Kärnäkoski Fortress
| Kärnäkoski fortress | |
|---|---|
|
Kärnäkoski fortress walls | |
|
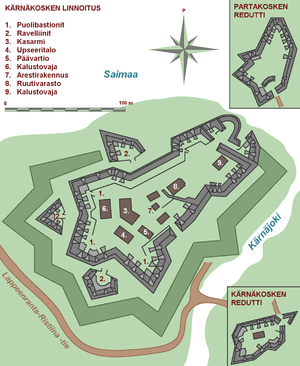
Plan of Kärnäkoski fortress and the Kärnäkoski and Partakoski redoubts | |
 Kärnäkoski fortress Kärnäkoski fortress shown within modern-day Finland | |
| Coordinates | 61°16′N 27°43′E / 61.26°N 27.71°E |
| Type | Fortress |
| Site information | |
| Open to the public | Yes |
| Condition | Largely restored |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1791-1793 |
| In use | 1793–1835 |
Kärnäkoski Fortress is a bastion fortress in Finland located in Kärnäkoski, Savitaipale built by Russia between 1791 and 1793 to protect Saint Petersburg.
Kärnäkoski fortress as part of the South-Eastern Finland fortification system
Kärnäkoski Fortress was part of a larger South-Eastern Finland fortification system built to protect Saint Petersburg, the capital of Russian Empire. After the Russo-Swedish War (1788-1790), and particularly in the light of the Swedish victories in the Battle of Porrassalmi and the naval Battle of Svensksund, Russian empress Catherine II decided to strengthen the defences in the north-western border of the empire. The construction of a large fortification system in south-eastern Finland was entrusted to general Alexander Suvorov.
To protect the capital three concentric fortress chains were built, with Kärnäkoski fortress belonging to the outermost chain located very near the border. Kärnäkoski fortress was built to both defend against a possible land-based attack from the isthmus between Saimaa lake the Gulf of Finland and to provide a base for the recently formed Russian Saimaa fleet.
Construction
General Suvorov, responsible for the construction of the South-Eastern Finland fortification system, selected the mouth of Kärnäjoki river on the isthmus between Saimaa lake and Kuolimojärvi lake near the Lappeenranta-Ristiina road as a location for one of the new border fortresses. The location allowed the fortress to guard the border between Sweden and Russia, control the traffic going via the road and monitor the shipping routes in western Saimaa. The area near the fortress had been a site for several engagements between Swedish and Russian troops in the Russo-Swedish War that had just ended.
Kärnäkoski Fortress was constructed between 1791 and 1793. The designers of the fortress were French engineering officers who had fled the French Revolution to Russia. Kärnäkoski fortress was built according to the traditional French bastion system. However, instead of a uniform regular bastion shape, the fortress was built as an irregular shape and followed the terrain, most likely because of the limited space available.
The western and southern sides of the fortress were guarded by three demi-bastions. Also three outworks, ravelins, were built in front the main fortress wall. The less-vulnerable eastern and northern sides that were mostly protected by lake shore were defended only with tenailles. An earthwork wall and a moat surrounded the fortress and the outworks. The fortress had a rear gate in the northern tip where it was possible to reach the ships and to get water. 55 cannon positions were built on fortress walls.
Inside the fortress were built barracks, guardhouse, officers quarters, brig and gunpowder magazine. The wooden buildings have been later demolished, and now only remnants of stone bases remain of them.
In addition to the main fortress, two additional supporting forts, redoubts, were built in the vicinity. The Kärnäkoski redoubt, also called the Mountain fort, was built 600 metres away from the main fortress to guard one entrance to the isthmus where the fortress was built. Partakoski redoubt was built two kilometres to north-west to guard the other side.
1400 Russian soldiers and local peasants took part in building Kärnäkoski fortress. A substantial number of workers perished from hard work and illnesses.
Fortress was used for only a short time
Kärnäkoski fortress guarded the Russian north-western border for only 15 years. During that time the fortress was also one of the bases for the Russian Saimaa fleet. Other bases were the Lappeenranta Fortress and Olavinlinna castle in Savonlinna.
After the Russian-Swedish border moved westwards to Tornionjoki river in 1809 after the Finnish War, the fortresses in south-eastern Finland lost their military value, Kärnäkoski fortress among them. Tsar Nicholas I closed down the now-unnecessary inland fortresses in 1835. As a result the fortresses were disarmed, the buildings and remaining equipment were auctioned and the walls and fortifications were left untended.
Kärnäkoski fortress was built to protect against the Swedish threat, but never did see action against the intended enemy. During the Finnish War, the only war between Sweden and Russia when the fortress was in use, the battles took place far from the fortress after Swedish army retreated from the border before Russian advance avoiding battle. A century later in the Civil War of Finland the area nearby did see several battles.
Kärnäkoski fortress today
Today Kärnäkoski fortress is a tourist attraction, although there are no guided tours or other tourist or travel services in the fortress, simply guidance signs.
Finnish National Board of Antiquities and Finnish Ministry of the Environment have listed the fortress area as nationally significant cultural historic landmark. Finnish National Board of Antiquities has restored Kärnäkoski fortress to its former shape together with other fortresses in south-eastern Finland. Walls were repaired and the fortress area was restored and cleared. The work was finished in 1997.
An inventory of the vegetation in the fortress area was conducted in 1987, based on which work began to maintain an old meadow biotope vegetation in the area. The area was reaped and cleared of young trees. Currently sheep are allowed to graze in the area during summer to maintain a traditional pasture in order to provide a suitable habitat for organisms that have become vulnerable after traditional agriculture began to modernize.
Other historical buildings nearby are an old barge harbor, mill and saw built in the 1830s and a double-arch stone bridge from 1886. The mill has not been used since the 1950s, but was restored by a local village organization in 2002.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||