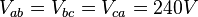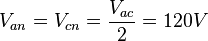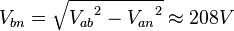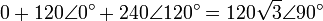High-leg delta

High-leg delta (also known as wild-leg or red-leg delta) is a type of electrical service connection for three-phase electric power installations. It is one of the several types of three-phase service setups. It is used to provide an additional voltage that is half the phase-to-phase voltage. For example, 120 V lighting equipment and 240 volt motors can be fed off the same 3-phase 240 volt distribution system, where relatively a small part of the load is lighting.
Supply
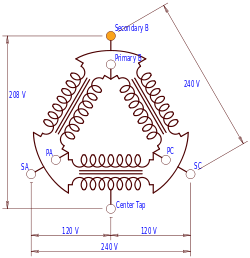

High-leg delta service is supplied in one of two ways. One is by a transformer having four wires coming out of the secondary, the three phases, plus a neutral connected as a center-tap on one of the windings. Another method requires two transformers. One transformer is connected to one phase of the overhead primary distribution circuit to provide the 'lighting' side of the circuit (this will be the larger of the two transformers), and a second transformer is connected to another phase on the circuit and its secondary is connected to one side of the 'lighting' transformer secondary, and the other side of this transformer is brought out as the 'high leg'. The voltages between the three phases are the same in magnitude, however the voltage magnitudes between a particular phase and the neutral vary. The phase-to-neutral voltage of two of the phases will be half of the phase-to-phase voltage. The remaining phase-to-neutral voltage will be √3 times half the phase-to-phase voltage. In some applications, the transformer is connected such that the 'B' phase is the 'high' leg.
An alternative system is a corner-grounded delta, [1] but this system does not provide the half phase-to-phase voltage useful for lighting.
Explanation
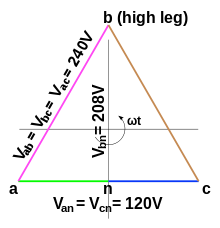
Consider the low-voltage side of a 120/240 V high leg delta connected transformer, where the 'b' phase is the 'high' leg. The line-to-line voltage magnitudes are all the same:
Because the winding between the 'a' and 'c' phases is center-tapped, the line-to-neutral voltages for these phases are as follows:
But the phase-neutral voltage for the 'b' phase is different:
This can be proven by writing a KVL equation, using angle notation, starting from the grounded neutral:
or:
Advantages
If the "hot" wire is ignored, the system is just the split-phase system, which is familiar.
Where the three-phase load is small relative to the total load, two individual transformers may be used instead of the three for a "full delta" or a three-phase transformer, thus providing a variety of voltages at reduced cost. This is called "open-delta high-leg", and has a reduced capacity relative to a full delta.[2][3][4]
Disadvantages
Phase balancing is not great, but it is not worse than split-phase system.
One of the phase-to-neutral voltage (phase 'B') is different from the other two. This can be fixed with an autotransformer, but that is an added expense.
Commonly there is a high-leg to neutral load limit.[5] One transformer manufacturer's page suggests that High-leg to neutral loading to not exceed 5% of transformer capacity.[6]
Applications
It is often found in older installations. This type of service is usually supplied using 240 V line-to-line and 120 V line-to-neutral. In some ways, the high leg delta service provides the best of both worlds: a line-to-line voltage that is higher than the usual 208 V that most three-phase services have, and a line-to-neutral voltage (on two of the phases) sufficient for connecting appliances and lighting. Thus, large pieces of equipment will draw less current than with 208 V, requiring smaller wire and breaker sizes. Lights and appliances requiring 120 V can be connected to phases 'A' and 'C' without requiring an additional step-down transformer.
In the United States, according to Article 110.15 of the 2005 National Electrical Code, panelboards connected to this type of transformer must explicitly identify the high leg, preferably by coloring it orange.
Current practice is to give separate services for single-phase and three-phase loads, e.g., 120 V split-phase (lighting etc.) and 240 V to 600 V three-phase (for large motors). However, many jurisdictions forbid more than one class for a premises' service, and the choice may come down to 120/240 split-phase, 208 single-phase or three-phase (delta), 120/208 three-phase (wye), or 277/480 three-phase (wye).
See also
- Transformer
- Three-phase electric power
- Electric power distribution
- Mains electricity
- Mains electricity by country
- Scott-T transformer
References
- ↑ "Corner-Grounded Delta (Grounded B Phase) Systems" (PDF). Schneider Electric. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- ↑ "Transformer Basics Chapter 3". Federalpacific.com. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- ↑ Electrician's Calculations Manual - Nick Fowler - Google Boeken. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- ↑ Illustrated Guide to the 1999 National Electrical Code - John E. Traister, Bradford Maher - Google Boeken. Books.google.com. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- ↑ Fowler, Nick (2011). Electrician's Calculations Manual 2nd Edition. McGraw-Hill. pp. 3–5. ISBN 9780071770170.
- ↑ Federal pacific
- sea.siemens.com
- NFPA 70: National Electrical Code, 2005 Ed.
- Square D Bulletin on Corner-Grounded Delta