Hurricane Flossy (1956)
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS/NWS) | |
 | |
| Formed | September 21, 1956 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | September 30, 1956 |
| Highest winds |
1-minute sustained: 90 mph (150 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 980 mbar (hPa); 28.94 inHg |
| Fatalities | 15 total |
| Damage | $24.9 million (1956 USD) |
| Areas affected | Yucatán Peninsula, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia |
| Part of the 1956 Atlantic hurricane season | |
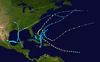
Hurricane Flossy originated from a tropical disturbance in the eastern Pacific Ocean and moved across Central America into the Gulf of Mexico as a tropical depression on September 21, 1956, which became a tropical storm on September 22 and a hurricane on September 23. The hurricane peaked with maximum sustained winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) before it struck the central Gulf coast of the United States as a Category 1 hurricane on September 24, and evolved into an extratropical cyclone on September 25.[1] It was the first hurricane to affect oil refining in the Gulf of Mexico. The tropical cyclone led to flooding in New Orleans, and broke a drought across the eastern United States. The death toll was 15, and total damages reached $24.8 million (1956 USD).[2][3]
Meteorological history

A tropical disturbance moved northward, crossing Guatemala from the eastern Pacific ocean into the northwest Caribbean Sea between September 20 and September 21. It became a tropical cyclone soon after emerging into the Caribbean, and moved across the Yucatán Peninsula as a tropical depression before becoming a tropical storm in the Gulf of Mexico on September 22 and a hurricane on September 23. It turned sharply east-northeast across the Mouth of the Mississippi river on September 24 as a minor hurricane.[4] The storm continued east-northeast and made landfall in Florida east of Pensacola. The system evolved into an extratropical cyclone soon after passing out of the Sunshine State and continued moving east to northeast hugging the Atlantic Seaboard to near the Virginia Capes before moving slowly through the shipping lanes between Canada and Bermuda, blocked by a high pressure system in southeast Canada.[5]
Preparations
By the morning of September 22, hurricane watches were posted for the upper Texas and Louisiana coasts.[6] By the morning of September 24, hurricane warnings were in effect from Grand Isle, Louisiana to Fort Walton Beach, Florida while storm warnings were in effect from Morgan City, Louisiana to St. Marks, Florida.[7] The approach of the hurricane led to the evacuation of 15 aircraft from Florida to Ardmore Air Force Base, in Oklahoma.[8]
Impact

Gulf of Mexico
This was the first hurricane to cause significant disruption to oil refining in the Gulf of Mexico.[9] Several hundred active wells went out of service, and drilling came to a halt for a few days during and after the cyclone's passage. One of Humble company's tenders saw three-quarters of its mooring chains compromised, which swung it around into an adjacent oil platform, causing $200,000 in damage (1956 USD).[10] The cost to downtime in production was greater than the damage Flossy created to the oil rigs.[11] There was no loss of life.[12] Due to the impact of Flossy on oil refining in the Gulf of Mexico, the American Petroleum Institute formed a committee called Fundamental Research on Weather Forecasting. Their goal was to use mathematical models and historic data to better predict hurricane formation and path. Studies went on into 1962, but no reliable forecast mechanism was found.[11]
United States
In Louisiana, wind-blown sand from the beach spread over area highways due to the hurricane.[13] A total of 16.70 inches (424 mm) of rainfall fell at Golden Meadow, Louisiana. Burrwood, Louisiana's pressure fell to 29.03 inHg (983.1 hPa or mb). Hundreds lost their homes in the storm. The storm surge was significant enough to submerge Grand Isle, Louisiana. At Ostrica Lock, the storm tide reached 13 feet (4.0 m). Extensive coastal erosion was caused by the cyclone across the Mississippi Delta. In New Orleans, Louisiana, about 2.5 square miles (6.5 km2) were flooded as portions of the seawall were overtopped. Cattle drowned across the region, and crops such as citrus, sugar cane, and pecan were heavily damaged.[14]
Winds as high as 66 mph (106 km/h) struck coastal Mississippi.[15] A total of 16.30 inches (414 mm) of rain fell at Gulf Shores. In Montgomery, Alabama, the tent used to house the Eastern Hills Baptist Church was destroyed.[16] Across northern Florida, southern Alabama, and Georgia, Flossy was considered drought-breaking.[17] In southwest Georgia, high winds from Flossy damaged the corn and cotton crops.[13] The lowest pressure reported was 28.93 inches/979.8 hPa or mb at Pensacola Naval Air Station.[5] The storm tide at Laguna Beach, Florida, reached 7.4 feet (2.3 m) above mean sea level. As tides damaged some piers and small craft, and resulted in severe beach erosion. At least three tornadoes touched down throughout northern Florida in association with Flossy. One damaged or destroyed numerous structures in Gulf County; two others in Jefferson and Suwannee counties caused little or no damage.[3]
Further northeast, rains brought by Flossy helped relieve drought conditions across the Carolinas,[13] and were considered beneficial.[5] Winds as high as 45 miles per hour (72 km/h) were recorded in Washington, D.C.. The gas screw vessel Mary Anne was lost at the Hampton Roads Naval Base.[18] High tides caused by the then-extratropical cyclone led to water 2.5 feet (0.76 m) deep in sections of Norfolk.[5] The Back River Light collapsed during the storm, 127 years after it was built.[19] Severe flooding occurred along the state's coastline, including interior bays. This occurred despite efforts to curb the storm surge with 500 tons (454 tonnes) of broken rock.[20]
Total damages to Louisiana, Florida, Alabama, the Carolinas, and Virginia was $24.8 million (1956 USD).[3][4]
See also
- Other storms of the same name
- List of wettest tropical cyclones in Louisiana
- List of Florida hurricanes (1950–1974)
References
- ↑ National Hurricane Center. Atlantic Hurricane Database. Retrieved on 2008-02-27.
- ↑ W. F. Stokes, Jr. Remembering Hurricane Flossie. Retrieved on 2007-02-01.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Barnes, pp. 195
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Canadian Hurricane Center. Storms of 1956. Retrieved on 2007-02-01.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Gordon E. Dunn, Walter R. Davis, and Paul L. Moore. Hurricane Season of 1956. Retrieved on 2007-02-02.
- ↑ The Corpus Christi Times. Hurricane Believed Forming in Gulf. Retrieved on 2008-02-02.
- ↑ Associated Press. 'Flossy' Picks Up Added Fury. Retrieved on 2008-02-02.
- ↑ BrightNet Oklahoma. Ardmore Air Force Base: 1953–59. Retrieved on 2006-02-02.
- ↑ "History of the Offshore Oil and Gas Industry in Southern Louisiana Interim Report: Volume I: Papers on the Evolving Offshore Industry" (PDF). page 17. Retrieved on 2007-02-06.
- ↑ U. S. Department of the Interior Minerals Management Service. History of the Offshore Oil and Gas Industry in Southern Louisiana Interim Report: Volume I: Papers on the Evolving Offshore Industry. Retrieved on 2007-02-02.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Benfield Corporate Risk. A 65 Year history of hurricanes and some of their resultant impacts on the offshore industry. Retrieved on 2007-02-01.
- ↑ Dr. J. C. Jones and D. O'Shea. Gulf Coast hurricanes and their impact on offshore oil production. Retrieved on 2007-02-01.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 D. A. Richter and E. A. DiLoreto. The Transformation of Hurricane Flossy into an Extratropical Cyclone, September 25–29, 1956. Retrieved on 2008-02-03.
- ↑ David M. Roth. Louisiana Hurricane History: Late 20th Century. Retrieved on 2007-02-02.
- ↑ Charles S. Sullivan. Hurricanes of the Mississippi Gulf Coast: 1717 to Present. Gulf Publishing Company: Biloxi, 1984.
- ↑ Alicia Morris Atcheson. Eastern Hills Baptist Celebrates 50 Years. Retrieved on 2007-02-01.
- ↑ Associated Press. Hurricane Flossy Diminished Into Rainstorm Over Southern Georgia. Retrieved on 2008-02-02.
- ↑ David M. Roth and Hugh Cobb.Virginia Hurricane History: Late Twentieth Century. Retrieved on 2007-02-02.
- ↑ "Historic Light Station Information and Photography: Virginia". United States Coast Guard Historian's Office. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ↑ The City of Lewes, Delaware. LEWES FLOOD FACTS AND THE NATIONAL FLOOD INSURANCE PROGRAM. Retrieved on 2007-02-02.
Further reading
- U. S. Daily Weather Map Series
- Jay Barnes (2007). Florida's Hurricane History. UNC Press. ISBN 0-8078-3068-2.
| |||||||||||||