Ilgachuz Range
| Ilgachuz Range | |
|---|---|
|
Satellite image of the Ilgachuz Range | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Far Mountain |
| Elevation | 2,410 m (7,910 ft) |
| Coordinates | 52°47′12.1″N 125°19′23.9″W / 52.786694°N 125.323306°W |
| Geography | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | British Columbia |
| District | Range 3 Coast Land District |
| Range coordinates | 52°46′N 125°18′W / 52.77°N 125.3°WCoordinates: 52°46′N 125°18′W / 52.77°N 125.3°W |
| Parent range | Chilcotin Plateau |
| Borders on | Rainbow and Itcha Range |
| Geology | |
| Orogeny | Anahim hotspot volcanism |
| Period | 5 million years (Pliocene) |
| Type of rock | Shield volcano |
The Ilgachuz Range is a name given to an extinct shield volcano in British Columbia, Canada. It is not a mountain range in the normal sense, because it was formed as a single volcano that has been eroded for the past 5 million years. It lies on the Chilcotin Plateau, located some 350 kilometres (220 mi) north-northwest of Vancouver and 30 km north of Anahim Lake. The highest peak of the range is Far Mountain. The range supports a unique grassland ecosystem. This type of grassland has not been seen anywhere else in central and southern British Columbia. The climate is cool and dry; typical of higher elevations of the Interior Plateau.
The 280 kilometres (174 mi) long West Road River rises in the Ilgachuz Range and flows east to its confluence with the Fraser River between Prince George and Quesnel. It drains an area of approximately 12,000 km2, and dropping over 900 m before joining with the Fraser.
Geology and history
Origins
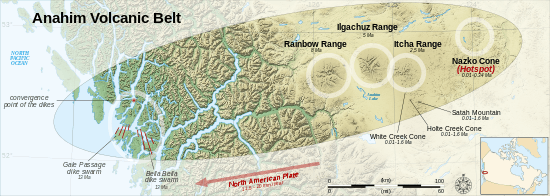
The Ilgachuz Range began erupting about 5 million years ago and has grown steadily since then. Like all of the Anahim volcanoes, the Ilgachuz Range has its origins in the Anahim hotspot—a plume of magma rising from the Earth's mantle in central British Columbia. The hotspot remains in a fixed position, while the North American Plate drifts over it at a rate of 2 to 3.3 centimetres per year. The upwelling of the hot magma creates volcanoes, and each individual volcano erupts for a few million years before the movement of the plate carries it away from the rising magma. However, where hotspots occur under continental crust, basaltic magma is trapped in the less dense continental crust, which is heated and melts to form rhyolites. These rhyolites can be quite hot and form violent eruptions, despite their low water content.
The hotspot has existed for at least 13 million years, and the Anahim Volcanic Belt stretches almost 600 kilometres (400 mi) away from the hotspot. More recently, the hotspot has formed the Itcha Range and Nazko Cone, a cinder cone east of the Ilgachuz Range and the youngest Anahim volcano. The Ilgachuz Range is the largest of these, although the Rainbow Range is the largest of all volcanoes in the Anahim Volcanic Belt.
First Nations
The first recorded ascent of the Ilgachuz Range was by the South Carrier and Chilcotin tribes. They have lived in the area for hundreds of years, travelling when necessary to hunt and trap animals such as beaver, caribou, moose, and to gather plants and roots. Fishing camps were also established in the area.
The Ilgachuz Range is, or was, an important source of obsidian for the South Carrier and Chilcotin tribes. Obsidian was greatly desired because very sharp arrowheads and cutting knives could be made from it. Like all glass and some other types of naturally occurring rocks, obsidian breaks with a characteristic conchoidal fracture, creating razorlike edges. It was also used for jewelry. Anahim obsidian was traded extensively throughout the BC Interior and up and down the Coast from Bella Coola. Red ochre used in paint and decoration was also obtained from this area.
Structure

The Ilgachuz Range is the second largest shield volcano in the Anahim Volcanic Belt which includes other immediately nearby ranges, the Rainbow Range and Itcha Range. It stands at 2,410 metres (7,907 ft) above sea level - slightly shorter than its neighbor, Rainbow Range. It has a diameter of 25 km (16 mi). The Ilgachuz Range was created by two chemically separate magmatic periods; an early complex series of trachyte and rhyolite eruptions, and late extrusion of a sequence of basaltic lava flows.[1] Evacuation of the volcano's magma chamber resulted in the failure of one or more centrally located calderas. It is divided into Precaldera, Dome Forming, Intra Caldera and Shield Forming assembages.
The Precaldera Assemblage is best exposed on the east side of Pipe Organ Mountain where it contains a bedded pile over 300 m thick of weakly consolidated, moderately to extremely different, pyroclastics, flows and deposits of uncertain origin. Colours range from mottled green to grey, yellow, ochre, red and white. A green tuffbreccia composed of pumice fragments, feldspar crystals and minor debris is recognizable in several areas.[1]

The Dome Forming Assemblages include most of the rhyolite domes, related flows and the Ilgachuz Comendite. The northerly domes are subcircular talus mounds of plate sized pieces of light to dark grey, slightly porphyritic, flowbanded rhyolite with minor obsidian. Massive to banded chalcedony blobs and veinlets are related with these domes. The southern domes are somewhat different in nature, comprising intrusive and extrusive phases of cream colored porphyries. The Sax Dome contains an upper portion of cream coloured, aphanitic to fine quartz porphyry felsite with abnormal green glass filled fractures, and a lower unit of microsyenite with red and green glassy zenocrysts.[1]
The Intra Caldera Assemblage is best exposed on the north edge of the caldera. The lower unit, indicative of caldera formation, is an epiclastic boulder-landslide deposit, roughly bedded and dipping into the caldera. Similar material, grading up into finer debris flows and possibly lahars, has been uncertainly known in the gap between Phacelia Peak and Calliope Mountain suggesting this area is the southern edge of the caldera. Alternatively, largely unsorted breccia and debris deposits exist on the ridge north of Saxifraga Peak, possibly indicating the main, or a subsidiary, caldera edge.[1]
The Shield Forming Assemblage contains a series of basalt and minor comendite eruptions, and is best exposed on Far Mountain and Mount Scot. The basalts issued from fissure vents primarily located peripheral to the calderas. Brick red cinder deposits are considered to be a late phase of this assemblage.[1]
Provincial Park
Surrounding and including the range is Itcha Ilgachuz Provincial Park, a 112,000 hectare park of unique landscape in the West Chilcotin Uplands while the Rainbow Range lies partly in the Tweedsmuir South Provincial Park. The park includes volcanic landforms, alpine environments, and forest sites scattered with wetlands.
Itcha Ilgachuz Provincial Park is extremely remote and unroaded; the closest communities are Anahim Lake, Alexis Creek, Nimpo Lake, Redstone, and Nazko. The closest major centre is Quesnel, located approximately 200 km east of the park.
Subsidiary peaks
Peaks within the Ilgachuz Range include:
- Calliope Mountain
- Camlick Mountain
- Campanula Peak
- Cindercone Peak
- Crepis Peak
- Far Mountain
- Go-around Mountain
- Hump Mountain
- Mizzen Mountain
- Mount Scot
- Phacelia Peak
- Pipe Organ Mountain
- Saxifraga Mountain
- Tundra Mountain
See also
- Rainbow Range
- Itcha Range
- Anahim hotspot
- Anahim Volcanic Belt
- List of volcanoes in Canada
- Itcha Ilgachuz Provincial Park
- Tweedsmuir South Provincial Park
- Volcanism of Canada
- Volcanism of Western Canada
