Iota Leonis
| |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Leo |
| Right ascension | 11h 23m 55.45273s[1] |
| Declination | +10° 31′ 46.2195″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.00[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F3 V[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.420[4] |
| B−V color index | +0.456[4] |
| Variable type | Suspected[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −10.3[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +141.45[1] mas/yr Dec.: −79.14[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 41.26 ± 1.16[1] mas |
| Distance | 79 ± 2 ly (24.2 ± 0.7 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.62−1.70[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.1[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 11.5[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.98[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,739[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.06[9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 16[7] km/s |
| Age | 1.7[7] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
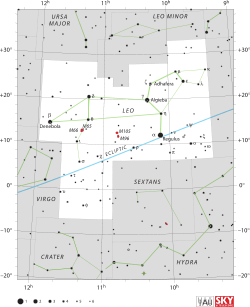
Iota Leonis is a star in the constellation Leo.
It was known as 太微右垣三, "the Third (Star) of the Right Wall of the Supreme Palace Enclosure" or 次將 (Tsze Tseang, Mandarin cìjiàng), "the Vice-General", in traditional Chinese astronomy[10]
Iota Leonis is of stellar classification F3 V and apparent visual magnitude +3.94. It is a spectroscopic binary, which means it is a binary star with components that are too close together to be able to resolve individually through a telescope.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 van Leeuwen, Floor (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752v1, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357 Note: see VizieR catalogue I/311.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "iot Leo -- Spectroscopic binary". SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2010-04-07.
- ↑ Abt, Helmut A. (January 2009), "MK Classifications of Spectroscopic Binaries", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 180 (1): 117–118, Bibcode:2009ApJS..180..117A, doi:10.1088/0067-0049/180/1/117
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Rufener, F. (October 1976). "Second catalogue of stars measured in the Geneva Observatory photometric system". Astronomy & Astrophysics Supplement Series 26: 275–351. Bibcode:1976A&AS...26..275R.
- ↑ Kukarkin, B. V. et al. (1981). Nachrichtenblatt der Vereinigung der Sternfreunde e.V. (Catalogue of suspected variable stars). Moscow, Academy of Sciences USSR Shternberg. Bibcode:1981NVS...C......0K.
- ↑ Wilson, R. E. (1953). General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocities. Washington D.C.: Carnegie Institute. Bibcode:1953GCRV..C......0W. Retrieved 2009-10-24.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Bi, S.-L.; Basu, Sarbani; Li, L.-H. (February 2008). "Seismological Analysis of the Stars γ Serpentis and ι Leonis: Stellar Parameters and Evolution". The Astrophysical Journal 673 (2): 1093–1105. Bibcode:2008ApJ...673.1093B. doi:10.1086/521575.
- ↑ Malagnini, M. L.; Morossi, C. (November 1990), "Accurate absolute luminosities, effective temperatures, radii, masses and surface gravities for a selected sample of field stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 85 (3): 1015–1019, Bibcode:1990A&AS...85.1015M
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Balachandran, Suchitra (May 1, 1990). "Lithium depletion and rotation in main-sequence stars". Astrophysical Journal, Part 1 354: 310–332. Bibcode:1990ApJ...354..310B. doi:10.1086/168691.
- ↑ Richard Hinckley Allen: Star Names — Their Lore and Meaning: Leo
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||