John F. Kurtzke
| John Kurtzke | |
|---|---|
 John Kurtzke Veteran Admin | |
| Fields | Neurology, Neuroepidemiology |
| Institutions | Georgetown University |
| Alma mater | Weill Cornell Medical College |
| Known for | Expanded Disability Status Scale |
| Notable awards | 1999 Charcot Award, 1997 Dystel Prize |
John Kurtzke is a pioneering neuroepidemiologist and Professor of Neurology at Georgetown University who is best known for his creation of the Expanded Disability Status Scale and for his research on multiple sclerosis (MS).
After graduating from Cornell University Medical College in 1952, Dr. Kurtzke started his career in the field of neurology as Chief of the Neurology Service at the Veteran’s Affairs (VA) Medical Centers in Coatesville, PA, from 1956 to 1963, and then in Washington, DC, from 1963 to 1995, where he became Professor of Neurology at Georgetown University, where he is currently Professor Emeritus.




Most of his work deals with multiple sclerosis (MS). In particular, Dr Kurtzke is widely known for his Expanded Disability Status Scale or EDSS (a method of quantifying disability in multiple sclerosis)[1] and for his pioneering work in the field of neuroepidemiology, a branch of epidemiology he helped to establish in 1967 with Dr. Len Kurland and Dr. Milton Alter.[2]
He is the leading world expert on geo-medical patterns in multiple sclerosis.[3][4][5] Kurtzke's results have played a major role in promoting the study of the viral component of MS susceptibility.[6]
The author of more than 200 peer-reviewed articles,[7][8][9] he has received several awards including the 1999 Charcot Award by the Multiple Sclerosis International Federation[10] and the 1997 Dystel prize for MS research awarded by the American Academy of neurology.[11]
In 2009, the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC) and the American Academy of Neurology Foundation (AANF) have created the John F. Kurtzke, MD, FAAN, Clinician-Scientist Development Three-Year Award, a jointly-sponsored fellowship in multiple sclerosis research, "to honor the contributions of Dr. Kurtzke and inspire new MS healthcare professionals to follow in his path."[12]
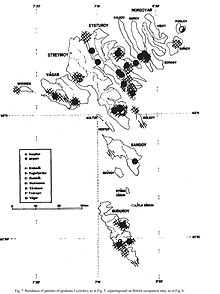
Like Klaus Lauer,[13] J. Kurtzke has dedicated a large part of his work to the study of MS in the Faroe Islands, with extensive studies dealing with the British occupation of the islands.,[14][15][16][17][18] starting what the New York Times called the MS "medical detective story".[19]
References
- ↑ Kurtzke JF (November 1983). "Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS)". Neurology 33 (11): 1444–52. doi:10.1212/WNL.33.11.1444. PMID 6685237.
- ↑ Dr V Feigin, personal communication with Dr J Kurtzke.
- ↑ http://www.direct-ms.org/pdf/GeneralInfoMS/CompstonStory.pdf[]
- ↑ http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2FBF00312546
- ↑ http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-010-9534-1_4
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22685062
- ↑ http://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/arcneu/ane-2006/ane062e.pdf
- ↑ http://www.va.gov/MS/Professionals/research/KurtzkeMonograph.pdf
- ↑ http://www.va.gov/MS/Professionals/research/Kurtzke_Slides.pdf
- ↑ http://rm2-msif-live.torchboxapps.com/en/research/msif_research_awards/the_charcot.html[]
- ↑ http://www.nationalmssociety.org/ms-clinical-care-network/researchers/get-funding/john-dystel-prize/index.aspx[]
- ↑ http://www.cmscfoundation.org/news2/press-releases/46-press-releases/125-new-multiple-sclerosis-fellowship-created-in-the-name-of-pioneer-neuroepidemiologist-john-f-kurtzke-md-faan[]
- ↑ Lauer K (1988). "Multiple sclerosis in relation to industrial and commercial activities in the Faroe Islands". Neuroepidemiology 7 (4): 228–33. doi:10.1159/000110155. PMID 3264057.
- ↑ Kurtzke JF, Hyllested K (January 1979). "Multiple sclerosis in the Faroe Islands: I. Clinical and epidemiological features". Annals of Neurology 5 (1): 6–21. doi:10.1002/ana.410050104. PMID 371519.
- ↑ Kurtzke JF, Hyllested K (1988). "Validity of the epidemics of multiple sclerosis in the Faroe Islands". Neuroepidemiology 7 (4): 190–227. doi:10.1159/000110154. PMID 3264056.
- ↑ http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1600-0404.1993.tb04211.x/abstract
- ↑ http://www.karger.jp/Article/Pdf/110917
- ↑ http://www.neurology.org/content/36/3/307.abstract
- ↑ http://www.nytimes.com/1982/06/22/science/ms-a-medical-detective-story.html
External links
- Confavreux C (June 2012). "An unchanging man faced with changing times". Brain 135 (Pt 6): 1663–5. doi:10.1093/brain/aws135. PMID 22628387.
- Feigin V, Kurtzke JF, Korczyn A, Beghi E, Brown A (2009). "Bridging the gap between experimental and non-experimental neuroepidemiology, and ultimately - between neuroepidemiological research and practice: round table discussion at the First International Congress on Clinical Neurology and Epidemiology". Neuroepidemiology 33 (4): 296–304. PMID 20443239.
- Kurtzke JF, Hyllested K (January 1979). "Multiple sclerosis in the Faroe Islands: I. Clinical and epidemiological features". Annals of Neurology 5 (1): 6–21. doi:10.1002/ana.410050104. PMID 371519.
- portrait by E. Granieri. Once on page, press "look inside" icon
- Kurtzke JF, Hyllested K, Arbuckle JD et al. (December 1988). "Multiple sclerosis in the Faroe Islands. IV. The lack of a relationship between canine distemper and the epidemics of MS". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 78 (6): 484–500. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.1988.tb03692.x. PMID 3223236.
- Audio podcast and transcript of interview by Consortium of MS centers
- Kurtzke JF (December 2002). "No creative medical science without humor". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 55 (12): 1214–7. doi:10.1016/S0895-4356(02)00530-9. PMID 12547452.
- Kurtzke JF (May 2005). "Epidemiology and etiology of multiple sclerosis". Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America 16 (2): 327–49. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2005.01.013. PMID 15893675.
- Kurtzke JF, Hyllested K, Heltberg A (May 1995). "Multiple sclerosis in the Faroe Islands: transmission across four epidemics". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 91 (5): 321–5. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.1995.tb07015.x. PMID 7639059.
- One of the first papers of Kurtzke (1954)
- Wallin MT, Culpepper WJ, Coffman P et al. (June 2012). "The Gulf War era multiple sclerosis cohort: age and incidence rates by race, sex and service". Brain 135 (Pt 6): 1778–85. doi:10.1093/brain/aws099. PMID 22628389.
- Kurtzke JF (September 2013). "Epidemiology in multiple sclerosis: a pilgrim's progress". Brain 136 (Pt 9): 2904–17. doi:10.1093/brain/awt220. PMID 23983034.
- Börü UT, Taşdemir M, Güler N et al. (2011). "Prevalence of multiple sclerosis: door-to-door survey in three rural areas of coastal Black Sea regions of Turkey". Neuroepidemiology 37 (3-4): 231–5. doi:10.1159/000334316. PMID 22133733.
- Kurtzke JF (May 2000). "Multiple sclerosis in time and space--geographic clues to cause". Journal of Neurovirology. 6 Suppl 2: S134–40. PMID 10871801.
- Kurtzke JF (2011). "On the prevalence of multiple sclerosis in Serbia". Neuroepidemiology 37 (2): 107–8. doi:10.1159/000331234. PMID 21921644.
- Kurtzke JF, Hyllested K (1988). "Validity of the epidemics of multiple sclerosis in the Faroe Islands". Neuroepidemiology 7 (4): 190–227. doi:10.1159/000110154. PMID 3264056.
- Boström I, Callander M, Kurtzke JF, Landtblom AM (November 2009). "High prevalence of multiple sclerosis in the Swedish county of Värmland". Multiple Sclerosis (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) 15 (11): 1253–62. doi:10.1177/1352458509345909. PMID 19805442.
- Wallin MT, Page WF, Kurtzke JF (September 2009). "Migration and multiple sclerosis in Alaskan military veterans". Journal of Neurology 256 (9): 1413–7. doi:10.1007/s00415-009-5123-5. PMID 19377862.
- Cabrera-Gómez JA, Kurtzke JF, González-Quevedo A, Lara-Rodríguez R (January 2009). "An epidemiological study of neuromyelitis optica in Cuba". Journal of Neurology 256 (1): 35–44. doi:10.1007/s00415-009-0009-0. PMID 19224310.
- Kurtzke JF (October 1993). "Epidemiologic evidence for multiple sclerosis as an infection". Clinical Microbiology Reviews 6 (4): 382–427. doi:10.1128/CMR.6.4.382. PMC 358295. PMID 8269393.
- Kurtzke JF (2008). "Historical and clinical perspectives of the expanded disability status scale". Neuroepidemiology 31 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1159/000136645. PMID 18535394.
- Wallin MT, Page WF, Kurtzke JF (January 2004). "Multiple sclerosis in US veterans of the Vietnam era and later military service: race, sex, and geography". Annals of Neurology 55 (1): 65–71. doi:10.1002/ana.10788. PMID 14705113.
- Kurtzke JF, Heltberg A (January 2001). "Multiple sclerosis in the Faroe Islands: an epitome". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 54 (1): 1–22. doi:10.1016/S0895-4356(00)00268-7. PMID 11165464.
- Rasmussen HB, Kvinesdal BB, Clausen J (July 1992). "Seroreactivity to human T cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type 1 and related retroviruses in multiple sclerosis patients from Denmark and the Faroes". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 86 (1): 91–4. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.1992.tb08061.x. PMID 1325731.
- Kurtzke JF, Hyllested K (March 1986). "Multiple sclerosis in the Faroe Islands. II. Clinical update, transmission, and the nature of MS". Neurology 36 (3): 307–28. doi:10.1212/wnl.36.3.307. PMID 3951697.
- Kurtzke JF, Hyllested K (1978). "Multiple sclerosis in the Faroes: 1. Clinical and epidemiologic features". Transactions of the American Neurological Association 103: 201–5. PMID 757058.