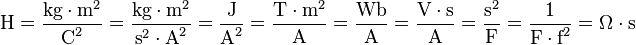Henry (unit)
| Henry | |
|---|---|
|
An inductor composed of a wire wound around a magnetic core used to confine and guide the induced magnetic field. | |
| Unit information | |
| Unit system | SI derived unit |
| Unit of | Inductance |
| Symbol | H |
| Named after | Joseph Henry |
| In SI base units: | 1 H = 1 kg·m2·s−2·A−2 |
In physics, and electronics, the henry (symbol H) is the SI derived unit of inductance.[1] It is named after Joseph Henry (1797–1878), the American scientist who discovered electromagnetic induction independently of and at about the same time as Michael Faraday (1791–1867) in England.[2] The magnetic permeability of a vacuum is 4π×10−7 H/m (henry per meter).
The National Institute of Standards and Technology provides guidance for American users of SI to write the plural as henries.[3]:31
Definition
If the rate of change of current in a circuit is one ampere per second and the resulting electromotive force is one volt, then the inductance of the circuit is one henry. Other equivalent combinations of SI units are as follows:[4]
where
A = ampere,
C = coulomb,
F = farad,
J = joule,
kg = kilogram,
m = meter,
s = second,
Wb = weber,
T = tesla,
V = volt,
f = frequency
Ω = ohm.
Yrneh
The name "Yrneh" (reversing the letters of "Henry") is said to have been used for a measure of reluctance, the reciprocal of the Henry, defined as: 1 Yrneh = 1 Henry-1.[5] This word is not listed in the Oxford English Dictionary.[6]
See also
Notes and references
- ↑ Rowlett, Russ. "How Many? A Dictionary of Units of Measurement". University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
- ↑ Herbert S. Bailey, Jr. "A Princeton Companion".
- ↑ Ambler Thompson & Barry N. Taylor (2008). "NIST Special Publication 811: Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI)" (PDF). National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 2013-03-21.
- ↑ "Essentials of the SI: Base & derived units". The NIST Reference on Constants, Units and Uncertainty. National Institute of Standards and Technology.
- ↑ Cardarelli, F. (2003). Encyclopaedia of Scientific Units, Weights and Measures. Their SI Equivalences and Origins. Springer. p. 24. ISBN 978-1-4471-1122-1.
- ↑ Full OED consulted online 1 March 2015
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||