, СССР, 15 новых независимых государств Census of the Russian Empire, Soviet Union, 15 new independent states
- ↑ http://kaliningrad.gks.ru/wps/wcm/connect/rosstat_ts/kaliningrad/resources/4444fd004ee286c58269833467c8ff84/%D0%92%D0%BE%D0%B7%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BD%D1%8B%D0%B5+%D0%BA%D0%BE%D1%8D%D1%84%D1%84%D0%B8%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%82%D1%8B+%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B6%D0%B4%D0%B0%D0%B5%D0%BC%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8.pdf
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 Arena - Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia. Sreda.org
- ↑ 2012 Survey Maps. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), August 27, 2012. Retrieved September 24, 2012.
- ↑ Military Balance 2009
- ↑ Bill Gertz, "Russia Transfers Nuclear Arms to Baltics," Washington Times, 3 January 2001, p. 1.
- ↑ "Russia to move missiles to Baltic". bbc.co.uk (BBC). 2008-11-05. Retrieved 12 November 2008.
- ↑ "Russia 'halts missile deployment'". bbc.co.uk (BBC). 2009-01-28. Retrieved 2009-01-28.
- ↑ "Dmitry Medvedev, Russia President, Says Missiles May Target U.S. Missile Defense Sites". Huffington Post. 2011-11-23.
- ↑ "S-400 Missiles Deployed in Russia's Baltic Fleet." RIA Novosti, April 9, 2012.
- ↑ "Russia launches new missile defense to cover Atlantic." RT. November 29, 2011
- ↑ "Russia has stationed Iskander missiles in western region" RT. Dec 16, 2013
- ↑ "Kaliningrad Region - Introduction". Russia: All Regions Trade & Investment Guide. CTEC Publishing LLC. 2008.
- ↑ "Regions and territories: Kaliningrad". BBC News. 2009-05-15. Retrieved 2009-06-05.
- ↑ Regional administration's website (Russian)
- ↑ Валовой региональный продукт на душу населения Федеральная служба государственной статистики
- ↑ "EDB Fakel". OKB Fakel. Retrieved 2009-06-04.
- ↑ "OKB Fakel (Russian Federation)". Jane's Space Systems and Industry. 2008-12-17. Retrieved 2009-06-04.
- ↑ How Products Are Made: Amber
Sources
- Областная Дума Калининградской области. Закон №30 от 18 января 1996 г. «О вступлении в действие Устава (Основного Закона) Калининградской области», в ред. Закона №219 от 25 апреля 2013 г. «О внесении изменений в Устав (Основной Закон) Калининградской области и отдельные законодательные акты Калининградской области». Вступил в силу по истечении десяти дней со дня официального публикования, за исключением пункта 5 статьи 15 и подпункта "б" статьи 22 в части подписания постановлений областной Думы председателем областной Думы, которые введены в действие одновременно со вступлением в силу Федерального закона от 06.10.1999 №184-ФЗ "Об общих принципах организации законодательных (представительных) и исполнительных органов государственной власти субъектов Российской Федерации". Опубликован: "Янтарный край", №20, 26 января 1996 г. (Oblast Duma of Kaliningrad Oblast. Law #30 of January 18, 1996 On the Charter (Basic Law) of Kaliningrad Oblast Taking Effect, as amended by the Law #219 of April 25, 2013 On Amending the Charter (Basic Law) of Kaliningrad Oblast and Various Legislative Acts of Kaliningrad Oblast. Effective as of the date ten days after the official publication date, with the exception of item 5 of Article 15 and the portion of subitem "b" of Article 22 dealing with the signing of the resolutions of the Oblast Duma by the Chair of the Oblast Duma, which take effect simultaneously with the Federal Law #184-FZ of October 6, 1999 "On the General Principles of the Organization of the Legislative (Representative) and Executive Organs of the State Power in the Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation".).
- Калининградская областная Дума. Закон №463 от 27 мая 2010 г. «Об административно-территориальном устройстве Калининградской области», в ред. Закона №281 от 6 декабря 2013 г. «О порядке рассмотрения Калининградской областной Думой предложений о присвоении наименований географическим объектам или их переименовании, информирования населения и выявления его мнения о присвоении наименований географическим объектам или их переименовании на территории Калининградской области». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Калининградская правда" (вкладыш "Ведомости Правительства Калининградской области"), №112, 26 июня 2010 г. (Kaliningrad Oblast Duma. Law #463 of May 27, 2010 On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Kaliningrad Oblast, as amended by the Law #281 of December 6, 2013 On the Process Used by the Kaliningrad Oblast Duma to Consider the Proposals to Assign Names to Geographic Objects or to Rename Them, to Inform the Populace and Gather Their Opinion on Assigning Names to Geographic Objects or Renaming Them on the Territory of Kaliningrad Oblast. Effective as of the day of the official publication.).
- Simon Grunau, Preußische Chronik. Hrsg. von M. Perlbach etc., Leipzig, 1875.
- A. Bezzenberger, Geographie von Preußen, Gotha, 1959
- Областная Дума Калининградской области. Закон №30 от 18 января 1996 г. «О вступлении в действие Устава (Основного Закона) Калининградской области», в ред. Закона №219 от 25 апреля 2013 г. «О внесении изменений в Устав (Основной Закон) Калининградской области и отдельные законодательные акты Калининградской области». Вступил в силу по истечении десяти дней со дня официального публикования, за исключением пункта 5 статьи 15 и подпункта "б" статьи 22 в части подписания постановлений областной Думы председателем областной Думы, которые введены в действие одновременно со вступлением в силу Федерального закона от 06.10.1999 №184-ФЗ "Об общих принципах организации законодательных (представительных) и исполнительных органов государственной власти субъектов Российской Федерации". Опубликован: "Янтарный край", №20, 26 января 1996 г. (Oblast Duma of Kaliningrad Oblast. Law #30 of January 18, 1996 On the Charter (Basic Law) of Kaliningrad Oblast Taking Effect, as amended by the Law #219 of April 25, 2013 On Amending the Charter (Basic Law) of Kaliningrad Oblast and Various Legislative Acts of Kaliningrad Oblast. Effective as of the date ten days after the official publication date, with the exception of item 5 of Article 15 and the portion of subitem "b" of Article 22 dealing with the signing of the resolutions of the Oblast Duma by the Chair of the Oblast Duma, which take effect simultaneously with the Federal Law #184-FZ of October 6, 1999 "On the General Principles of the Organization of the Legislative (Representative) and Executive Organs of the State Power in the Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation".).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kaliningrad Oblast. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Kaliningrad Oblast. |
- Official website of Kaliningrad Oblast (Russian)
- A. Liucija Arbusauskaité "The Soviet Policy Towards the "Kaliningrad Germans" 1945-1951" chapter in "Themenheft: Eingliederung und Ausgrenzung. Beiträge aus der Historischen Migrationsforschung. Hrsg.: Jochen Oltmer Osnabrück: IMIS, 1999. ISSN 0949-4723
- Master's thesis by Sergey Naumkin on the possibility of Kaliningrad integrating with the EU as a special economic zone
- Life in Kaliningrad Oblast (Russian)
- Spuren der Vergangenheit / Следы Пρошлого (Traces of the past) This site by W.A. Milowskij, a Kaliningrad resident, contains hundreds of interesting photos, often with text explanations, of architectural and infrastructural artifacts of the territory's long German past. (German) (Russian)
- City and Reagen News
 |
Baltic Sea | |
|
 |
| Baltic Sea | |
| ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| |
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||