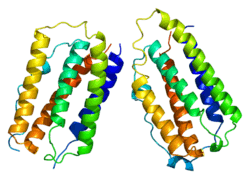
IFNB1
Interferon beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNB1 gene.[1] The natural and recombinant protein forms have antiviral, antibacterial, and anticancer properties.[2]
Interferon beta 1a (tradenames: Avonex and Rebif) and Interferon beta 1b (tradenames: Betaseron/Betaferon) are used as drugs.
References
Further reading
- Biron CA, Nguyen KB, Pien GC (2002). "Innate immune responses to LCMV infections: natural killer cells and cytokines.". Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 263: 7–27. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-56055-2_2. PMID 11987821.
- Conti L, Fantuzzi L, Del Cornò M et al. (2005). "Immunomodulatory effects of the HIV-1 gp120 protein on antigen presenting cells: implications for AIDS pathogenesis.". Immunobiology 209 (1–2): 99–115. doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2004.02.008. PMID 15481145.
- Bekisz J, Schmeisser H, Hernandez J et al. (2005). "Human interferons alpha, beta and omega". Growth Factors 22 (4): 243–51. doi:10.1080/08977190400000833. PMID 15621727.
- Copeland KF (2006). "Modulation of HIV-1 transcription by cytokines and chemokines". Mini reviews in medicinal chemistry 5 (12): 1093–101. doi:10.2174/138955705774933383. PMID 16375755.
- Silverman RH, Sengupta DN (1991). "Translational regulation by HIV leader RNA, TAT, and interferon-inducible enzymes". J. Exp. Pathol. 5 (2): 69–77. PMID 1708818.
- Flores I, Mariano TM, Pestka S (1991). "Human interferon omega (omega) binds to the alpha/beta receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (30): 19875–7. PMID 1834641.
- May LT, Sehgal PB (1985). "On the relationship between human interferon alpha 1 and beta 1 genes". J. Interferon Res. 5 (3): 521–6. PMID 2414376.
- Francois DT, Katona IM, June CH et al. (1988). "Examination of the inhibitory and stimulatory effects of IFN-alpha, -beta, and -gamma on human B-cell proliferation induced by various B-cell mitogens". Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 48 (3): 297–306. doi:10.1016/0090-1229(88)90023-2. PMID 3135963.
- Conradt HS, Egge H, Peter-Katalinic J et al. (1987). "Structure of the carbohydrate moiety of human interferon-beta secreted by a recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cell line". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (30): 14600–5. PMID 3667593.
- Blank KJ, McKernan LN, Murasko DM (1985). "Poly I:C or IFN-alpha/beta treatment inhibits macrophage induced T cell proliferation". J. Interferon Res. 5 (1): 215–21. doi:10.1089/jir.1985.5.215. PMID 3872918.
- Derynck R, Content J, DeClercq E et al. (1980). "Isolation and structure of a human fibroblast interferon gene". Nature 285 (5766): 542–7. doi:10.1038/285542a0. PMID 6157094.
- Taniguchi T, Ohno S, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Muramatsu M (1980). "The nucleotide sequence of human fibroblast interferon cDNA". Gene 10 (1): 11–5. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(80)90138-9. PMID 6157601.
- Houghton M, Easton MA, Stewart AG et al. (1981). "The complete amino acid sequence of human fibroblast interferon as deduced using synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers of reverse transcriptase". Nucleic Acids Res. 8 (13): 2885–94. doi:10.1093/nar/8.13.2885. PMC 324132. PMID 6159580.
- Goeddel DV, Shepard HM, Yelverton E et al. (1981). "Synthesis of human fibroblast interferon by E. coli". Nucleic Acids Res. 8 (18): 4057–74. doi:10.1093/nar/8.18.4057. PMC 324219. PMID 6159584.
- Houghton M, Stewart AG, Doel SM et al. (1981). "The amino-terminal sequence of human fibroblast interferon as deduced from reverse transcripts obtained using synthetic oligonucleotide primers". Nucleic Acids Res. 8 (9): 1913–31. doi:10.1093/nar/8.9.1913. PMC 324047. PMID 6159597.
- Wetzel R (1981). "Assignment of the disulphide bonds of leukocyte interferon". Nature 289 (5798): 606–7. doi:10.1038/289606a0. PMID 6162107.
- Lawn RM, Adelman J, Franke AE et al. (1981). "Human fibroblast interferon gene lacks introns". Nucleic Acids Res. 9 (5): 1045–52. doi:10.1093/nar/9.5.1045. PMC 326735. PMID 6164984.
- Shepard HM, Leung D, Stebbing N, Goeddel DV (1982). "A single amino acid change in IFN-beta1 abolishes its antiviral activity". Nature 294 (5841): 563–5. doi:10.1038/294563a0. PMID 6171735.
- Content J, De Wit L, Pierard D et al. (1982). "Secretory proteins induced in human fibroblasts under conditions used for the production of interferon beta". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79 (9): 2768–72. doi:10.1073/pnas.79.9.2768. PMC 346287. PMID 6178110.
- Fiers W, Remaut E, Devos R et al. (1983). "The human fibroblast and human immune interferon genes and their expression in homologous and heterologous cells". Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., B, Biol. Sci. 299 (1094): 29–38. doi:10.1098/rstb.1982.0103. PMID 6183692.
PDB gallery |
|---|
| | 1au1: HUMAN INTERFERON-BETA CRYSTAL STRUCTURE |
|
|
|
|
|---|
| | By family | |
|---|
| By function/
cell | |
|---|
| Index of signal transduction |
|---|
| | Description |
- Intercellular
- neuropeptides
- growth factors
- cytokines
- hormones
- Cell surface receptors
- ligand-gated
- enzyme-linked
- G protein-coupled
- immunoglobulin superfamily
- integrins
- neuropeptide
- growth factor
- cytokine
- Intracellular
- adaptor proteins
- GTP-binding
- MAP kinase
- Calcium signaling
- Lipid signaling
- Pathways
- hedgehog
- Wnt
- TGF beta
- MAPK ERK
- notch
- JAK-STAT
- apoptosis
- hippo
- TLR
|
|---|
|
|