Inferior ganglion of vagus nerve
| Inferior ganglion of vagus nerve | |
|---|---|
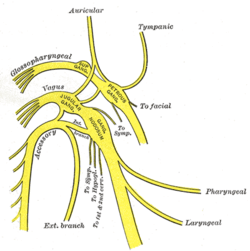 Plan of upper portions of glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves ("Gang. nodosum" visible at center) | |
| Details | |
| Latin |
Ganglion nodosum, ganglion inferius nervi vagi |
From | vagus nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Gray's | p.911 |
| MeSH | A08.340.390.550 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | g_02/12384714 |
| TA | A14.2.01.157 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The nodose ganglion (ganglion of the trunk; inferior ganglion of vagus nerve) is cylindrical in form, of a reddish color, and 2.5 cm (0.98 in) in length. It is located in the height of the transverse process of the first cervical vertebra (atlas).
Passing through it is the cranial portion of the accessory nerve, which blends with the vagus below the ganglion.
As opposed to the jugular ganglion of the vagus nerve, the inferior or nodose ganglion is larger.
Function
It is chiefly visceral afferent in function concerning sensation of heart, larynx, lungs and alimentary tract from the pharynx to the transverse colon. These visceral afferents synapse centrally in the nucleus solitarius.
Both ganglia are traversed by parasympathetic, and perhaps some sympathetic fibres.
Preganglionic motor fibres (ganglionic branches) from the dorsal vagal nucleus and the special visceral efferents from the nucleus ambiguus, which descend to the inferior vagal ganglion form a band skirting the ganglion.
Additional images
-
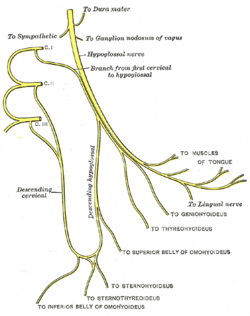
Plan of hypoglossal nerve.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (X)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||