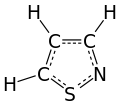
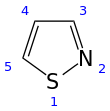
Isothiazole
| |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 288-16-4 | |||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:35600 | ||
| ChemSpider | 60838 | ||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| PubChem | 67515 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Molecular formula |
C3H3NS | ||
| Molar mass | 85.13 g·mol−1 | ||
| Boiling point | 114 °C (237 °F; 387 K)[1] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | -0.5 (of conjugate acid) [2] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds |
thiazole, isoxazole | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
An isothiazole, or 1,2-thiazole, is a type of organic compound containing a five-membered aromatic ring that consists of three carbon atoms, one nitrogen atom, and one sulfur atom.[3] Isothiazole is a member of a class of compounds known as azoles. In contrast to the isomeric thiazole, the two heteroatoms are in adjacent positions.
The ring structure of isothiazole is incorporated into larger compounds with biological activity such as the pharmaceutical drugs ziprasidone and perospirone.
References
- ↑ Isothiazoles, D. W. Brown and M. Sainsbury, page 513
- ↑ Zoltewicz, J. A. & Deady, L. W. Quaternization of heteroaromatic compounds. Quantitative aspects. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 22, 71-121 (1978).
- ↑ Heterocyclic Chemistry, 3rd Edition, J.A. Joule, K. Mills, and G.F. Smith, page 394