Ingenol mebutate
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
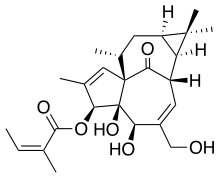
| (1aR,2S,5R,5aS,6S,8aS,9R,10aR)-5,5a-Dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)-1,1,7,9-tetramethyl-11-oxo-1a,2,5,5a,6,9,10,10a-octahydro-1H-2,8a-methanocyclopenta[a]cyclpropa[e][10]annulen-6-yl (2Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoate | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Picato |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | entry |
| |
| |
| Topical (gel) | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Below detection level |
| Identifiers | |
| 75567-37-2 | |
| D06BX02 | |
| PubChem | CID 6918670 |
| ChemSpider | 26325194 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:66913 |
| Synonyms | PEP005, ingenol-3-angelate |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C25H34O6 |
| 430.534 g/mol | |
|
SMILES
| |
| |
Ingenol mebutate (ingenol-3-angelate, LEO Pharma trade name Picato) is a substance found in the sap of the plant Euphorbia peplus[1] and an inducer of cell death. A gel formulation of the drug has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)[2] and by the European Medicines Agency (EMA)[3] for the topical treatment of actinic keratosis. Two different strengths of the gel are approved for use on either the face and scalp (0.015%) or the trunk and extremities (0.05%), respectively.[4]
Results from four multicenter, randomized, double-blind studies have shown that ingenol mebutate gel applied topically for 2 to 3 days is effective for field treatment of actinic keratoses.[5]
Adverse effects
Irritations of the application site are very common. This includes redness, scaling, crusting, pain, pruritus, and sometimes infection. Other side effects include eye irritation such as periorbital edema (3% of patients in studies), headache (2%) and nasopharyngitis (running nose, 2%).[6]
Interactions
As ingenol mebutate is practically not absorbed through the skin, interactions with oral drugs are unlikely.[7][8]
Chemistry
The substance is an ester of the diterpene ingenol and angelic acid. A 14-step synthesis of (+)-ingenol from (+)-3-carene, which is a relatively inexpensive constituent of turpentine, was published in July 2013.[9]
References
- ↑ Fallen RS, Gooderham M (2012). "Ingenol mebutate: An introduction". Skin Therapy Lett 17 (2): 1–3. PMID 22358305.
- ↑ Picato Drug Details at Drugs@FDA
- ↑ European Public Assessment Report (EPAR) for Picato
- ↑ Picato® Gel label at Drugs@FDA
- ↑ Lebwohl M, Swanson N, Anderson LL, Melgaard A, Xu Z, Berman B (2012). "Ingenol Mebutate Gel for Actinic Keratosis". N Engl J Med 336 (11): 1010–1019. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1111170. PMID 22417254.
- ↑ Drugs.com: Picato Side Effects in Detail
- ↑ Picato FDA Professional Drug Information
- ↑ Haberfeld, H, ed. (2013). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
- ↑ Jorgensen, L.; McKerrall, S. J.; Kuttruff, C. A.; Ungeheuer, F.; Felding, J.; Baran, P. S. (2013). "14-Step Synthesis of (+)-Ingenol from (+)-3-Carene". Science 341 (6148): 878–882. doi:10.1126/science.1241606. PMID 23907534.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||