Immigration Act of 1917
.svg.png) | |
| Other short titles | Asiatic Barred Zone Act |
|---|---|
| Legislative history | |
| |
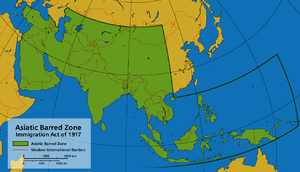
On February 5, 1917, the United States Congress passed the Immigration Act of 1917 (also known as the Asiatic Barred Zone Act) with an overwhelming majority, overriding President Woodrow Wilson's December 14, 1916, veto. This act added to the number of undesirables banned from entering the country, including but not limited to “homosexuals”, “idiots”, “feeble-minded persons”, "criminals", “epileptics”, “insane persons”, alcoholics, “professional beggars”, all persons “mentally or physically defective”, polygamists, and anarchists. Furthermore, it barred all immigrants over the age of sixteen who were illiterate. The most controversial part of the law was the section that designated an "Asiatic Barred Zone", a region that included much of Asia and the Pacific Islands from which people could not immigrate. Previously, only the Chinese had been excluded from admission to the country. Attempts at introducing literacy tests were previously vetoed by Grover Cleveland in 1897 and William Taft in 1913. Wilson also objected to this clause in the Immigration Act, but it was still passed by Congress on the fourth attempt.
Anxiety in the United States about immigration has often been directed toward immigrants from China and Japan. The Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 barred Chinese from entering the US. The Gentlemen's Agreement of 1907 was made with Japan to regulate Japanese immigration to the US.[1] The Immigration Act of 1917 is one of many immigration acts during this time period which arose from nativist and xenophobic sentiment. These immigration laws were intentional efforts to control the composition of immigrant flow into the United States.
The McCarran-Walter Act
The Chinese Exclusion Act was repealed in 1943. The Luce-Celler Act of 1946 ended discrimination against Asian Indians and Filipinos, who were accorded the right to naturalization, and allowed a quota of 100 immigrants per year. The Immigration Act of 1917 was later altered formally by the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1952, known as the McCarran-Walter Act. It extended the privilege of naturalization to Japanese, Koreans, and other Asians.[2] The McCarran-Walter Act revised all previous laws and regulations regarding immigration, naturalization, and nationality, and collected into one comprehensive statute.[3]
See also
- Anarchist Exclusion Act
- Chinese Exclusion Act (United States)
References
- ↑ Van Nuys, Frank (2002), Americanizing the West: Race, Immigrants, and Citizenship, 1890–1930, Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, pp. 19, 72, ISBN 0-7006-1206-8.
- ↑ “Commentary on Excerpt of the McCarran-Walter Act, 1952”, American Journal Online: The Immigrant Experience, Primary Source Microfilm, (1999), Reproduced in History Resource Center, Farmington Hills, MI: Gale Group, February 9, 2007
- ↑ "McCarran-Walter Act”, Dictionary of American History, 7 vols, Charles Scribner's Sons, (1976), Reproduced in History Resource Center, Farmington Hills, MI: Gale Group, February 9, 2007
External links
- UDayton.edu Timeline of Asian Pacific Americans and Immigration Law
- AILF.org Closed Borders and Mass Deportations: The Lessons of the Barred Zone Act
- PBS.org Text of the Act describing the limits of the Asiatic Barred Zone
- GaleGroupe.com "Immigration Act of 1917, Literacy Test"
- Helen F. Eckerson, "Immigration and National Origins"
- Immigration of Illiterates over Age Sixteen Prohibited, May 1, 1917