Jolla
 | |
| Private | |
| Industry | Mobile devices, Consumer Electronics/Devices |
| Founded | Pirkkala, Finland (March 29, 2011) |
| Founder |
|
| Headquarters | Helsinki, Finland |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people | |
| Products | Smartphones with Linux-based Sailfish OS continuing the previous work of the MeeGo project |
Number of employees | 150 developers |
| Website | Jolla.com blog.jolla.com |
Jolla Oy[1] (sometimes referred to as Jolla Ltd.) is an independent designer, developer and vendor of various mobile devices[2] as well as their open Sailfish OS and Mer Core open source projects.[3] Headquartered in Helsinki, Finland, Jolla has research and development (R&D) office in Helsinki and Tampere and also an R&D department and office in Cyberport Hong Kong, and they are establishing R&D and operations in China.
Jolla, in Finnish, is pronounced 'yolla'.
History
Nokia, after rapidly losing marketshare in the smartphone market, decided to create a new operating system based on Linux, naming it Maemo. After merging with Intel's Moblin project (also an open source Linux system), the project was renamed MeeGo.
In October 2011, many of the MeeGo team left Nokia to form Jolla, utilizing funding from Nokia's "Bridge" program which helps establish and support start-up companies formed by ex-Nokia employees.[4][5][6]
Nokia paid employees leaving the company €25,000, but had not given any rights to patents or other intellectual property to Jolla. While Jolla's Sailfish OS can be considered a direct successor to Nokia and Intel's MeeGo and the N9 mobile phone, only its software is based on the open-sourced components of MeeGo, while the closed-source user interface design for all future devices had to be developed from scratch.
Sailfish
Jolla went public on 6 July 2012, announcing its intention to develop new smartphones which utilized a gesture-oriented user interface. They named their operating system "Sailfish", which is a result of Mer and includes a gesture-based user interface developed using the Qt, QML and HTML5, as did Nokia's N9.
Jolla co-operate with others to grow their application's and MeeGo ecosystem.[7] Jolla announced on 17 September 2013 that their phone will be capable of running most Android applications, though without direct access to the Google Play Store.[8]
Products
Hardware
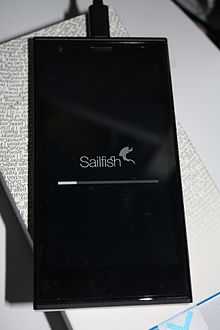
- Jolla Mobile Phone - smartphone with 4.5 in IPS qHD display, 16 GB storage, 1 GB RAM, a microSD slot and an 8 MP camera.
- Jolla Tablet - Sailfish OS 2.0 64-bit Intel's CPU tablet with 7.85 in IPS display, 32GB storage, 2GB RAM, Micro SD slot, 5MP main and 2MP front camera
- The Other Half - replaceable back cover to the Jolla phone, which can be used as hardware extension for various purposes. It has NFC and power connection to main smartphone, can have own RAM, CPU, software or hardware, can influence on smartphone performance as easy replaceable accessory or extension. E.g. used to change appearance and ambience settings, or connect the hardware keyboard.
- Jolla's Sailfish OS has been fully operational on Acer T231H, with 23 in screen as well as on Dell notebooks.[10]
- Jolla's Sailfish OS is also operational on tablets such as: Acer Iconia tab W500;[11] O2 Joggler;[12] and Exopc.[13]
Because the Sailfish OS use the MERproject.org core it is easy to run it on any hardware platform. While hardware needs a specific kernel all software above follows the standard and rules developed in frames of MERproject.org and can be just settled on the kernel. This allows to run Sailfish OS and software it can handle (not only Sailfish-native) on any hardware. Because Sailfish OS and MERproject.org core are open source both enthusiasts and vendors can do this for free like in the examples mentioned above.
Ecosystem
One of elements of the ecosystem is the Harbour.Jolla.com site, which is devoted for submitting, managing and selling applications at the Jolla Store. Consumers can install available software directly on their Sailfish devices.
Software can be submitted on a free or commercial basis, utilizing either the Sailfish OS or Android OS applications.
Currently, the Jolla Harbour and Jolla Store support only free applications. The subsystem for payments is under active development to avoid problems with monetizing software.
For developers and software enthusiasts, sailfishos.org collects and publishes here [14] an online compendium of knowledge, links and instructions on:[15]
- software porting and migration to Sailfish OS;
- similarities and differences between Harmattan and Sailfish;
- guides on how to port MeeGo 1.2 Harmattan applications for both the Nokia N9 and the Sailfish operating system;
- porting framework;
- application porting tutorials and examples (QtQuick QML applications, the Flickr Qt 5, SDL / OpenGL ES applications);
- Qt Quick Components map to Sailfish Silica.
Software
Sailfish OS is able to run:
- Sailfish-native apps;
- Android apps using built in Sailfish OS compatibility layer the Alien Dalvik from Myriad Group;
- MeeGo-native apps if its user's interface is usable under Sailfish interface;
- in general all Linux apps compiled for Sailfish device or binaries with RPM storage standard, also in console mode or as a non-graphic terminal.
All Android software available from the Jolla "harbour" store were tested with a real Jolla device. Android or MeeGo or Linux software can be downloaded from any 3rd party e.g. Google store or any other source, due to Sailfish OS openness policy. From launch, this has given the devices access to a large number of applications, which was estimated above 0.5M unique software pieces at the time of the device launch.
Because Sailfish is Linux and use Qt and Sailfish SDK is in Qt, it is possible to port applications without significant effort, including the following sources:
- Qt (ported from other Qt-supported operating systems such as Symbian, Maemo, MeeGo, Windows and other projects with Qt source code)
- MeeGo (because Sailfish has inherited much of the MeeGo work using the MER core)
- Unix and Linux (usually command-line applications or other UI limitations are possible, RPM makes downloading easier)
- HTML5 (using the installed Mozilla-based browser or directly the OS implementation of HTML5)
- Android (either porting to be a Sailfish-native app or with corrections needed for UI)
For easy porting and development the Sailfish SDK emulates the whole device, the OS and its behaviour using isolated virtual machine on host computer e.g. Windows or Mac or Linux. As it is fully emulated, not simulated, and Jolla strongly declares it is possible to test behaviour like with real device when using Jolla SDK developer's environment. So it is possible to develop and test software without using a Jolla device.
Terminology
Jolla, the company name, means dinghy (a small agile boat) in Finnish. It can also be recognized as an ironic joke about the "burning platform memo" which contained suggestion "jump into the cold sea water" or "burn with platform" considering Nokia business. It has "accidentally leaked" from former Nokia CEO Stephen Elop in February 2011.[16]
See also
- Sailfish OS - the operating system by Jolla, further developed by Jolla legacy of MeeGo OS by Nokia&Intel partnership
- Sailfish Alliance - the alliance of companies involved in Sailfish OS
- Mer core - the core stack of code by merproject.org, one of main parts of Sailfish OS, free open source software
- MeeGo - the predecessor of the Linux MeeGo Sailfish OS, developed by partnership of Nokia & Intel
- Nokia
References
- ↑ "Jolla Oy", Business Information System (the Finnish National Board of Patents and Registration, and the Finnish Tax Administration), retrieved July 18, 2012
- ↑ "Twitter / JollaSuomi: Jolla's Sailfish OS is also". Twitter.com. Retrieved 2013-07-10.
- ↑ Jolla at LinkedIn. "LinkedIn". LinkedIn. LinkedIn. Retrieved 10 November 2013.
- ↑ "Many former Nokia employees start businesses of their own", Helsingin Sanomat
- ↑ Lunden, Ingrid. "Nokia Bridge: Nokia’s Incubator Gives Departing Employees €25k And More To Pursue Ideas That Nokia Has Not". techcrunch.com. techcrunch.com. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ↑ Tung, Liam. "Inside Nokia Bridge: How Nokia funds ex-employees' new start-ups". zdnet.com. © 2013 CBS Interactive. Retrieved 7 June 2013.
- ↑ Davies, Chris. "Jolla Mobile CEO: "MeeGo is not dead"". slashgear.com. SlashGear. Retrieved 19 August 2012.
- ↑ "Jolla Sailfish OS Andriod Support". The Register. Retrieved 15 December 2013.
- ↑ "MoMo Helsinki – May 20th – Featuring Jolla Love Day". Mobile Monday. Retrieved 2014-02-18.
- ↑ LordKelvan, -. "Sailfish OS on 23" screen". youtube.com. LordKelvan. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- ↑ Sfiet_Konstantin, -. "Sailfish on an Acer Iconia tab W500". vimeo.com. Vimeo.com DMCA. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- ↑ vgrade100, -. "Sailfishos running on O2 Joggler. Modesetting xorg driver on gma500_gfx kernal driver with mesa-llvm". youtube.com. vgrade100. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- ↑ vgrade100, -. "Sailfish on Exopc #merproject". youtube.com. vgrade100. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- ↑ "Porting/Harmattan". SailfishOS. Retrieved 2014-02-18.
- ↑ "Porting/Harmattan". sailfishos.org/wiki/. https://sailfishos.org/. Retrieved 25 January 2014.
- ↑ Zieler, Chris. "Nokia CEO Stephen Elop rallies troops in brutally honest 'burning platform' memo? (update: it's real!)". engadget.com. Retrieved 10 December 2012.
External links
- Official website
- Jolla smartfon prototype and Sailfish OS presentation by Chief Designer Martin Schüle, 2013
- Sailfish OS wiki - almost everything about the Sailfish OS and related subjects
- FAQ about Jolla & Sailfish OS
- Jolla to launch Sailfish OS Smartphone in India on September 23
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||