KIAA1841
| KIAA1841 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | KIAA1841 | ||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1918925 HomoloGene: 19038 GeneCards: KIAA1841 Gene | ||||||
| |||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||
| Entrez | 84542 | 71675 | |||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000162929 | ENSMUSG00000042208 | |||||
| UniProt | Q6NSI8 | Q8BUP8 | |||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001129993 | XM_006514807 | |||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001123465 | XP_006514870 | |||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 2: 61.29 – 61.39 Mb | Chr 11: 23.56 – 23.63 Mb | |||||
| PubMed search | |||||||
KIAA1841 is a gene in humans that encodes a protein known as KIAA1841 (uncharacterized protein KIAA1841). KIAA1841 is targeted for the nucleus and it predicted to play a role in regulating transcription.
Gene
Location
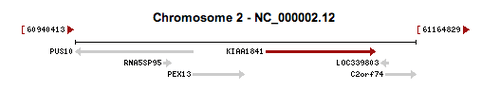
KIAA1841 is located on the long arm of chromosome 2 (2q14), starting at 61297486 and ending at 61349294. The KIAA1841 gene spans 52809 base pairs and is orientated on the ++ strand. The coding region is made up of 4292 base pairs and the protein sequence of 718 amino acids.[1]
Gene Neighborhood
Genes PEX13 and C2orf74 neighbor KIAA1841 on chromosome 2.[2]
Expression
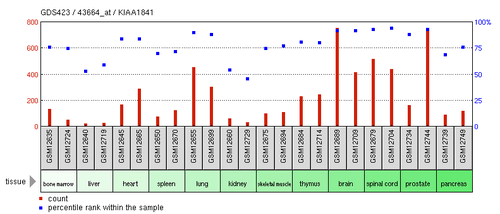
KIAA1841 is highly expressed in reproductive structures and nervous tissue. These include the brain, prostate, cervix, ear and nervous tissue. It is intermediately expressed in the lungs and spinal cord.[3][4] KIAA1841 is expressed at low levels in a wide range of tissues throughout the human body.
Transcript Variants
In humans, the KIAA1841 gene produces 18 alternatively spliced transcript variants as well as 3 unspliced. From the 18 spliced variants 4 form a protein product. The main transcript in humans is transcript ID ENST00000402291, or OTTHUMT00000325477.[5][6][7]
Homology
Paralogs
There are no paralogs of KIAA1841[8]
Orthologs
Below is a table of a variety of orthologs of the human KIAA1841. The table include closely, intermediately and distantly related orthologs.
| Species | Common Name | NCBI Accession # | Sequence Length | Protein Identity | mRNA Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo Sapiens | Human | NP_001123465.1 | 718 | 100% | 100% |
| Odobenus Rosmarus Divergens | Walrus | XP_004397774.1 | 718 | 94% | 97% |
| Canis Lupus Familiaris | Grey Wolf | XP_538505 | 718 | 92% | 96% |
| Equus Caballus | Horse | XP_001495879.1 | 765 | 93% | 96% |
| Mus Musculus | Mouse | NP_082136.2 | 718 | 89% | 94% |
| Echinops Telfairi | Hedgehog | XP_004710320.1 | 718 | 86% | 92% |
| Pelodiscus Sinensis | Soft-Shelled Turtle | XP_006122225.1 | 718 | 78% | 88% |
| Anas Platyrhynchos | Mallard Duck | XP_005016968.1 | 719 | 78% | 87% |
| Gallus Gallus | Red Junglefowl | NP_001186348.1 | 718 | 76% | 87% |
| Xenopus (Silurana) tropicalis | Western Clawed Frog | XP_004914757.1 | 715 | 71% | 83% |
| Danio Rerio | Zebrafish | XP_001333668.2 | 735 | 60% | 73% |
| Drosophila Melanogaster | Fruit Fly | NP_648346.1 | 889 | 38% | 62% |
| Apis Mellifera | Western Honey Bee | XP_006559923.1 | 849 | 40% | 62% |
| Anopheles Gambiae | Mosquito | XP_558222.3 | 806 | 40% | 61% |
Orthologs of the human protein KIAA1841 are listed above in descending order or date of divergence and then ascending order of percent identity. KIAA1841 is highly conserved throughout all orthologs, this is demonstrated with a 40% identity in the least similar ortholog. KAA1841 has evolved slowly and evenly over time.[9][10]
Homologous Domains
The domain of unknown function 3342 is conserved in all orthologs. It is the highest conserved region of the protein. Conservation of this domain was traced all the way back to a fungus called Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, which diverged 1216 millions of years ago from humans.[11]
Protein
General Properties
The molecular weight of KIAA1841 is 82 kiloDaltons. The isoelectric point is 6.5. The protein sequence is not rich or low in any amino acids. There are two stretches of non-polar regions, which are capable of being transmembrane regions. There is a stretch of 21 0’s from 254-275 and a stretch of 24 0’s from 420-444.1 The DUF3342 domain stretches from 147-449.[12]
| KIAA1841 | DUF3342 | N Terminus | C Terminus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isoelectric Point | 6.5 | 6.74 | 5.5 | 8.2 |
| Positive Charge (%) | 13.8 | 13.2 | 11.7 | 15.9+ |
| Negative Charge (%) | 14.4 | 13.5 | 14.2 | 14.5 |
| Net Charge | -0.6 | -0.3 | -2.5 | 1.4 |
| Major Hydrophobics (%) | 24.8 | 28.7 | 27.2 | 22.3 |
Composition
There is an even distribution of amino acids comprising KIAA1841. The percent composition of each amino acid is fairly consistent throughout the orthologs of the protein. The most distant ortholog displays the most variance in amino acid composition. There is a higher percent composition of alanine, histidine and leucine and a lower composition of lysine.
The protein sequence of KIAA1841 is not rich or low in any amino acids. The same is true for Mus musculus, Danio rerio, Drosophila melanogaster but not true for the most distantly related. Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis is rich is histidine. Humans and closely related orthologs are composed of 2.2% to 3.8% histidine compared to 5% in Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis.
Domains
The DUF3342 domain stretches from 147-449 on KIAA1841 and has a molecular weight of 35.7 kdal. The DUF domain is low in G (2%) and rich is C (6.3%). Both of the non-polar stretches in the protein are located within the DUF domian. One at the beginning and one at the end.
The domain (DUF3342) of unknown function is a part of the pfam11822 family. This family of proteins has yet to be functionally characterized and it is found in bacteria. This domain is usually between 170 amino acids and 303 amino acids in length. The N terminal half of this protein family is a BTB-like domain. BTB domains multifunctional protein-protein interaction motif that is involved in a number of different cellular functions, including roles in regulating transcription, cytoskeleton dynamics, gating and assembly of ion channels and is involved with ubiquitination of proteins. BTB domain structures are highly conversed and are found on proteins that only have one or two other types of domains.
Post-translational modifications
KIAA1841 is highly phosphorylated post modification. There are 37 predicted phosphorylated sites. There is one leucine-rich nuclear export signal toward the end of the protein. There is one sulfated tyrosine, which strengthens protein-protein interactions. Two motifs with high probability of post translational modification sumoylation sites were found. Sumoylation sites are involved in a number of cellular processes, including nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation and protein stability.
Secondary Structure
KIAA1841 is primarily composed of alpha helices and beta sheets. Alpha helices comprise the majority of the protein, this is true for the DUF domain and both terminuses. The DUF domain has slightly less beta sheets compared to the protein as a whole and the C terminus has an even smaller amount of beta sheets comprising it’s secondary structure.[13][14]
| KIAA1841 | DUF3342 | N Terminus | C Terminus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2° Structure: α Helice (%) | 68 | 68 | 63.9 | 70.1 |
| 2° Structure: β Sheet (%) | 61 | 49.2 | 60.8 | 35.8 |
| 2° Structure: β Turn (%) | 14.1 | 9.9 | 12.8 | 15.4 |
Subcellular Localization
Protein KIAA1841 is targeted to the nucleus.[15]
Interacting Proteins
KIAA1841 was found to interact with SRPK1 (Serine/arginine- rich protein-specific kinase 1).[16] The interaction was detected via a protein kinase assay. SRPK1 localizes to the nucleus and the cytoplasm. By regulating intracellular localization of splicing factors it is thought to play a role in regulating both constitutive and alternative splicing. KIAA1841 is also found in the nucleus and is thought to play a role in regulating transcription.
Clinical Signifcance
Disease Association
Diseases associated with this gene are crohn’s disease, celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease.[17][18]
References
- ↑ "NCBI gene database". NCBI.
- ↑ "NCBI gene database". NCBI.
- ↑ "GEO profiles". NCBI geo profiles.
- ↑ "EST profiles". NCBI EST profiles.
- ↑ "Emsembl". Vega.
- ↑ "Genecards". The Gene Human Database.
- ↑ "Aceview". NCBI.
- ↑ "Genecards". The Gene Human Database.
- ↑ "BLAST". NCBI.
- ↑ Hedges, SB. "TimeTree". Bioinformatics.
- ↑ "Biology Workbench". San Diego Supercomputer Center.
- ↑ "SAPS". Statistical Analysis of Protein Sequence, Biology Workbench.
- ↑ "PELE". San Diego Supercomputer Center.
- ↑ "CHOFAS (Predict Secondary Structure of PS". Chou-Fasman.
- ↑ "PSORT II". Expasy.
- ↑ "IntAct". EMNL-EBI.
- ↑ "NCBI gene database". NCBI.
- ↑ "Genecards". The Gene Human Database.