Iron(III) phosphate
 | |
-phosphate-pentahydrate-sample.jpg) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Iron(III) phosphate | |
| Other names
Ferric orthophosphate, Ferric phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 10045-86-0 (anhydrous) 13463-10-0 (dihydrate) | |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 24861 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
FeO4P |
| Molar mass | 150.82 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow-brown solid |
| Density | 3.056 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.87 g/cm3 (20 °C, dihydrate) |
| Melting point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) (dihydrate) decomposes[1] |
| anhydrous: insoluble dihydrate: 0.642 g/100 mL (100 °C)[1] | |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Specific heat capacity (C) |
180.5 J/mol·K (dihydrate)[1] |
| Std molar entropy (S |
171.3 J/mol·K (dihydrate)[1] |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
-1888 kJ/mol (dihydrate)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  [2] [2] |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335[2] | |
| P261, P305+351+338[2] | |
| EU classification | |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26, S36 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Iron(III) phosphate is the inorganic compound with the formula FePO4. Several related materials are known, including four polymorphs of FePO4 and two polymorphs of the dihydrate FePO4·(H2O)2. These materials find several technical applications as well as occurring in the mineral kingdom.[3][4]
Structure
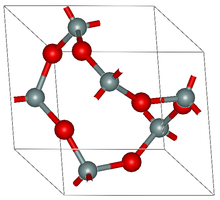
The most common form of FePO4 adopts the structure of α-quartz. As such the P and Fe have tetrahedral molecular geometry. At high pressures, a phase change occurs to a more dense structure with octahedral Fe centres. Two orthorhombic structures and a monoclinic phase are also known. In the two polymorphs of the dihydrate, the Fe center is octahedral with two mutually cis water ligands.[5]
Uses
Iron(III) phosphate is one of the few molluscicides approved for use in the practice of organic farming.[6] Unlike the older metaldehyde, it is non-toxic to pets and wildlife.
It can be used in steel and metal manufacturing processes. When bonded to a metal surface, iron phosphate prevents further oxidation of the metal. Its presence is partially responsible for the corrosion resistance of the Iron pillar of Delhi.
Iron phosphate coatings are also primarily used as base coatings for paint in order to increase adhesion to the iron or steel substrate, and is often used in rustproofing as well. It can also be used for bonding fabrics, wood, and other materials to these surfaces as well. Iron phosphate coatings are usually applied as part of a painting or powder coating process.
Iron phosphate can also be used as an intercalation electrode in a lithium-ion battery despite having low electronic conductivity. However, in recent years its use as an electrode material has been increasingly more common as materials engineers have overcome the electronic conductivity issue. FePO4 is an ideal electrode material for batteries in electric vehicles due to its thermal stability and generally good cyclability.
Interestingly, as of 3/20/15, Ferric Orthophosphate is listed as an ingredient in Carolina Enriched Rice, Extra Long Grain. "Ingredients: Enriched Long Grain Rice [Rice, Niacin, Iron (Ferric Orthophosphate), Thiamin (Thiamin Mononitrate), Folic Acid]." Questions? Comments? Call 1-800-226-9522. Riviana Foods, Houston, Texas 77019[7]
Legislation
Iron(III) phosphate is not allowed as food additive in European Union. It was withdrawn from the list of allowed substances in the directive 2002/46/EC in 2007.
Safety
Can cause eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. May be harmful if swallowed. Avoid inhalation of dusts.
See also
- Iron(II) phosphate, the lower phosphate of iron
- Lithium iron phosphate battery, a battery that uses iron phosphate
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "iron(III) phosphate dihydrate". chemister.ru. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Sigma-Aldrich Co., Iron(III) phosphate dihydrate. Retrieved on 2014-05-03.
- ↑ Roncal-Herrero, T., Rodriguez-Blanco, J.D., Benning, L.G., Oelkers, E.H. (2009) Precipitation of Iron and Aluminum Phosphates Directly from Aqueous Solution as a Function of Temperature from 50 to 200°C. Crystal Growth & Design, 9, 5197-5205. doi: 10.1021/cg900654m.
- ↑ Song, Y.; Zavalij, P. Y.; Suzuki, M.; Whittingham, M. S. (2002). "New Iron(III) Phosphate Phases: Crystal Structure and Electrochemical and Magnetic Properties" (PDF). Inorganic Chemistry 41 (22): 5778–5786. doi:10.1021/ic025688q. PMID 12401083. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ↑ Zaghib, K.; Julien, C. M. (2005-01). "Structure and electrochemistry of FePO4·2H2O hydrate". Journal of Power Sources 142: 279–284. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.09.042. Retrieved 3 July 2014. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 889/2008". European Union law. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ↑ See 32oz. Package Carolina Rice
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Iron(III) phosphate. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||