International System of Units
- For a topical guide to this subject, see Outline of the metric system.

The International System of Units (French: Système International d'Unités, SI) is the modern form of the metric system and is the world's most widely used system of measurement, used in both commerce and science. It comprises a coherent system of units of measurement built on seven base units. It defines twenty-two named units, and includes many more unnamed coherent derived units. The system also establishes a set of twenty prefixes to the unit names and unit symbols that may be used when specifying multiples and fractions of the units.
The system was published in 1960 as the result of an initiative that started in 1948. It is based on the metre-kilogram-second system of units (MKS) rather than any variant of the centimetre–gram–second system (CGS). SI is intended to be an evolving system, so prefixes and units are created and unit definitions are modified through international agreement as the technology of measurement progresses and the precision of measurements improves. The 25th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in 2014, for example, discussed a proposal to change the definition of the kilogram.[1]
The motivation for the development of the SI was the diversity of units that had sprung up within the CGS systems and the lack of coordination between the various disciplines that used them. The CGPM, which was established by the Metre Convention of 1875, brought together many international organizations to not only agree on the definitions and standards of the new system but also agree rules on writing and presenting measurements in a standardised manner around the world.
The International System of Units has been adopted by most developed countries, however, the adoption has not been universal in all English-speaking countries. While metrication in the United States is consistent in science, medicine, government, and various fields of technology and engineering, common measurements are mostly performed in customary units, although these have officially been defined in terms of SI units. The United Kingdom has officially adopted a policy of partial metrication, with no intention of replacing imperial units entirely. Canada has adopted the SI for most governmental, medical and scientific purposes and for such varied uses as grocery weights, weather reports, traffic signs and gasoline sales, but imperial units are still legally permitted and remain in common use throughout many sectors of Canadian society, particularly in the building trade and the railway sector.
History

The metric system was first implemented during the French Revolution (1790s) with just the metre and kilogram as standards of length and mass[Note 1] respectively. In the 1830s Carl Friedrich Gauss laid the foundations for a coherent system based on length, mass and time. In the 1860s a group working under the auspices of the British Association for the Advancement of Science formulated the requirement for a coherent system of units with base units and derived units. The inclusion of electrical units into the system was hampered by the customary use of more than one set of units, until 1900 when Giovanni Giorgi identified the need to define one single electrical quantity as a fourth base quantity alongside the original three base quantities.
Meanwhile, in 1875, the Treaty of the Metre passed responsibility for verification of the kilogram and metre against agreed prototypes from French to international control. In 1921 the Treaty was extended to include all physical quantities including electrical units originally defined in 1893.
In 1948 an overhaul of the metric system was set in motion which resulted in the development of the "Practical system of units" which, on its publication in 1960, was given the name "The International System of Units". In 1954 the 10th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) identified electric current as the fourth base quantity in the practical system of units and added two more base quantities—temperature and luminous intensity—making six base quantities in all. The units associated with these quantities were the metre, kilogram, second, ampere, kelvin and candela. In 1971 a seventh base quantity, amount of substance represented by the mole, was added to the definition of SI.
Early development
The metric system was developed from 1791 onwards by a committee of the French Academy of Sciences, commissioned by the National Assembly and Louis XVI to create a unified and rational system of measures.[4] The group, which included Antoine Lavoisier (the "father of modern chemistry") and the mathematicians Pierre-Simon Laplace and Adrien-Marie Legendre,[5]:89 used the same principles for relating length, volume and mass that had been proposed by the English clergyman John Wilkins in 1668[6][7] and the concept of using the Earth's meridian as the basis of the definition of length, originally proposed in 1670 by the French abbot Mouton.[8][9]
On 30 March 1791, the Assembly adopted the committee's proposed principles for the new decimal system of measure and authorized a survey between Dunkirk and Barcelona to establish the length of the meridian. On 11 July 1792, the committee proposed the names metre, are, litre and grave for the units of length, area, capacity and mass, respectively. The committee also proposed that multiples and submultiples of these units were to be denoted by decimal-based prefixes such as centi for a hundredth and kilo for a thousand.[10]:82
The law of 7 April 1795 (loi du 18 germinal) defined the terms gramme and kilogramme, which replaced the former terms gravet (correctly milligrave) and grave, and on 22 June 1799 (after Pierre Méchain and Jean-Baptiste Delambre had completed the meridian survey) the definitive standard mètre des Archives and kilogramme des Archives were deposited in the Archives nationales. On 10 December 1799 (a month after Napoleon's coup d'état), the law by which the metric system was to be definitively adopted in France (loi du 19 frimaire[16]) was passed.[17]
During the first half of the nineteenth century there was little consistency in the choice of preferred multiples of the base units – typically the myriametre (10000 metres) was in widespread use in both France and parts of Germany, while the kilogram (1000 grams) rather than the myriagram was used for mass.[2]
In 1832, the German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss, assisted by Wilhelm Weber, implicitly defined the second as a base unit when he quoted the earth's magnetic field in terms of millimetres, grams, and seconds.[11] Prior to this, the strength of the earth’s magnetic field had only been described in relative terms. The technique used by Gauss was to equate the torque induced on a suspended magnet of known mass by the earth’s magnetic field with the torque induced on an equivalent system under gravity. The resultant calculations enabled him to assign dimensions based on mass, length and time to the magnetic field.[18]
In the 1860s James Clerk Maxwell, William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) and others working under the auspices of the British Association for the Advancement of Science, built on Gauss' work and formalised the concept of a coherent system of units with base units and derived units. The principle of coherence was successfully used to define a number of units of measure based on the centimetre–gram–second (CGS) system of units (CGS), including the erg for energy, the dyne for force, the barye for pressure, the poise for dynamic viscosity and the stokes for kinematic viscosity.[14]
Metre Convention
| CGPM Vocabulary | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A French-inspired initiative for international cooperation in metrology led to the signing in 1875 of the Metre Convention.[5]:353–354 Initially the convention only covered standards for the metre and the kilogram. A set of 30 prototypes of the metre and 40 prototypes of the kilogram,[Note 3] in each case made of a 90% platinum-10% iridium alloy, were manufactured by the British firm Johnson, Matthey & Co and accepted by the CGPM in 1889. One of each was selected at random to become the International prototype metre and International prototype kilogram that replaced the mètre des Archives and kilogramme des Archives respectively. Each member state was entitled to one of each of the remaining prototypes to serve as the national prototype for that country.[20]
The treaty established three international organisations to oversee the keeping of international standards of measurement:[21]
- General Conference on Weights and Measures (Conférence générale des poids et mesures or CGPM) – a meeting every four to six years of delegates from all member states that receives and discusses a report from the CIPM and that endorses new developments in the SI on the advice of the CIPM.
- International Committee for Weights and Measures (Comité international des poids et mesures or CIPM) – a committee that meets annually at the BIPM and is made up of eighteen individuals of high scientific standing, nominated by the CGPM to advise the CGPM on administrative and technical matters
- International Bureau of Weights and Measures (Bureau international des poids et mesures or BIPM) – an international metrology centre at Sèvres in France that has custody of the International prototype kilogram, provides metrology services for the CGPM and CIPM, houses the secretariat for these organisations and hosts their formal meetings. Initially its prime metrological purpose was a periodic recalibration of national prototype metres and kilograms against the international prototype.
In 1921 the Metre Convention was extended to include all physical units, including the ampere and others defined by the Fourth International Conference of Electricians in Chicago in 1893, thereby enabling the CGPM to address inconsistencies in the way that the metric system had been used.[12][22]:96
The official language of the Metre Convention is French[23] and the definitive version of all official documents published by or on behalf of the CGPM is the French-language version.[22]:94
Towards the SI
At the close of the 19th century three different systems of units of measure existed for electrical measurements: a CGS-based system for electrostatic units, also known as the Gaussian or ESU system, a CGS-based system for electromechanical units (EMU) and an MKS-based system ("international system")[24] for electrical distribution systems. Attempts to resolve the electrical units in terms of length, mass and time using dimensional analysis was beset with difficulties—the dimensions depended on whether one used the ESU or EMU systems.[15] This anomaly was resolved in 1900 when Giovanni Giorgi published a paper in which he advocated using a fourth base unit alongside the existing three base units. The fourth unit could be chosen to be electric current , voltage, or electrical resistance.[25]
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries a number of non-coherent units of measure based on the gram/kilogram, the centimetre/metre and the second, such as the Pferdestärke (metric horsepower) for power,[26][Note 4] the darcy for permeability[27] and the use of "millimetres of mercury" for the measurement of both barometric and blood pressure were developed or propagated, some of which incorporated standard gravity in their definitions.
At the end of the Second World War, a number of different systems of measurement were in use throughout the world. Some of these systems were metric system variations, whereas others were based on customary systems of measure. In 1948, after representations by the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) and by the French Government, the 9th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) asked the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM) to conduct an international study of the measurement needs of the scientific, technical, and educational communities and "to make recommendations for a single practical system of units of measurement, suitable for adoption by all countries adhering to the Metre Convention".[28]
On the basis of the findings of this study, the 10th CGPM in 1954 decided that an international system should be derived from six base units to provide for the measurement of temperature and optical radiation in addition to mechanical and electromagnetic quantities. Six base units were recommended: the metre, kilogram, second, ampere, degree Kelvin (later renamed kelvin), and candela. In 1960, the 11th CGPM named the system the International System of Units, abbreviated SI from the French name, Le Système International d'Unités.[22]:110[29] The BIPM has also described SI as "the modern metric system".[22]:95 The seventh base unit, the mole, was added in 1971 by the 14th CGPM.[30]
International System of Quantities
The International System of Quantities defines the quantities that are measured using SI units.
SI Brochure and conversion factors

The CGPM publishes a brochure which defines and presents SI.[22] Its official version is in French, in line with the Metre Convention.[22]:102 It leaves some scope for local interpretation, particularly regarding names and terms in different languages, so for example the United States' National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has produced a version of the CGPM document (NIST SP 330) which clarifies local interpretation for English-language publications that use American English[31] and another document (NIST SP 811) that gives general guidance for the use of SI in the United States and conversion factors between SI and customary units.[32]
The writing and maintenance of the CGPM brochure is carried out by one of the committees of the International Committee for Weights and Measures (CIPM), the Consultative Committee for Units (CCU). The CIPM nominates the chairman of this committee, but the committee includes representatives of various other international bodies rather than CIPM or CGPM nominees.[33][Note 5] This committee thus provides a forum for the bodies concerned to provide input to the CIPM in respect of ongoing enhancements to SI.
The definitions of the terms "quantity", "unit", "dimension" etc. that are used in the SI Brochure are those given in the International vocabulary of metrology, a publication produced by the Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology (JCGM), a working group consisting of eight international standards organisations under the chairmanship of the director of the BIPM.[34] The quantities and equations that define the SI units are now referred to as the International System of Quantities (ISQ), and are set out in the International Standard ISO/IEC 80000 Quantities and Units.
Units and prefixes
The International System of Units consists of a set of base units, a set of derived units with special names, and a set of decimal-based multipliers that are used as prefixes. The term SI Units covers all three categories, but the term coherent SI units includes only base units and coherent derived units.[22]:103–106
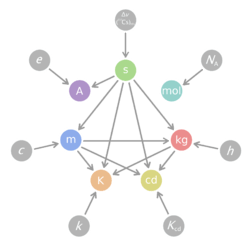
Base units
The SI base units are the building blocks of the system and all other units are derived from them. When Maxwell first introduced the concept of a coherent system, he identified three quantities that could be used as base units: mass, length and time. Giorgi later identified the need for an electrical base unit. Theoretically any one of electrical current, potential difference, electrical resistance, electrical charge or a number of other quantities could have provided the base unit, with the remaining units then being defined by the laws of physics. In the event, the unit of electric current was chosen for SI. Another three base units (for temperature, substance and luminous intensity) were added later.
| Unit name |
Unit symbol |
Quantity name |
Definition (Incomplete)[n 1] | Dimension symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| metre | m | length |
|
L |
| kilogram[n 2] | kg | mass |
|
M |
| second | s | time |
|
T |
| ampere | A | electric current |
|
I |
| kelvin | K | thermodynamic temperature |
|
Θ |
| mole | mol | amount of substance |
|
N |
| candela | cd | luminous intensity |
|
J |
The original definitions of the various base units in the above table were made by the following authorities:
All other definitions result from resolutions by either CGPM or the CIPM and are catalogued in the SI Brochure. | ||||
Derived units
The derived units in the SI are formed by powers, products or quotients of the base units and are unlimited in number.[22]:103[31]:3 Derived units are associated with derived quantities, for example velocity is a quantity that is derived from the base quantities of time and length, so in SI the derived unit is metres per second (symbol m/s). The dimensions of derived units can be expressed in terms of the dimensions of the base units.
Coherent units are derived units that contain no numerical factor other than 1—quantities such as standard gravity and density of water are absent from their definitions. In the example above, one newton is the force required to accelerate a mass of one kilogram by one metre per second squared. Since the SI units of mass and acceleration are kg and m⋅s−2 respectively and F ∝ m × a, the units of force (and hence of newtons) is formed by multiplication to give kg⋅m⋅s−2. Since the newton is part of a coherent set of units, the constant of proportionality is 1.
For the sake of convenience, some derived units have special names and symbols.[13] Such units may themselves be used in combination with the names and symbols for base units and for other derived units to express the units of other derived quantities. For example, the SI unit of force is the newton (N), the SI unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa)—and the pascal can be defined as "newtons per square metre" (N/m2).[38]
| Name | Symbol | Quantity | Expressed in terms of other SI units |
Expressed in terms of SI base units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| radian | rad | angle | m⋅m−1 | |
| steradian | sr | solid angle | m2⋅m−2 | |
| hertz | Hz | frequency | s−1 | |
| newton | N | force, weight | kg⋅m⋅s−2 | |
| pascal | Pa | pressure, stress | N/m2 | kg⋅m−1⋅s−2 |
| joule | J | energy, work, heat | N⋅m | kg⋅m2⋅s−2 |
| watt | W | power, radiant flux | J/s | kg⋅m2⋅s−3 |
| coulomb | C | electric charge or quantity of electricity | s⋅A | |
| volt | V | voltage (electrical potential difference), electromotive force | W/A | kg⋅m2⋅s−3⋅A−1 |
| farad | F | electric capacitance | C/V | kg−1⋅m−2⋅s4⋅A2 |
| ohm | Ω | electric resistance, impedance, reactance | V/A | kg⋅m2⋅s−3⋅A−2 |
| siemens | S | electrical conductance | A/V | kg−1⋅m−2⋅s3⋅A2 |
| weber | Wb | magnetic flux | V⋅s | kg⋅m2⋅s−2⋅A−1 |
| tesla | T | magnetic field strength | Wb/m2 | kg⋅s−2⋅A−1 |
| henry | H | inductance | Wb/A | kg⋅m2⋅s−2⋅A−2 |
| degree Celsius | °C | temperature relative to 273.15 K | K | |
| lumen | lm | luminous flux | cd⋅sr | cd |
| lux | lx | illuminance | lm/m2 | m−2⋅cd |
| becquerel | Bq | radioactivity (decays per unit time) | s−1 | |
| gray | Gy | absorbed dose (of ionizing radiation) | J/kg | m2⋅s−2 |
| sievert | Sv | equivalent dose (of ionizing radiation) | J/kg | m2⋅s−2 |
| katal | kat | catalytic activity | s−1⋅mol | |
| Notes 1. The radian and steradian, once given special status, are now considered dimensionless derived units.[31]:3 2. The ordering of this table is such that any derived unit is based only on base units or derived units that precede it in the table. | ||||
Prefixes
Prefixes are added to unit names to produce multiple and sub-multiples of the original unit. All multiples are integer powers of ten, and above a hundred or below a hundredth all are integer powers of a thousand. For example, kilo- denotes a multiple of a thousand and milli- denotes a multiple of a thousandth, so there are one thousand millimetres to the metre and one thousand metres to the kilometre. The prefixes are never combined, so for example a millionth of a metre is a micrometre, not a millimillimetre. Multiples of the kilogram are named as if the gram were the base unit, so a millionth of a kilogram is a milligram, not a microkilogram.[22]:122[32]:14
| Multiples | Prefix name | deca | hecto | kilo | mega | giga | tera | peta | exa | zetta | yotta | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prefix symbol | da | h | k | M | G | T | P | E | Z | Y | ||
| Factor | 100 | 101 | 102 | 103 | 106 | 109 | 1012 | 1015 | 1018 | 1021 | 1024 | |
| Fractions | Prefix name | deci | centi | milli | micro | nano | pico | femto | atto | zepto | yocto | |
| Prefix symbol | d | c | m | μ | n | p | f | a | z | y | ||
| Factor | 100 | 10−1 | 10−2 | 10−3 | 10−6 | 10−9 | 10−12 | 10−15 | 10−18 | 10−21 | 10−24 | |
Non-SI units accepted for use with SI
Although, in theory, SI can be used for any physical measurement, the CIPM has recognized that some non-SI units still appear in the scientific, technical, and commercial literature, and will continue to be used for many years to come. In addition, certain other units are so deeply embedded in the history and culture of the human race that they will continue to be used for the foreseeable future. The CIPM has catalogued several such units and published them in the SI Brochure so that their use may be consistent around the world. These units have been grouped as follows:[22]:123–129[32]:7–11 [Note 6]
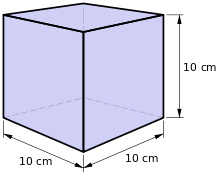
Being one thousandth of a cubic metre, the litre is not a coherent unit of measure with respect to SI.
- Non-SI units accepted for use with the SI (Table 6):
- Certain units of time, angle, and legacy non-SI metric units have a long history of consistent use. Most of mankind has used the day and its non-decimal subdivisions as a basis of time and, unlike the foot or the pound, these were the same regardless of where they were being measured. The radian, being 1/2π of a revolution, has mathematical advantages but it is cumbersome for navigation, and, as with time, the units used in navigation have a large degree of consistency around the world. The tonne, litre, and hectare were adopted by the CGPM in 1879 and have been retained as units that may be used alongside SI units, having been given unique symbols. The catalogued units are
- minute, hour, day, degree of arc, minute of arc, second of arc, hectare, litre, tonne, and astronomical unit
- Non-SI units whose values in SI units must be obtained experimentally (Table 7).
- Physicists often use units of measure that are based on natural phenomena, particularly when the quantities associated with these phenomena are many orders of magnitude greater than or less than the equivalent SI unit. The most common ones have been catalogued in the SI Brochure together with consistent symbols and accepted values, but with the caveat that their physical values need to be measured.[Note 7]
- electronvolt, dalton/unified atomic mass unit, Planck constant, and electron mass
- Other non-SI units (Table 8):
- A number of non-SI units that had never been formally sanctioned by the CGPM have continued to be used across the globe in many spheres including health care and navigation. As with the units of measure in Tables 6 and 7, these have been catalogued by the CIPM in the SI Brochure to ensure consistent usage, but with the recommendation that authors who use them should define them wherever they are used.
- Non-SI units associated with the CGS and the CGS-Gaussian system of units (Table 9)
- The SI manual also catalogues a number of legacy units of measure that are used in specific fields such as geodesy and geophysics or are found in the literature, particularly in classical and relativistic electrodynamics where they have certain advantages: The units that are catalogued are:
Writing unit symbols and the values of quantities
Before 1948, the writing of metric quantities was haphazard. In 1879, the CIPM published recommendations for writing the symbols for length, area, volume and mass, but it was outside its domain to publish recommendations for other quantities. Beginning in about 1900, physicists who had been using the symbol "μ" for "micrometre" (or "micron"), "λ" for "microlitre", and "γ" for "microgram" started to use the symbols "μm", "μL" and "μg", but it was only in 1935, a decade after the revision of the Metre Convention that the CIPM formally adopted this proposal and recommended that the symbol "μ" be used universally as a prefix for 10−6.[39]
In 1948, the ninth CGPM approved the first formal recommendation for the writing of symbols in the metric system when the basis of the rules as they are now known was laid down.[40] These rules were subsequently extended by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and now cover unit symbols and names, prefix symbols and names, how quantity symbols should be written and used and how the values of quantities should be expressed.[22]:104,130 Both ISO and the IEC have published rules for the presentation of SI units that are generally compatible with those published in the SI Brochure.[41] As of August 2013 ISO and IEC were in the process of merging their standards for quantities and units into a single set of compatible documents identified as the ISO/IEC 80000 Standard. The rules covering printing of quantities and units are part of ISO 80000-1:2009.[42]
Unit names
Names of units follow the grammatical rules associated with common nouns: in English and in French they start with a lowercase letter (e.g., newton, hertz, pascal), even when the symbol for the unit begins with a capital letter. This also applies to "degrees Celsius", since "degree" is the unit.[43][44] In German, however, the names of units, as with all German nouns, start with capital letters.[45] The spelling of unit names is a matter for the guardians[Note 8] of the language concerned – the official British and American spellings for certain SI units differ – British English, as well as Australian, Canadian and New Zealand English, uses the spelling deca-, metre, and litre whereas American English uses the spelling deka-, meter, and liter, respectively.[46]
Likewise, the plural forms of units follow the grammar of the language concerned: in English, the normal rules of English grammar are used, e.g. "henries" is the plural of "henry".[47][32]:31 However, the units lux, hertz, and siemens have irregular plurals in that they remain the same in both their singular and plural form.
In English, when unit names are combined to denote multiplication of the units concerned, they are separated with a hyphen or a space (e.g. newton-metre or newton metre). The plural is formed by converting the last unit name to the plural form (e.g. ten newton-metres).
Unit names as adjectives
In English, a space is recommended between the number and the unit symbol when used as an adjective, e.g. "a 25 kg sphere".
The normal rules of English apply to unit names, where a hyphen is incorporated into the adjectival sense, e.g. "a 25-kilogram sphere".[48]
Chinese and Japanese
Chinese uses traditional logograms for writing the unit names, while in Japanese unit names are written in the phonetic katakana script; in both cases symbols are written using the internationally recognised Latin and Greek characters.
- Japanese
A set of characters representing various metric units was created in Japan in the late 19th century. Characters exist for three base units: the metre (米), litre (升) and gram (克). These were combined with a set of six prefix characters – kilo- (千), hecto- (百), deca- (十), deci- (分), centi- (厘) and milli- (毛) – to form an additional 18 single-character units. The seven length units (kilometre to millimetre), for example, are 粁, 粨, 籵, 米, 粉, 糎 and 粍. These characters, however, are not in common use today; instead, units are written out in katakana, the Japanese syllabary used for foreign borrowings, such as "キロメートル" (kiromētoru) for "kilometre". A few Sino-Japanese words for these units remain in use in Japanese, most significantly "平米" (heibei) for "square metre", but otherwise borrowed pronunciations are used.
These characters are examples of the rare phenomenon of single-character loan words – a foreign word represented by a single Japanese character – and form the plurality of such words. Similar characters were also coined for other units, such as British units, though these also have fallen out of use; see Single character gairaigo: Metric units and Single character gairaigo: Other units for a full list.
- Chinese
The basic units are metre (米 mǐ), litre (升 shēng), gram (克 kè), and second (秒 miǎo), while others include watt (瓦 wǎ). Prefixes include deci- (分 fēn), centi- (厘 lí), milli- (毫 háo), micro- (微 wēi), and kilo- (千 qiān). These are combined to form disyllabic characters, such as 厘米 límǐ "centimetre" or 千瓦 qiānwǎ "kilowatt".[49] In the 19th century various compound characters were also used, similar to Japanese, either imported or formed on the same principles, such as 瓩 for 千瓦 qiānwǎ (kilowatt) or 糎 for 厘米. These are generally not used today – for example centimetres is usually written 厘米 límǐ – but are occasionally found in older or technical writing.[50]
Unit symbols and the values of quantities
Although the writing of unit names is language-specific, the writing of unit symbols and the values of quantities is consistent across all languages and therefore the SI Brochure has specific rules in respect of writing them.[22]:130–135 The guideline produced by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)[51] clarifies language-specific areas in respect of American English that were left open by the SI Brochure, but is otherwise identical to the SI Brochure.[47]
General rules
General rules[Note 9] for writing SI units and quantities apply to text that is either handwritten or produced using an automated process:
- The value of a quantity is written as a number followed by a space (representing a multiplication sign) and a unit symbol; e.g., 2.21 kg, 7.3×102 m2, 22 K. This rule explicitly includes the percent sign (%)[22]:134 and the symbol for degrees of temperature (°C).[22]: 133 Exceptions are the symbols for plane angular degrees, minutes, and seconds (°, ′, and ″), which are placed immediately after the number with no intervening space.
- Symbols are mathematical entities, not abbreviations, and as such do not have an appended period/full stop (.), unless the rules of grammar demand one for another reason, such as denoting the end of a sentence.
- A prefix is part of the unit, and its symbol is prepended to the unit symbol without a separator (e.g., k in km, M in MPa, G in GHz). Compound prefixes are not allowed.
- Symbols for derived units formed by multiplication are joined with a centre dot (·) or a non-breaking space; e.g., N·m or N m.
- Symbols for derived units formed by division are joined with a solidus (/), or given as a negative exponent. E.g., the "metre per second" can be written m/s, m s−1, m·s−1, or m/s. Only one solidus should be used; e.g., kg/(m·s2) and kg·m−1·s−2 are acceptable, but kg/m/s2 is ambiguous and unacceptable.

Note the lowercase letters (neither "metres" nor "seconds" were named after people), the space between the value and the units, and the superscript "2" to denote "squared".
- The first letter of symbols for units derived from the name of a person is written in upper case; otherwise, they are written in lower case. E.g., the unit of pressure is named after Blaise Pascal, so its symbol is written "Pa", but the symbol for mole is written "mol". Thus, "T" is the symbol for tesla, a measure of magnetic field strength, and "t" the symbol for tonne, a measure of mass. Since 1979, the litre may exceptionally be written using either an uppercase "L" or a lowercase "l", a decision prompted by the similarity of the lowercase letter "l" to the numeral "1", especially with certain typefaces or English-style handwriting. The American NIST recommends that within the United States "L" be used rather than "l".
- Symbols of units do not have a plural form; e.g., 25 kg, not 25 kgs.
- Uppercase and lowercase prefixes are not interchangeable. E.g., the quantities 1 mW and 1 MW represent two different quantities; the former is the typical power requirement of a hearing aid (1 milliwatt or 0.001 watts), and the latter the typical power requirement of a suburban train (1 megawatt or 1000000 watts).
- The 10th resolution of CGPM in 2003 declared that "the symbol for the decimal marker shall be either the point on the line or the comma on the line." In practice, the decimal point is used in English-speaking countries and most of Asia, and the comma in most of Latin America and in continental European languages.[52]
- Spaces should be used as a thousands separator (1000000) in contrast to commas or periods (1,000,000 or 1.000.000) to reduce confusion resulting from the variation between these forms in different countries.
- Any line-break inside a number, inside a compound unit, or between number and unit should be avoided. Where this is not possible, line breaks should coincide with thousands separators.
- Since the value of "billion" and "trillion" can vary from language to language, the dimensionless terms "ppb" (parts per billion) and "ppt" (parts per trillion) should be avoided. However, no alternative is suggested in the SI Brochure.
Printing SI symbols
Further rules[Note 9] are specified in respect of production of text using printing presses, word processors, typewriters and the like.
- Symbols are written in upright (Roman) type (m for metres, s for seconds), so as to differentiate from the italic type used for quantities (m for mass, s for displacement). By consensus of international standards bodies, this rule is applied independent of the font used for surrounding text.
- In Chinese, Japanese, and Korean language computing (CJK), some of the commonly used units, prefix–unit combinations, or unit–exponent combinations have been allocated predefined single characters taking up a full square. Unicode includes these in its CJK Compatibility and letter-like symbols sub-ranges for back compatibility, without necessarily recommending future usage. These are summarised in Unicode symbols. The cursive ℓ, a letter-like symbol, has been used in a number of countries in addition to China and Japan as a symbol for the litre, but this is not currently recommended by any standards body.
- In print, the space used as a thousands separator (commonly called a thin space) is typically narrower than that used between words.
Realisation of units
Metrologists carefully distinguish between the definition of a unit and its realisation. The definition of each base unit of the SI is drawn up so that it is unique and provides a sound theoretical basis on which the most accurate and reproducible measurements can be made. The realisation of the definition of a unit is the procedure by which the definition may be used to establish the value and associated uncertainty of a quantity of the same kind as the unit. A description of the mise en pratique[Note 10] of the base units is given in an electronic appendix to the SI Brochure.[54][22]:168–169
The published mise en pratique is not the only way in which a base unit can be determined: the SI Brochure states that "any method consistent with the laws of physics could be used to realise any SI unit."[22]:111 In the current (2012) exercise to overhaul the definitions of the base units, various consultative committees of the CIPM have required that more than one mise en pratique shall be developed for determining the value of each unit. In particular:
- At least three separate experiments be carried out yielding values having a relative standard uncertainty in the determination of the kilogram of no more than 5×10−8 and at least one of these values should be better than 2×10−8. Both the Watt balance and the Avogadro project should be included in the experiments and any differences between these be reconciled.[55][56]
- When the kelvin is being determined, the relative uncertainty of the Boltzmann constant derived from two fundamentally different methods such as acoustic gas thermometry and dielectric constant gas thermometry be better than one part in 10−6 and that these values be corroborated by other measurements.[57]
Post-1960 changes
The preamble to the Metre Convention read "Desiring the international uniformity and precision in standards of weight and measure, have resolved to conclude a convention ...".[23] Changing technology has led to an evolution of the definitions and standards that has followed two principal strands – changes to SI itself and clarification of how to use units of measure that are not part of SI, but are still nevertheless used on a worldwide basis.
Changes to the SI
Since 1960 the CGPM has made a number of changes to SI. These include:
- The 13th CGPM (1967) renamed the "degree Kelvin" (symbol °K) to the "kelvin" (symbol K)[22]:156
- The 14th CGPM (1971) added the mole (symbol mol) to the list of base units.[58]
- The 14th GCPM (1971) added the pascal (symbol Pa) for pressure and the siemens (symbol S) for electrical conductance to the list of named derived units.[22]:156
- The 15th CGPM (1975) added the becquerel (symbol Bq) for "activity referred to a radionuclide" and the gray (symbol Gy) for ionizing radiation to the list of named derived units[22]:156
- In order to distinguish between "absorbed dose" and "dose equivalent", the 16th CGPM (1979) added the sievert (symbol Sv) to the list of named derived units as the unit of dose equivalent.[22]:158
- The 16th CGPM (1979) clarified that in a break with convention either the letter "L" or the letter "l" may be used as a symbol for the litre.[22]:159

- The 21st CGPM (1999) added the katal (symbol kat) for catalytic activity to the list of named derived units.[22]:165
- In its original form (1960), the SI defined prefixes for values ranging from pico- (symbol p) having a value of 10−12 to tera- (symbol T) having a value of 1012. The list was extended at the 12th CGPM (1964),[22]:152 at the 15th CGPM (1975)[22]:158 and at the 19th CGPM (1991)[22]:164 to give the current range of prefixes.
In addition, advantage was taken of developments in technology to redefine many of the base units enabling the use of higher precision techniques.
Retention of non-SI units
Although, in theory, SI can be used for any physical measurement, it is recognised that some non-SI units still appear in the scientific, technical and commercial literature, and will continue to be used for many years to come. In addition, certain other units are so deeply embedded in the history and culture of the human race that they will continue to be used for the foreseeable future. The CIPM has catalogued such units and included them in the SI Brochure so that they can be used consistently.
The first such group comprises the units of time and of angles and certain legacy non-SI metric units. Most of mankind has used the day and its subdivisions as a basis of time with the result that the second, minute, hour and day, unlike the foot or the pound, were the same regardless of where it was being measured. The second has been catalogued as an SI unit, its multiples as units of measure that may be used alongside the SI. The measurement of angles has likewise had a long history of consistent use – the radian, being 1/2π of a revolution, has mathematical niceties, but it is cumbersome for navigation, hence the retention of the degree, minute and second of arc. The tonne, litre and hectare were adopted by the CGPM in 1879 and have been retained as units that may be used alongside SI units, having been given unique symbols.
Physicists often use units of measure that are based on natural phenomena such as the speed of light, the mass of a proton (approximately one dalton), the charge of an electron and the like. These too have been catalogued in the SI Brochure with consistent symbols, but with the caveat that their physical values need to be measured.[Note 11]
In the interests of standardising health-related units of measure used in the nuclear industry, the 12th CGPM (1964) accepted the continued use of the curie (symbol Ci) as a non-SI unit of activity for radionuclides;[22]: 152 the becquerel, sievert and gray were adopted in later years. Similarly, the millimetre of mercury (symbol mmHg) was retained for measuring blood pressure.[22]: 127
Global adoption
SI has become the world's most widely used system of measurement, used in both everyday commerce and science.[60][61] The change to SI had little effect on everyday life in countries that used the metric system – the metre, kilogram, litre and second remained unchanged as did the way in which they were used – most of the changes only affected measurements in the workplace.[62] The CGPM has a role of recommending changes, but no formal role in the enforcement of such changes—another inter-governmental organisation, the International Organization of Legal Metrology (OIML) provides a forum for harmonisation of national standards and legislation in respect of metrology.
Both the degree and rate of adoption of SI varied from country to country—countries that had not adopted the metric system by 1960 and subsequently adopted SI did so directly as part of their metrication programs while others migrated from the CGS system of units to SI. In 1960, the world's largest economy was that of the United States, followed by the United Kingdom, West Germany, France, Japan, China and India.[63] The United States and the United Kingdom were non-metric, France and Germany had been using the metric system for about a century, and China had been using the metric system for 35 years, while India and Japan had adopted the metric system within the preceding five years. Other non-metric countries were those where the United Kingdom or the United States had considerable influence.[Note 12][64] These differences are brought out in the examples below:
United Kingdom and the former British Empire
Even though the use of metric units was legalised for trade in the UK in 1864, the UK had signed the Metre Convention in 1884 and the UK Parliament had defined the yard and the pound in terms of the metre and the kilogram in 1897, the UK continued to use the imperial system of measure[65] and to export the imperial system of units to the Empire.[Note 13] In 1932, the system of Imperial Preference was set up at the Ottawa Conference. Although Ireland left the Commonwealth in 1948 and South Africa in 1961,[66] both continued their close economic ties with the Commonwealth.[67]

When the SI standard was published in 1960, the only major Commonwealth country to have adopted the metric system was India. In 1863, the first reading of a bill that would have made the metric system compulsory passed its first reading in the House of Commons by 110 votes to 75. The bill, however, failed to make the statute book because of lack of parliamentary time.[10]:136 In 1965, after this and similar false starts the then Federation of British Industry informed the British Government that its members favoured the adoption of the metric system. The rationale behind the request was that 80% of British exports were to countries that used the metric system or that were considering changing to the metric system. The Board of Trade, on behalf of the Government, agreed to support a ten-year metrication programme. The government agreed to a voluntary policy requiring minimal legislation and costs to be borne where they fell. SI would be used from the outset.[68] The rest of the Commonwealth, South Africa and Ireland followed within a few years; in some countries such as South Africa and Australia metrication was mandatory rather than voluntary.[69][70]
By 1980 all apart from the United Kingdom, Canada and Ireland had effectively completed their programs. In the United Kingdom the breakdown of voluntary metrication in the mid-1970s[71]:§1.8 coincided with the United Kingdom's obligations as part of the EEC to adopt the metric system, resulting in legislation to force metrication in certain areas and the Eurosceptic movement adopting an anti-metrication stance and the United Kingdom seeking a number of derogations from the relevant EEC directives. Once the metrication of most consumer goods was completed in 2000, aspects of British life, especially in government, commerce and industry used SI.[71]:§1.6 & §1.10 Although SI or units approved for use alongside SI are used in most areas where units of measure are regulated[Note 14] imperial units are widely encountered in unregulated areas such as the press and everyday speech. Canada has adopted it for most purposes, but imperial units are still legally permitted and remain in common use throughout a few sectors of Canadian society, particularly in the buildings, trades and railways sectors.[72][73] The situation in Ireland, apart from road signs which were metricated in the early 2000s,[74] is similar to that in the United Kingdom.[75]
United States

Even though Congress set up a framework for the use of the metric system in the nineteenth century,[76][Note 15] the United States continues to use US customary units, based on English measure passed by parliament under the reign of Queen Anne in 1706, for most purposes apart from science and medicine,[77] though as a result of their Spanish heritage, metric units are used widely in Puerto Rico.[78]
On 10 February 1964, the National Bureau of Standards (now the National Institute of Standards and Technology) issued a statement that it was to use SI except where this would have an obvious detrimental effect. In 1968 Congress authorised the U.S. Metric Study the emphasis of which was to examine the feasibility of adopting SI.[79] The first volume was delivered in 1970.[80] The study recommended that the United States adopt the International System of units,[81] and in 1975 Congress passed the Metric Conversion Act of 1975 which established a national policy of coordinating and planning for the increased use of the metric measurement system in the United States.[82] Metrication was voluntary and to be coordinated by the United States Metric Board (USMB).[83]
Efforts during the Ford and Carter administrations to force metrication were seized on by many newspaper editorialists as being dictatorial.[5]:365 Public response included resistance, apathy, and sometimes ridicule.[84] The underlying reasons for this response include a relative uniformity of weights and measures (though, notably, US liquid measure differed by about 20% from British Imperial measure, which was adopted throughout the British Empire in 1824) inherited from the United Kingdom in 1776, a homogeneous economy and the influence of business groups and populists in Congress caused the country to look at the short-term costs associated with the change-over, particularly those that would be borne by the consumer rather than long-term benefits of efficiency and international trade. The Metrication Board was disbanded under President Ronald Reagan's direction in 1982.[5]:362–365
The 1988 Omnibus Foreign Trade and Competitiveness Act removed international trade barriers and amended the Metric Conversion Act of 1975, designating the metric system as "the Preferred system of weights and measures for United States trade and commerce". The legislation stated that the federal government has a responsibility to assist industry, especially small business, as it voluntarily converts to the metric system of measurement.[85] Exceptions were made for the highway and construction industries; the Department of Transportation planned to require metric units by 2000, but this plan was cancelled by the 1998 highway bill TEA21.[86] However, the U.S. military uses the metric system widely, partly because of the need to work with armed services from other nations.[87]

Although overall responsibility for labelling requirements of consumer goods lies with Congress and is therefore covered by federal law, details of labelling requirements for certain commodities are controlled by state law or by other authorities such as the Food and Drug Administration, Environmental Protection Agency and Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau.[88] The federal Fair Packaging and Labeling Act (FPLA), originally passed in 1964, was amended in 1992 to require consumer goods directly under its jurisdiction to be labelled in both customary and metric units. Some industries are engaged in efforts to amend this law to allow manufacturers to use only metric labelling.[89] The National Conference on Weights and Measures has developed the Uniform Packaging and Labeling Regulations (UPLR) which provides a standard approach to those sections of packaging law that are under state control. Acceptance of the UPLR varies from state to state – fourteen states accept it by merely citing it in their legislation.[90]

During the first decade of the 21st century, the EU directive 80/181/EEC had required that dual unit labelling of goods sold within the EU cease by the end of 2009. This was backed up by requests from other nations including Japan and New Zealand to permit metric-only labelling as an aid to trade with those countries.[88] Opinion in the United States was split – a bill to permit metric-only labelling at the federal level was to have been introduced in 2005 but significant opposition from the Food Marketing Institute, representing U.S. grocers, has delayed the introduction of the bill. During a routine decennial review of the directive in 2008, the EU postponed the sunset clause for dual units indefinitely.
Meanwhile, in 1999 the UPLR was amended to permit metric-only labelling and automatically became law in those states that accept UPLR "as is". By 1 January 2009, 48 out of 50 states permit metric-only labelling, either through UPLR or through their own legislation.[88] As of February 2013 the use of metric (and therefore SI) units in the United States does not follow any pattern. Dual-unit labelling on consumer goods is mandatory. Some consumer goods such as soft drinks are sold in metric quantities, others such as milk are sold in customary units. The engineering industry is equally split. The automotive industry is largely metric,[91] but aircraft such as the Boeing 787 Dreamliner were designed using customary units.[92]
European Union
In 1960, all the largest industrialised nations that had an established history of using the metric system were members of the European Economic Community (EEC).
In 1972, in order to harmonise units of measure as part of a programme to facilitate trade between member states, the EEC issued directive 71/354/EEC.[93] This directive catalogued units of measure that could be used for "economic, public health, public safety and administrative purposes" and also provided instructions for a transition from the existing units of measure that were in use. The directive replicated the CGPM SI recommendations and in addition pre-empted some of the additions whose use had been recommended by the CIPM in 1969, but had not been ratified by the CGPM.[Note 16] The directive also catalogued units of measure whose status would be reviewed by the end of 1977 (mainly coherent CGS units of measure) and also catalogued units of measure that were to be phased out by the end of 1977, including the use of obsolete names for the sale of timber such as the stere, the use of units of force and pressure that made use of the acceleration due to gravity,[Note 17] the use of non-coherent units of power such as the Pferdestärke (PS), the use of the calorie as a measure of energy and the stilb as a measure of luminance. The directive was silent in respect of units that were specific to one or two countries including the pond, pfund, livre (Dutch, German and French synonyms for 500 g), thereby effectively prohibiting their use as well.
When the directive was revisited during 1977, some of the older units that were being reviewed (such as millimetre of mercury for blood pressure)[Note 18] were retained but others were phased out, thereby broadly aligning the allowable units with SI. The directive was however overhauled to accommodate British and Irish interests in retaining the imperial system in certain circumstances.[95] It was reissued as directive 80/181/EEC. During subsequent revisions, the directive has reflected changes in the definition of SI. The directive also formalised the use of supplementary units, which in 1979 were permitted for a period of ten years. The cut-off date for the use of supplementary units was extended a number of times and in 2009 was extended indefinitely.[96]
India
India was one of the last countries to start a metrication programme before the advent of SI. When it became independent in 1947, both imperial and native units of measure were in use. Its metrication programme started in 1956 with the passing of the Standards of Weights and Measures Act. Part of the act fixed the value of the seer (a legacy unit of mass) to 0.9331 kg exactly; elsewhere the Act declared that from 1960 all non-metric units of measure were to be illegal.[97]
Four years after the Indian Government announced its metrication programme, SI was published. The result was that the initial metrication programme was a conversion to the CGS system of units and the subsequent adoption of SI has been haphazard. Fifty years later, many of the country's schoolbooks still use CGS or imperial units.[98] Originally the Indian Government had planned to replace all units of measure with metric units by 1960. In 1976 a new Weights and Measures Act replaced the 1956 Act which, amongst other things, required that all weighing devices be approved before being released onto the market place. However, in 2012, it was reported that traditional units were still encountered in small manufacturing establishments and in the marketplace alongside CGS, SI and imperial measures, particularly in the poorer areas.[99]
The use of the Indian numbering system of crores (10,000,000) and lakhs (100,000), which do not map onto the SI system of prefixes, is widespread and is often found alongside or in place of the western numbering system.[100]
Redefinition of units
After the metre was redefined in 1960, the kilogram remained the only SI base unit that relied on a specific physical artifact, the international prototype of the kilogram (IPK), for its definition and thus the only unit that was still subject to periodic comparisons of national standard kilograms with the IPK.[101] After the 1996–1998 recalibration, a clear divergence between the various prototype kilograms was observed.
At its 23rd meeting, held in 2007, the CGPM recommended that the CIPM should continue to investigate methods to provide exact fixed values for physical constants of nature that could then be used in the definitions of units of measure in place of the IPK, thus enabling the transition from explicit unit definitions to explicit constant definitions.[102][103]
At a meeting of the CCU held in Reading, United Kingdom, in September 2010, a resolution and draft changes to the SI Brochure that were to be presented to the next meeting of the CIPM in October 2010 were agreed to in principle.[104][105] The proposals that the CCU put forward were:
- In addition to the speed of light, four constants of nature – the Planck constant, an elementary charge, the Boltzmann constant and the Avogadro number – be defined to have exact values.
- The International prototype kilogram be retired
- The current definitions of the kilogram, ampere, kelvin and mole be revised.
- The wording of the definitions of all the base units be both tightened up and changed to reflect the change in emphasis from explicit unit to explicit constant definitions.
The CIPM meeting of October 2010 reviewed progress towards establishing fixed values for the constants but found that "the conditions set by the General Conference at its 23rd meeting have not yet been fully met. For this reason the CIPM does not propose a revision of the SI at the present time".[106]
At the 24th CGPM meeting, held in October 2011, the CIPM sponsored a resolution in which the requisite definition changes were agreed to in principle and in which the conditions required to be met before the redefinitions could be implemented were restated.[107]
By November 2014 the conditions set out at the 23rd meeting of the CGPM for the unit redefinitions had still not been met, and the 25th meeting of the CGPM, held in November 2014, adopted a similar resolution encouraging further work towards establishing fixed values for the fundamental constants.
See also
- History of measurement
- List of international common standards
- List of scientific units named after people
- Metre–tonne–second system of units
- Names of large numbers
- Names of small numbers
- Order of magnitude
Organisations
Standards and conventions
Notes
- ↑ The differences between "weight" and "mass" were only formally qualified in 1901.
- ↑ The 8th edition of the SI Brochure (2008) notes that [at that time of publication] the term "mise en pratique" had not been fully defined.
- ↑ The text "Des comparaisons périodiques des étalons nationaux avec les prototypes internationaux" (English: the periodic comparisons of national standards with the international prototypes) in article 6.3 of the Metre Convention distinguishes between the words "standard" (OED: "The legal magnitude of a unit of measure or weight") and "prototype" (OED: "an original on which something is modelled").
- ↑ Pferd is German for "horse" and stärke is German for "strength" or "power". The Pferdestärke is the power needed to raise 75 kg against gravity at the rate of one metre per second. (1 PS = 0.985 HP).
- ↑ These bodies include:
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) (United States)
- National Physical Laboratory (NPL) (British)
- International Astronomical Union (IAU)
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC)
- International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP)
- International Commission on Illumination (CIE) (French: Commission internationale de l'éclairage)
- Committee on Data for Science and Technology (CODATA) – an interdisciplinary committee of the International Council for Science.
- International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU)
- International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (IFCC)
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
- International Organization of Legal Metrology (OIML) (French: Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale)
- National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) (Japan)
- National Institute for Natural and Engineering Sciences (PTB) (Germany) (German: Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt)
- Federal Agency on Technical Regulating and Metrology
- ↑ This grouping and the reference to Tables 6, 7, 8, and 9 reflects the 8th Edition of the SI Brochure (2006)
- ↑ The CGPM have defined the metre in terms of the speed of light, so the speed of light has an exact value.
- ↑ For example, the Académie française in the case of French or Council for German Orthography (German: Rat für deutsche Rechtschreibung) in the case of German
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Except where specifically noted, these rules are common to both the SI Brochure and the NIST brochure.
- ↑ This term is a translation of the official [French] text of the SI Brochure
- ↑ The CGPM has defined the metre in terms of the speed of light, so the speed of light has an exact value.
- ↑ These countries included the Commonwealth countries (excluding India), Ireland, Burma, Liberia, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Nepal and Ethiopia
- ↑ In the context of this article, the word "Empire" excludes the United States.
- ↑ High-profile exceptions include road signs in the United Kingdom, (Irish road signs were converted to metric units during the first decade of the 21st century) the sale of draught beer and the sale of milk in returnable containers
- ↑ Use of the metric system was legalised in 1866, the Metre Convention was signed in 1875 and in 1893 the Mendenhall Order defined the pound and the yard in terms of the kilogram and metre respectively
- ↑ Angular units: degree, minute and second, Units of time:day, minute
- ↑ The units that made use of the acceleration due to gravity in their definitions included the kilogram-force/kilopond, torr, technical atmosphere, manometric units of pressure such as metres of water and millimetres of mercury
- ↑ The millimetre of mercury for blood pressure is one catalogued in Table 8 of SI Brochure.
References
- ↑ "Convocation of the General Conference on Weights and Measures (25th meeting)" (PDF). International Bureau of Weights and Measures. p. 32. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Amtliche Maßeinheiten in Europa 1842" [Official units of measure in Europe 1842] (in German). Retrieved 26 March 2011Text version of Malaisé's book
- ↑ Ferdinand Malaisé (1842). Theoretisch-practischer Unterricht im Rechnen [Theoretical and practical instruction in arithmetic] (in German). München. pp. 307–322. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- ↑ "The name "kilogram"". International Bureau of Weights and Measures. Retrieved 25 July 2006.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Alder, Ken (2002). The Measure of all Things—The Seven-Year-Odyssey that Transformed the World. London: Abacus. ISBN 0-349-11507-9.
- ↑ Quinn, Terry (2012). From artefacts to atoms : the BIPM and the search for ultimate measurement standards. Oxford University Press. p. xxvii. ISBN 978-0-19-530786-3.
he [Wilkins] proposed essentially what became ... the French decimal metric system
- ↑ Wilkins, John (1668). "VII". An Essay towards a Real Character and a Philosophical Language. The Royal Society. pp. 190–194.
"Reproduction (33 MB)" (PDF). Retrieved 6 March 2011.; "Transcription (126 kB)" (PDF). Retrieved 6 March 2011. - ↑ "Mouton, Gabriel". Complete Dictionary of Scientific Biography. encyclopedia.com. 2008. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- ↑ O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F. (January 2004), "Gabriel Mouton", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Tavernor, Robert (2007). Smoot's Ear: The Measure of Humanity. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-12492-7.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Brief history of the SI". International Bureau of Weights and Measures. Retrieved 12 November 2012.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Tunbridge, Paul (1992). Lord Kelvin, His Influence on Electrical Measurements and Units. Peter Pereginus Ltd. pp. 42–46. ISBN 0-86341-237-8.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Professor Everett, ed. (1874). "First Report of the Committee for the Selection and Nomenclature of Dynamical and Electrical Units". Report on the Forty-third Meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science held at Bradford in September 1873 (British Association for the Advancement of Science): 222–225. Retrieved 28 August 2013.
Special names, if short and suitable, would ... be better than the provisional designation 'C.G.S. unit of ...'.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Page, Chester H; Vigoureux, Paul, eds. (20 May 1975). The International Bureau of Weights and Measures 1875–1975: NBS Special Publication 420. Washington, D.C.: National Bureau of Standards. p. 12.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 J C Maxwell (1873). A treatise on electricity and magnetism 2. Oxford: Clarendon Press. pp. 242–245. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ↑ Bigourdan, Guillaume (2012) [1901]. Le Système Métrique Des Poids Et Mesures: Son Établissement Et Sa Propagation Graduelle, Avec L'histoire Des Opérations Qui Ont Servi À Déterminer Le Mètre Et Le Kilogramme (facsimile edition) [The Metric System of Weights and Measures: Its Establishment and its Successive Introduction, with the History of the Operations Used to Determine the Metre and the Kilogram] (in French). Ulan Press. p. 176. ASIN B009JT8UZU.
- ↑ Smeaton, William A. (2000). "The Foundation of the Metric System in France in the 1790s: The importance of Etienne Lenoir's platinum measuring instruments". Platinum Metals Rev. (Ely) 44 (3): 125–134. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- ↑ "The intensity of the Earth's magnetic force reduced to absolute measurement" (PDF).
- ↑ International Bureau of Weights and Measures (2006). Le Système International d'Unités (SI) – The International System of Units (SI) (PDF) (8th ed.). ISBN 92-822-2213-6
- ↑ Nelson, Robert A. (1981). "Foundations of the international system of units (SI)" (PDF). Phys. Teacher: 597
- ↑ "The Metre Convention". Bureau International des Poids et Mesures. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 22.4 22.5 22.6 22.7 22.8 22.9 22.10 22.11 22.12 22.13 22.14 22.15 22.16 22.17 22.18 22.19 22.20 22.21 22.22 22.23 22.24 22.25 22.26 International Bureau of Weights and Measures (2006), The International System of Units (SI) (PDF) (8th ed.), ISBN 92-822-2213-6
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Convention du mètre / The Metre Convention" (PDF) (in French and English). (Non-authoritative English translation by T.J. Quinn). CGPM. 1921. Retrieved 18 August 2013.
- ↑ Fenna, Donald (2002). Weights, Measures and Units. Oxford University Press. International unit. ISBN 0-19-860522-6.
- ↑ "In the beginning... Giovanni Giorgi". International Electrotechnical Commission. 2011. Retrieved 5 April 2011.
- ↑ "Die gesetzlichen Einheiten in Deutschland" [List of units of measure in Germany] (PDF) (in German). Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). p. 6. Retrieved 13 November 2012.
- ↑ "Porous materials: Permeability" (PDF). Module Descriptor, Material Science, Materials 3. Materials Science and Engineering, Division of Engineering, The University of Edinburgh. 2001. p. 3. Retrieved 13 November 2012.
- ↑ 9th CGPM (1948): Resolution 6
- ↑ 11th CGPM (1960): Resolution 12
- ↑ 14th CGPM (1971):Resolution 3
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 31.4 Thompson, Ambler; Taylor, Barry N. (2008). The International System of Units (SI) (Special publication 330) (PDF). Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 18 June 2008.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 Thompson, Ambler; Taylor, Barry N. (2008). Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) (Special publication 811) (PDF). Gaithersburg, MD:: National Institute of Standards and Technology.
- ↑ "Criteria for membership of the CCU". Bureau International des Poids et Mesures. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
- ↑ "The International Vocabulary of Metrology (VIM)".
- ↑ Quantities Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry, IUPAC
- ↑ Page, Chester H; Vigoureux, Paul, eds. (20 May 1975). The International Bureau of Weights and Measures 1875–1975: NBS Special Publication 420. Washington, D.C.: National Bureau of Standards. pp. 238–244.
- ↑ McKenzie, A.E.E (1961). Magnetism and Electricity. Cambridge University Press. p. 322.
- ↑ "Units & Symbols for Electrical & Electronic Engineers". Institution of Engineering and Technology. 1996. pp. 8–11. Retrieved 19 August 2013.
- ↑ McGreevy, Thomas (1997). Cunningham, Peter, ed. The Basis of Measurement: Volume 2 – Metrication and Current Practice. Pitcon Publishing (Chippenham) Ltd. pp. 222–224. ISBN 0 948251 84 0.
- ↑ "Resolution 7 of the 9th meeting of the CGPM (1948): Writing and printing of unit symbols and of numbers". International Bureau of Weights and Measures. Retrieved 6 November 2012.
- ↑ Thompson, A; Taylor, B N (5 October 2010). "The NIST Guide for the use of the International System of Units". Appendix C. Comments on the References of Appendix D – Bibliography. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- ↑ "ISO 80000-1:2009(en) Quantities and Units—Past 1:General". International Organization for Standardization. 2009. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- ↑ Russ Rowlett (14 July 2004). "Using Abbreviations or Symbols". University of North Carolina. Retrieved 11 December 2013.
- ↑ "SI Conventions". National Physical Laboratory. Retrieved 11 December 2013.
- ↑ Wörterbuch Englisch Dictionary German. Limassol: Eurobuch/Eurobooks. 1988.
- ↑ "The International System of Units" (PDF). pp. iii. Retrieved 27 May 2008.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 "Interpretation of the International System of Units (the Metric System of Measurement) for the United States" (PDF). Federal Register (National Archives and Records Administration) 73 (96): 28432–3. 9 May 2008. FR Doc number E8-11058. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
- ↑ "USMA FAQ on hyphenation for adjective forms". Retrieved 2 April 2014.
- ↑ Frysinger, James R.; Yin, Pin; Jih, Justin; Jih, Yeeming (2010). "SI Unit and Prefix Names in Chinese". Metric Methods. Retrieved 1 November 2012.
- ↑ Victor Mair, "Polysyllabic characters in Chinese writing", Language Log, 2011 August 2
- ↑ Thompson, A.; Taylor, B. N. (July 2008). "NIST Guide to SI Units – Rules and Style Conventions". National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 29 December 2009.
- ↑ Williamson, Amelia A (March–April 2008). "Period or Comma? Decimal Styles over Time and Place" (PDF). Science Editor (Council of Science Editors) 31 (2): 42. Retrieved 19 May 2012.
- ↑ "Avogadro Project". National Physical Laboratory. Retrieved 19 August 2010.
- ↑ "What is a mise en pratique?". International Bureau of Weights and Measures. Retrieved 10 November 2012.
- ↑ "Recommendations of the Consultative Committee for Mass and Related Quantities to the International Committee for Weights and Measures." (PDF). 12th Meeting of the CCM. Sèvres: Bureau International des Poids et Mesures. 26 March 2010. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
- ↑ "Recommendations of the Consultative Committee for Amount of Substance – Metrology in Chemistry to the International Committee for Weights and Measures." (PDF). 16th Meeting of the CCQM. Sèvres: Bureau International des Poids et Mesures. 15–16 April 2010. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
- ↑ "Recommendations of the Consultative Committee for Thermometry to the International Committee for Weights and Measures." (PDF). 25th Meeting of the CCT. Sèvres: Bureau International des Poids et Mesures. 6–7 May 2010. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
- ↑ pg 221 – McGreevy
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 "International Recommendation R 52 – Hexagonal weights – Metrological and technical requirements" (PDF). International Organization of Legal Metrology. 2004. Retrieved 28 December 2012.
- ↑ "Official BIPM definitions". Retrieved 26 November 2012.
- ↑ "Essentials of the SI: Introduction". National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 26 November 2012.
- ↑ "White Paper on Metrication (1972) – Summary and Conclusions" (PDF). London: Department of Trade and Industry Consumer and Competition Policy Directorate. para 22–23.
- ↑ Dutta, M. (2008). "Chapter 3: Optimum Currency Areas: U.S. Dollar, Euro and Asian Money" (PDF). Rutgers University. Table 3.1. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- ↑ Page, Chester H; Vigoureux, Paul, eds. (20 May 1975). The International Bureau of Weights and Measures 1875–1975: NBS Special Publication 420. Washington, D.C.: National Bureau of Standards. p. 244.
- ↑ "White Paper on Metrication (1972) – Summary and Conclusions" (PDF). London: Department of Trade and Industry Consumer and Competition Policy Directorate. para 19.
- ↑ Cinchon, Deborah (1996). "APPENDIX B – Guyana and Belize: The Commonwealth of Nations". Country studies. Library of Congress. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
- ↑ Fram, Nicholas (17 May 2006). Decolonization, the Commonwealth, and British Trade, 1945–2004 (PDF) (BA (Hons) thesis). Stanford University.
- ↑ "White Paper on Metrication (1972) – Summary and Conclusions" (PDF). London: Department of Trade and Industry Consumer and Competition Policy Directorate. para 42–45.
- ↑ "South Africa Metrication". South African Government. 15 September 1977. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ↑ "Final Annual Report (1980–1981) of the (Australian) Metric Conversion Board (MCB)". Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 "Final Report of the Metrication Board (1980)" (PDF). London: Department of Trade and Industry Consumer and Competition Policy Directorate.
- ↑ "Weights and Measures Act". Retrieved 26 November 2012.
- ↑ Weights and Measures Act, Retrieved 2012-09-18, Act current to 18 September 2012. "Canadian units (5) The Canadian units of measurement are as set out and defined in Schedule II, and the symbols and abbreviations therefor are as added pursuant to subparagraph 6(1)(b)(ii)."
- ↑ "Roads go metric across country today". RTÉ News. 20 January 2005. p. 9. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
- ↑ "National Plan to Improve Literacy and Numeracy in Schools: Submission to the Department of Education and Skills" (PDF). Irish Business and Employers Confederation. February 2011. p. 9. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
- ↑ Barbrow, Louis E.; Judson, Lewis V. (March 1976) [First published October 1963]. "Weights and Measures Standards of the United States – A brief history, Special Publication 447". National Bureau of Standards. pp. 10–20. LCCN 76-600055.
- ↑ "Appendix G : Weights and Measures". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- ↑ Porter, Darwin; Prince, Danforth (2006). Frommer's Puerto Rico (8th ed.). Wiley Publishing. p. 58. ISBN 978-0-471-78740-2.
- ↑ "The United States and the Metric System" (PDF). Office of Weights and Measures/Metric Program. October 1997. NIST LC1136. Retrieved 23 August 2013.
- ↑ Simone, Daniel V (December 1970). U.S. Metric Study Report – International Standards. National Bureau of Standards. Special Publication 345-1.
- ↑ Rowlett, Russ (8 August 2000). "The Metric System in the United States". How Many? A Dictionary of Units of Measurement. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina. Retrieved 21 January 2013.
Henceforth it shall be the policy of the National Bureau of Standards to use the units of the International System (SI), as adopted by the 11th General Conference of Weights and Measures (October 1960), except when the use of these units would obviously impair communication or reduce the usefulness of a report.
- ↑ Ford, Gerald R (23 December 1975). Wooley, John; Peters, Gerhard, eds. "Statement on Signing the Metric Conversion Act of 1975.". The American Presidency Project. Retrieved 21 August 2013.
- ↑ "The Metric System in the U.S.". Event-Based Science Project. 2003. Retrieved 21 August 2013.
- ↑ Martha Brockenbrough. "Whatever Happened to the Metric System?". MSN Encarta column. Archived from the original on 1 November 2009. Retrieved 21 January 2013.
- ↑ Cass, Ronald A. (Winter 1991). "Velvet Fist in an Iron Glove: The Omnibus Trade and Competitiveness Act of 1988" (PDF). Regulation (Washington DC: Cato Institute): 50–56. Retrieved 21 January 2013.
- ↑ "DYKT: Did You Know That". Lamar.colostate.edu. 5 June 2008. Retrieved 21 January 2013.
- ↑ "Guide for Identification and Development of Metric Standards" (PDF). Office of the Under Secretary of Defense Acquisition, Technology & Logistics. December 2003. p. 3. SD-10. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 88.2 Gentry, Elizabeth J. "Voluntary Metric Labeling" (PDF). National Institute of Standards and Technology. pp. 3–6. Retrieved 28 January 2013.
- ↑ "Forum on Permissible Metric-Only Labeling". NIST. 4 October 2006. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- ↑ Frysinger, James R. (2010). "The Uniform Packaging and Labeling Regulation (UPLR)". Metric Methods. Retrieved 28 January 2013.
- ↑ Greenslade, Joe (August 2012). "Why Specify ISO Standards For Metric Fasteners?". American Fastener Journal (Scotsdale, Arizona): 48–55. ISSN 1064-3834. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
The decision by General Motors, FORD, and Chrysler to adopt the metric system of measurement in design impacted all industrialized countries in the world. The car manufacturers wanted to be able to source products anywhere in the world and have the components be compatible regardless of where the parts were made, purchased or assembled.
- ↑ Reisman, Lisa (16 August 2011). "Not So Fast, Comac: C919 is DOA, But Boeing and Airbus Duopoly Dead Anyway". MetalMiner. Azul Partners. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ↑ "Council Directive 71/354/EEC: On the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to units of measurement". The Council of the European Communities. 18 October 1971. Retrieved 3 March 2012.
- ↑ Gupta, S.V. (2004). "Verification of commercial weights" (PDF). Paris: International Organisation of Legal Metrology. p. 6. Expert Report – OIML E 3 (2004). Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ↑ The Council of the European Communities (21 December 1979). "Council Directive 80/181/EEC of 20 December 1979 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to Unit of measurement and on the repeal of Directive 71/354/EEC". Retrieved 7 February 2009.
- ↑ The Council of the European Communities (27 May 2009). "Council Directive 80/181/EEC of 20 December 1979 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to Unit of measurement and on the repeal of Directive 71/354/EEC". Retrieved 14 September 2009.
- ↑ Mandavilli, Sujay Rao. "Metrication in India". Metric usage and metrication in other countries. US Metric Association. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ↑ Chakrabarti, Bhupati (10 February 2007). "Fifty years of the metric system in India and its adoption in our daily life" (PDF). Current Science (Bangalore: Current Science Association) 92 (3). Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ↑ Subramaniam, K; Bose, Arindam (14 July 2012). Measurement Units and Modes: The Indian Context (PDF). 12th International Congress on Mathematical Education (PDF). pp. 1973–1983. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ↑ "Style Sheet". Mumbai: Economic and Political Weekly. Retrieved 31 January 2013.
- ↑ "Redefining the kilogram". UK National Physical Laboratory. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
- ↑ Newell, David B. "A more fundamental International System of Units" (PDF). Physics Today. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
- ↑ Mills, Ian (September–October 2011). "Part II—Explicit-Constant Definitions for the Kilogram and for the Mole". Chemistry International 33 (5): 12–15. ISSN 0193-6484.
- ↑ Mills, Ian (29 September 2010). "On the possible future revision of the International System of Units, the SI" (PDF). CCU. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ↑ Mills, Ian (29 September 2010). "Draft Chapter 2 for SI Brochure, following redefinitions of the base units" (PDF). CCU. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ↑ "Towards the "new SI"". International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). Retrieved 20 February 2011.
- ↑ Resolution 1 – On the possible future revision of the International System of Units, the SI (PDF). 24th meeting of the General Conference on Weights and Measures. Sèvres, France. 17–21 October 2011. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
Further reading
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (1993). Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry, 2nd edition, Oxford: Blackwell Science. ISBN 0-632-03583-8. Electronic version.
- Unit Systems in Electromagnetism
- MW Keller et al. Metrology Triangle Using a Watt Balance, a Calculable Capacitor, and a Single-Electron Tunneling Device
- "The Current SI Seen From the Perspective of the Proposed New SI". Barry N. Taylor. Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, Vol. 116, No. 6, Pgs. 797–807, Nov–Dec 2011.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to International System of Units. |
- Official
- BIPM Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (SI maintenance agency) (home page)
- BIPM brochure (SI reference)
- ISO 80000-1:2009 Quantities and units – Part 1: General
- NIST Official Publications
- Rules for SAE Use of SI (Metric) Units
- International System of Units at DMOZ
- EngNet Metric Conversion Chart Online Categorised Metric Conversion Calculator
- U.S. Metric Association. 2008. A Practical Guide to the International System of Units
- History
- LaTeX SIunits package manual gives a historical background to the SI system.
- Research
- Pro-metric advocacy groups
- Pro-customary measures pressure groups
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



