Interstate 155 (Illinois)
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by Illinois DOT | ||||
| Length: | 32.13 mi[1] (51.71 km) | |||
| Existed: |
December 15, 1989 – I-55 to Hartsburg[2] October 29, 1992 – Full opening[3] – present | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| South end: |
| |||
|
| ||||
| North end: |
| |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
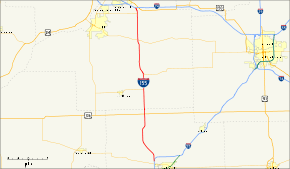
Interstate 155 (I-155) is a north–south spur of Interstate 55 that provides an interstate connection for the Illinois cities of Peoria and Lincoln. The northern terminus for the interstate is just east of Peoria, at Interstate 74 exit 101 in Morton. The southern terminus, which is northwest of Lincoln, is located on I-55 at exit 127. The interstate is 32.13 miles (51.71 km) long.[1]
I-155 was created to replace Illinois Route 121 (abbreviated IL 121). Prompted by safety concerns at a major intersection near Morton, state transportation officials replaced the entire route with a limited-access freeway. The interstate was built in several segments from 1970 to 1992, a period that included a ten-year delay due to a lawsuit over right-of-way. I-155 fully opened to traffic on October 29, 1992.[2][3]
Route description

Interstate 155 runs north from Interstate 55 just northwest of Lincoln, intersecting U.S. Route 136 east of Emden. 5 miles (8 km) north of U.S. 136, eastbound Illinois Route 122 joins I-155 traveling north, directly east of Delavan. The two highways run concurrent for 4 miles (6 km) before Illinois 122 runs east to Hopedale. Further north, the highway crosses the Mackinaw River beside a steel truss bridge serving old Illinois Route 121.[4]
East of Tremont, I-155 intersects Illinois Route 9. 4 miles (6 km) later is Main Street, the first of three northbound exits to Morton. (There are only two southbound exits, at Queenwood Road and Illinois Route 98 – Birchwood Street). The highway passes to the west of Morton before intersecting Interstate 74 at a trumpet interchange about 8 miles (13 km) southeast of downtown Peoria.[4]
Surrounded mostly by prime land used for farming soybeans and corn, Interstate 155 is a four-lane freeway through rural central Illinois. In addition to Morton, Peoria, and Lincoln, I-155 also serves a number of small farm towns located between Peoria and Lincoln. The largest city directly served by I-155 is Tremont; however, the highway mainly carries traffic traveling to and from Peoria and Springfield.[5]
History
I-155 was built on the right-of-way of former IL 121. In the early 1960s, the department of transportation opened IL 98, an east–west two-lane highway running west from downtown Morton to Pekin. Within a few years, the intersection of IL 98 and IL 121 would be known as the "Killer Corner," as traffic volumes increased between Springfield and Peoria on IL 121. Between when IL 98 was opened and when the corner was closed in 1989 for construction of a full interchange, 15 people were killed as a result of automobile accidents at the corner.[3] Led by key supporters—U.S. Representative Robert Michel, former Illinois Department of Transportation (IDOT) transportation engineer Jack Harland, and pro-freeway organization "Route 121 by '91" chairman Jim Unland—IDOT initiated plans to upgrade IL 121 to a four-lane freeway.[5] Near Hopedale, a short portion of IL 121 was reconstructed in the early 1970s to replace a bridge over the Mackinaw River. The interchange with I-55 was built, but barricaded to traffic.
In 1976, an injunction won by Peoria attorney Timothy Swain Sr. halted further construction on the highway for ten years.[2][5] The lawsuit was filed by Swain regarding the amount of right-of-way the freeway would consume on his 440 acre (178 hectare) farm near Delavan. A U.S. District Court judge sided with IDOT on building the road, but the U.S. Seventh District Court of Appeals overturned the decision, forcing IDOT to rewrite its environmental impact statement regarding the Swain farm. In 1986 IDOT struck a deal with Swain, agreeing to reroute the road and take only 40 acres (16 hectares) of land, ending the lawsuit and resuming construction activities.[5] A portion of the road from I-55 to Hartsburg opened on December 15, 1989, about 7 miles (11 km) in length.[2] The freeway was opened in full on October 29, 1992, at a ceremony attended by Governor Jim Edgar.[3] The total cost of construction for I-155 was US$130 million.[2] Of this, $10 million was provided by federal funding.[5]
Illinois initially applied for the new freeway to be designated Interstate 37, but on December 7, 1990, the request was deferred by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO), pending approval by the Federal Highway Administration to add the freeway into the Interstate System. In addition, AASHTO suggested using a 3-digit number when the application was resubmitted.[6] Later, the state submitted another application to AASHTO for the freeway to be named Interstate 155. On June 9, 1991, the AASHTO application was approved and granted when Interstate 155 was completed.[7]
Exit list
| County | Location | mi[1] | km | Exit | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logan | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0 | Southbound exit and northbound entrance; signed as exits 0A (south) and 0B (north) | ||
| 6.04 | 9.72 | 6 | Hartsburg | |||
| 10.25 | 16.50 | 10 | ||||
| Tazewell | 15.26 | 24.56 | 15 | South end of IL 122 overlap | ||
| 18.48 | 29.74 | 19 | North end of IL 122 overlap | |||
| 22.41 | 36.07 | 22 | Townline Road | |||
| Tremont | 25.52 | 41.07 | 25 | |||
| 28.46 | 45.80 | 28 | Broadway Road | |||
| Morton | 29.19 | 46.98 | 29 | Main Street | Northbound exit and southbound entrance | |
| 30.26 | 48.70 | 30 | Queenwood Road | Southbound exit and northbound entrance | ||
| 30.97 | 49.84 | 31 | ||||
| 32.13 | 51.71 | — | Northbound exit and southbound entrance | |||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| ||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Illinois Technology Transfer Center (2006). "T2 GIS Data". Retrieved 2007-11-08.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Finke, Doug (1989-12-16). "Cold it was, but finally open". The State Journal-Register (Springfield, IL).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Smothers, Michael (1992-10-30). "31-mile superhighway opens after 30-year drive for safer road". Peoria Journal-Star.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Google Maps". Google. 2009-04-21. Retrieved 2009-04-21.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Williams, Christopher R. (1992-10-25). "Freeway's rocky success story: Four-lane link finally done, but it wasn't easy". Peoria Journal-Star. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- ↑ American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (1990-12-07). "Route Numbering Committee Agenda" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-12-24.
- ↑ American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (1991-06-09). "Route Numbering Committee Agenda" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-12-24.
Route map: Bing
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||
