Hindi
| Hindi | |
|---|---|
|
हिन्दी or मानक हिन्दी Hindī or Mānak Hindī | |
|
The word "Hindi" in Devanagari script | |
| Pronunciation | Hindustani pronunciation: [ˈmaːnək ˈɦin̪d̪iː] |
| Native to |
India Significant communities in South Africa, Nepal |
Native speakers | 180 million (1991)[1] |
|
Indo-European
| |
|
Devanagari (Brahmic) Hindi Braille | |
| Signed Hindi | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
| Regulated by | Central Hindi Directorate[4] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 |
hi |
| ISO 639-2 |
hin |
| ISO 639-3 |
hin |
Linguist list |
hin-hin |
| Glottolog |
hind1269[5] |
| Linguasphere |
59-AAF-qf |
|
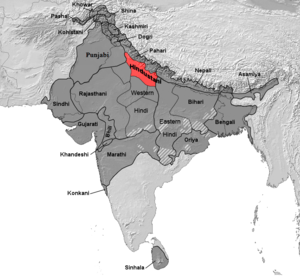
Areas (red) where Hindustani (Khariboli/Kauravi) is the native language, compared to all Indic languages (dark grey) | |
Hindi (हिन्दी), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (मानक हिन्दी), is a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language. Hindustani is the native language of most people living in Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, and Rajasthan.[6] Modern Standard Hindi is one of the official languages of India.
As of 2009, the best figure Ethnologue could find for speakers of actual Hindustani Hindi was 180 million in 1991.[1] In the 2001 Indian census, 258 million (258,000,000) people in India reported Hindi to be their native language.[7] However, this number included millions of people who were native speakers of related languages but who thought of their speech as a dialect of Hindi.
Official status

Article 343 (1) of the Indian constitution states "The official language of the Union shall be Hindi in Devanagari script. The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of the Union shall be the international form of Indian numerals."[3]
Article 351 of the Indian constitution states "It shall be the duty of the Union to promote the spread of the Hindi language, to develop it so that it may serve as a medium of expression for all the elements of the composite culture of India and to secure its enrichment by assimilating without interfering with its genius, the forms, style and expressions used in Hindustani and in the other languages of India specified in the Eighth Schedule, and by drawing, wherever necessary or desirable, for its vocabulary, primarily on Sanskrit and secondarily on other languages."[8]
It was envisioned that Hindi would become the sole working language of the Union Government by 1965 (per directives in Article 344 (2) and Article 351),[9] with state governments being free to function in the language of their own choice. However, widespread resistance to the imposition of Hindi on non-native speakers, especially in South India (such as the those in Tamil Nadu), Maharashtra, and West Bengal, led to the passage of the Official Languages Act of 1963, which provided for the continued use of English indefinitely for all official purposes, although the constitutional directive for the Union Government to encourage the spread of Hindi was retained and has strongly influenced its policies.
At the state level, Hindi is the official language of the following Indian states: Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttarakhand. Each may also designate a "co-official language"; in Uttar Pradesh, for instance, depending on the political formation in power, this language is generally Urdu. Similarly, Hindi is accorded the status of official language in the following Union Territories: Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra & Nagar Haveli, Daman & Diu, National Capital Territory.
National-language status for Hindi is a long-debated theme. An Indian court clarified that Hindi is not the national language of India because the constitution does not mention it as such.[10]
Outside of Asia, Hindi is also an official language in Fiji. The Constitution of Fiji declares three official languages: English, Fijian, and Hindi. The Hindi spoken there is Fiji Hindi, a form of Awadhi, not Modern Standard Hindi's Hindustani.
History
The dialect of Hindustani on which Standard Hindi is based is Khariboli, the vernacular of Delhi and the surrounding western Uttar Pradesh and southern Uttarakhand . This dialect acquired linguistic prestige in the Mughal Empire (1600s) and became known as Urdu, "the language of the court". In the late 19th century, the movement standardising a written language from Khariboli, for the Indian masses in North India, started to standardise Hindi as a separate language from Urdu, which was learnt by the elite. In 1881 Bihar accepted Hindi as its sole official language, replacing Urdu, and thus became the first state of India to adopt Hindi.
After independence, the government of India instituted the following conventions:
- standardisation of grammar: In 1954, the Government of India set up a committee to prepare a grammar of Hindi; The committee's report was released in 1958 as "A Basic Grammar of Modern Hindi"
- standardisation of the orthography, using the Devanagari script, by the Central Hindi Directorate of the Ministry of Education and Culture to bring about uniformity in writing, to improve the shape of some Devanagari characters, and introducing diacritics to express sounds from other languages.
The Constituent Assembly adopted Hindi as the Official Language of the Union on 14 September 1949. Hence, it is celebrated as Hindi Day.
Comparison with Modern Standard Urdu
Linguistically, Hindi and Urdu are the same language. Hindi is written in the Devanagari script and uses more Sanskrit words, whereas Urdu is written in the Perso-Arabic script and uses more Arabic and Persian words.
Script
Hindi is written in Devanagari script (देवनागरी लिपि devanāgarī lipi) also called Nagari. Devanagari consists of 11 vowels and 33 consonants and is written from left to right.
Sanskrit vocabulary
Formal Standard Hindi draws much of its academic vocabulary from Sanskrit. Standard Hindi loans words are divided into five principal categories:
- Tatsam (तत्सम / same as that) words: These are words which are spelled the same in Hindi as in Sanskrit (except for the absence of final case inflections).[11] They include words inherited from Sanskrit via Prakrit which have survived without modification (e.g. Hindustani nām / Sanskrit nāma, "name"; Hindustani Suraj / Sanskrit Surya, "sun"),[12] as well as forms borrowed directly from Sanskrit in more modern times (e.g. prārthanā, "prayer").[13] Pronunciation, however, conforms to Hindi norms and may differ from that of classical Sanskrit. Amongst nouns, the tatsam word could be the Sanskrit non-inflected word-stem, or it could be the nominative singular form in the Sanskrit nominal declension.
- Ardhatatsam (अर्धतत्सम) words: Such words have typically undergone sound changes subsequent to being borrowed.
- Tadbhav (तद्भव / born of that) words: These are words that are spelled differently from in Sanskrit but are derivable from a Sanskrit prototype by phonological rules (e.g. Sanskrit karma, "deed" becomes Pali kamma, and eventually Hindi kām, "work").[11]
- Deshaj (देशज) words: These are words that were not borrowings but do not derive from attested Indo-Aryan words either. Belonging to this category are onomatopoetic words.
- Videshī (विदेशी/ 'Foreign') words: these include all loanwords purportedly from sources other than Indo-Aryan, but the most frequent sources identified in this category have been not only Persian and Arabic, but also the Indo-European Portuguese and English.
The Hindi standard, from which much of the Persian, Arabic and English vocabulary has been purged and replaced by neologisms compounding tatsam words, is called Shuddha Hindi (pure Hindi), and is viewed as a more prestigious dialect over other more colloquial forms of Hindi.
Excessive use of tatsam words creates problems for native speakers. They may have Sanskrit consonant clusters which do not exist in native Hindi. The educated middle class of India may be able to pronounce such words, but others have difficulty. Persian and Arabic vocabulary given 'authentic' pronunciations cause similar difficulty.
Literature
Hindi literature is broadly divided into four prominent forms or styles, being Bhakti (devotional – Kabir, Raskhan); Shringar (beauty – Keshav, Bihari); Virgatha (extolling brave warriors); and Adhunik (modern).
Medieval Hindi literature is marked by the influence of Bhakti movement and the composition of long, epic poems. It was primarily written in other varieties of Hindi, particularly Avadhi and Braj Bhasha, but also in Khariboli. During the British Raj, Hindustani became the prestige dialect. Hindustani with heavily Sanskritised vocabulary or Sahityik Hindi (Literary Hindi) was popularised by the writings of Swami Dayananda Saraswati, Bhartendu Harishchandra and others. The rising numbers of newspapers and magazines made Hindustani popular with the educated people. Chandrakanta, written by Devaki Nandan Khatri, is considered the first authentic work of prose in modern Hindi. The person who brought realism in the Hindi prose literature was Munshi Premchand, who is considered as the most revered figure in the world of Hindi fiction and progressive movement.
The Dwivedi Yug ("Age of Dwivedi") in Hindi literature lasted from 1900 to 1918. It is named after Mahavir Prasad Dwivedi, who played a major role in establishing the Modern Hindi language in poetry and broadening the acceptable subjects of Hindi poetry from the traditional ones of religion and romantic love.
In the 20th century, Hindi literature saw a romantic upsurge. This is known as Chhayavaad (shadowism) and the literary figures belonging to this school are known as Chhayavaadi. Jaishankar Prasad, Suryakant Tripathi 'Nirala', Mahadevi Varma and Sumitranandan Pant, are the four major Chhayavaadi poets.
Uttar Adhunik is the post-modernist period of Hindi literature, marked by a questioning of early trends that copied the West as well as the excessive ornamentation of the Chhayavaadi movement, and by a return to simple language and natural themes.
Internet

Hindi has a presence on the internet,[14] but due to lack of standard encoding, search engines cannot be used to locate text.[15] Hindi is one of the seven languages of India that can be used to make web addresses.(URLs).[16] Hindi has also impacted the language of technology,[17] with words such as 'avatar' (meaning a spirit taking a new form) used in computer sciences, artificial intelligence and even robotics.
Sample text
The following is a sample text in High Hindi, of the Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (by the United Nations):
- Hindi
- अनुच्छेद 1 — सभी मनुष्यों को गौरव और अधिकारों के विषय में जन्मजात स्वतन्त्रता और समानता प्राप्त हैं। उन्हें बुद्धि और अन्तरात्मा की देन प्राप्त है और परस्पर उन्हें भाईचारे के भाव से बर्ताव करना चाहिए।
- Transliteration (IAST)
- Anucched 1 — Sabhī manuṣyõ ko gaurav aur adhikārõ ke vishay mẽ janmajāt svatantratā aur samāntā prāpt hai. Unhẽ buddhi aur antarātmā kī den prāpt hai aur paraspar unhẽ bhāīchāre ke bhāv se bartāv karnā cāhie.
- Transcription (IPA)
- ənʊtʃʰːeːd̪ eːk — səbʱiː mənʊʃjõː koː ɡɔːɾəʋ ɔːr əd̪ʱɪkaːɾõ keː maːmleː mẽː dʒənmədʒaːt̪ sʋət̪ənt̪ɾət̪aː pɾaːpt̪ hɛː. ʊnʱẽ bʊd̪ʱːɪ ɔːɾ ənt̪əɾaːt̪maː kiː d̪eːn pɾaːpt̪ hɛː ɔːɾ pəɾəspəɾ ʊnʱẽː bʱaːiːtʃaːɾeː keː bʱaːʋ seː bəɾt̪aːʋ kəɾnə tʃaːhɪeː.
- Gloss (word-to-word)
- Article 1 — All human-beings to dignity and rights' matter in from-birth freedom and equality acquired is. Them to reason and conscience's endowment acquired is and always them to brotherhood's spirit with behavior to do should.
- Translation (grammatical)
- Article 1 — All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
See also
- Hindi Divas – the official day to celebrate Hindi as a language.
- Hindustani (covers phonology, grammar, and orthography)
- Anti-Hindi agitations of Tamil Nadu
- List of Sanskrit and Persian roots in Hindi
- Languages of India and Languages with official status in India
- List of languages by number of native speakers in India
- The list of Hindi words at Wiktionary, the free dictionary
- List of English words of Hindi or Urdu origin
References
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hindi at Ethnologue (16th ed., 2009)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hindustani (2005). Keith Brown, ed. Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics (2 ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 0-08-044299-4.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Sequence of events with reference to official language of the Union".
- ↑ "Central Hindi Directorate: Introduction".
- ↑ Nordhoff, Sebastian; Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2013). "Hindi". Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
- ↑ Hindi (2005). Keith Brown, ed. Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics (2 ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 0-08-044299-4.
- ↑ "Data by speakers of language". Census of India. 2001. Retrieved 18 February 2013.
- ↑ "Constitution of India". Retrieved 21 March 2012.
- ↑ "Rajbhasha" (PDF) (in Hindi & English). india.gov.in. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 January 2012.
- ↑ "Hindi, not a national language: Court". The Hindu. 25 January 2010. Retrieved 20 March 2014.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Masica, p. 65
- ↑ Masica, p. 66
- ↑ Masica, p. 67
- ↑ "Usage of Hindi for websites". W3Techs.com. Retrieved 9 September 2013.
- ↑ Pann Yu Mon, Madhukar Pathak (2012). "Search Engines and Asian Languages". In Laurent Vannini, Hervé le Crosnier. Net.lang : towards the multilingual cyberspace (PDF). Caen: C&F éd. coord by Maaya Network. p. 174. ISBN 978-2-915825-09-1. Retrieved 9 September 2013.
- ↑ Eluvangal, Sreejiraj (4 April 2011). "URLs in 7 regional languages soon". DNA. Retrieved 9 September 2013.
- ↑ "Silicon Valley gets linguistic enlightenment from India". Retrieved 28 October 2013.
Bibliography
- Bhatia, Tej K. (11 September 2002). Colloquial Hindi: The Complete Course for Beginners. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-134-83534-8. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- Grierson, G. A. Linguistic Survey of India Vol I-XI, Calcutta, 1928, ISBN 81-85395-27-6 (searchable database).
- Koul, Omkar N. (2008). Modern Hindi grammar (PDF). Springfield, VA: Dunwoody Press. ISBN 978-1-931546-06-5. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- McGregor, R.S. (1995). Outline of Hindi grammar: With exercises (3. ed. ed.). Oxford: Clarendon Pr. ISBN 0-19-870008-3. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- Masica, Colin (1991). The Indo-Aryan Languages. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-29944-2.
- Ohala, Manjari (1999). "Hindi". In International Phonetic Association. Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: a Guide to the Use of the International Phonetic Alphabet. Cambridge University Press. pp. 100–103. ISBN 978-0-521-63751-0.
- Sadana, Rashmi (2012). English Heart, Hindi Heartland: the Political Life of Literature in India. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-26957-6. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- Shapiro, Michael C. (2001). "Hindi". In Garry, Jane; Rubino, Carl. An encyclopedia of the world's major languages, past and present. New England Publishing Associates. pp. 305–309.
- Shapiro, Michael C. (2003). "Hindi". In Cardona, George; Jain, Dhanesh. The Indo-Aryan Languages. Routledge. pp. 250–285. ISBN 978-0-415-77294-5.
- Snell, Rupert; Weightman, Simon (1989). Teach Yourself Hindi (2003 ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-142012-9.
- Taj, Afroz (2002) A door into Hindi. Retrieved 8 November 2005.
- Tiwari, Bholanath ([1966] 2004) हिन्दी भाषा (Hindī Bhasha), Kitab Pustika, Allahabad, ISBN 81-225-0017-X.
Dictionaries
- John Thompson Platts (1884), A dictionary of Urdū, classical Hindī, and English (reprint ed.), LONDON: H. Milford, p. 1259, retrieved 2011-07-06Oxford University
- Academic Room Hindi Dictionary Mobile App developed in the Harvard Innovation Lab (iOS, Android and Blackberry)
- McGregor, R.S. (1993), Oxford Hindi–English Dictionary (2004 ed.), Oxford University Press, USA.
Further reading
- Bhatia, Tej K A History of the Hindi Grammatical Tradition. Leiden, Netherlands & New York, NY: E.J. Brill, 1987. ISBN 90-04-07924-6
- Sadana, Rashmi, "Managing Hindi," The Caravan. April 2012.
External links
| Hindi edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
| Wikivoyage has a phrasebook for Hindi. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||