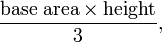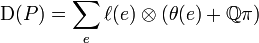Hilbert's third problem
The third on Hilbert's list of mathematical problems, presented in 1900, was the first to be solved. The problem is related to the following question: given any two polyhedra of equal volume, is it always possible to cut the first into finitely many polyhedral pieces which can be reassembled to yield the second? Based on earlier writings by Gauss,[1] Hilbert conjectured that this is not always possible. This was confirmed within the year by his student Max Dehn, who proved that the answer in general is "no" by producing a counterexample.
The answer for the analogous question about polygons in 2 dimensions is "yes" and had been known for a long time; this is the Bolyai–Gerwien theorem.
History and motivation
The formula for the volume of a pyramid,
had been known to Euclid, but all proofs of it involve some form of limiting process or calculus, notably the method of exhaustion or, in more modern form, Cavalieri's principle. Similar formulas in plane geometry can be proven with more elementary means. Gauss regretted this defect in two of his letters. This was the motivation for Hilbert: is it possible to prove the equality of volume using elementary "cut-and-glue" methods? Because if not, then an elementary proof of Euclid's result is also impossible.
Dehn's answer
Dehn's proof is an instance in which abstract algebra is used to prove an impossibility result in geometry. Other examples are doubling the cube and trisecting the angle.
We call two polyhedra scissors-congruent if the first can be cut into finitely many polyhedral pieces that can be reassembled to yield the second. Obviously, any two scissors-congruent polyhedra have the same volume. Hilbert asks about the converse.
For every polyhedron P, Dehn defines a value, now known as the Dehn invariant D(P), with the following property:
- If P is cut into two polyhedral pieces P1 and P2 with one plane cut, then D(P) = D(P1) + D(P2).
From this it follows
- If P is cut into n polyhedral pieces P1,...,Pn, then D(P) = D(P1) + ... + D(Pn)
and in particular
- If two polyhedra are scissors-congruent, then they have the same Dehn invariant.
He then shows that every cube has Dehn invariant zero while every regular tetrahedron has non-zero Dehn invariant. This settles the matter.
A polyhedron's invariant is defined based on the lengths of its edges and the angles between its faces. Note that if a polyhedron is cut into two, some edges are cut into two, and the corresponding contributions to the Dehn invariants should therefore be additive in the edge lengths. Similarly, if a polyhedron is cut along an edge, the corresponding angle is cut into two. However, normally cutting a polyhedron introduces new edges and angles; we need to make sure that the contributions of these cancel out. The two angles introduced will always add up to π; we therefore define our Dehn invariant so that multiples of angles of π give a net contribution of zero.
All of the above requirements can be met if we define D(P) as an element of the tensor product of the real numbers R and the quotient space R/(Qπ) in which all rational multiples of π are zero. For the present purposes, it suffices to consider this as a tensor product of Z-modules (or equivalently of abelian groups). However, the more difficult proof of the converse (see below) makes use of the vector space structure: Since both of the factors are vector spaces over Q, the tensor product can be taken over Q.
Let ℓ(e) be the length of the edge e and θ(e) be the dihedral angle between the two faces meeting at e, measured in radians. The Dehn invariant is then defined as
where the sum is taken over all edges e of the polyhedron P.
Further information
In light of Dehn's theorem above, one might ask "which polyhedra are scissors-congruent"? Sydler (1965) showed that two polyhedra are scissors-congruent if and only if they have the same volume and the same Dehn invariant. Børge Jessen later extended Sydler's results to four dimensions. In 1990, Dupont and Sah provided a simpler proof of Sydler's result by reinterpreting it as a theorem about the homology of certain classical groups.
Debrunner showed in 1980 that the Dehn invariant of any polyhedron with which all of three-dimensional space can be tiled periodically is zero.
Original question
Hilbert's original question was more complicated: given any two tetrahedra T1 and T2 with equal base area and equal height (and therefore equal volume), is it always possible to find a finite number of tetrahedra, so that when these tetrahedra are glued in some way to T1 and also glued to T2, the resulting polyhedra are scissors-congruent?
Dehn's invariant can be used to yield a negative answer also to this stronger question.
See also
References
- ↑ Carl Friedrich Gauss: Werke, vol. 8, pp. 241 and 244
- Dehn, Max (1901). "Ueber den Rauminhalt". Mathematische Annalen 55 (3): 465–478. doi:10.1007/BF01448001.
- Sydler, J.-P. (1965). "Conditions nécessaires et suffisantes pour l'équivalence des polyèdres de l'espace euclidien à trois dimensions". Comment. Math. Helv. 40: 43–80. doi:10.5169/seals-30629.
- Dupont, Johan; Sah, Chih-Han (1990). "Homology of Euclidean groups of motions made discrete and Euclidean scissors congruences". Acta Math. 164 (1–2): 1–27. doi:10.1007/BF02392750.
- Debrunner, Hans E. (1980). "Über Zerlegungsgleichheit von Pflasterpolyedern mit Würfeln". Arch. Math. (Basel) 35 (6): 583–587. doi:10.1007/BF01235384.
- Schwartz, Rich (2010). "The Dehn–Sydler Theorem Explained".
- Koji, Shiga; Toshikazu Sunada (2005), A Mathematical Gift, III: The Interplay Between Topology, Functions, Geometry, and Algebra, American Mathematical Society
External links
- Proof of Dehn's Theorem at Everything2
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Dehn Invariant", MathWorld.
- Dehn Invariant at Everything2
- Hazewinkel, M. (2001), "Dehn invariant", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4