HIST2H3C
| Histone cluster 2, H3c | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
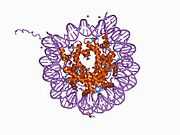
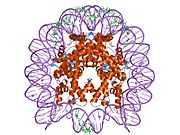
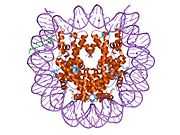
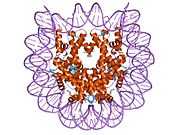
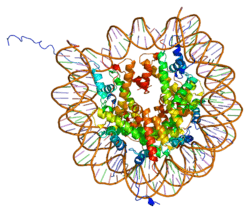 PDB rendering based on 1aoi. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | HIST2H3C ; H3; H3.2; H3/M; H3F2; H3FM; H3FN | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 142780 MGI: 2448355 HomoloGene: 134475 GeneCards: HIST2H3C Gene | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 126961 | 625328 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000183598 | ENSMUSG00000016559 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | Q71DI3 | P02301 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_021059 | NM_178216 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_066403 | NP_835734 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 149.78 – 149.79 Mb | Chr 1: 180.8 – 180.81 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
Histone H3.2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST2H3C gene.[1][2][3]
Function
Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. This structure consists of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a nucleosome, an octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H3 family. Transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails; instead, they contain a palindromic termination element. This gene is found in a histone cluster on chromosome 1. This gene is one of four histone genes in the cluster that are duplicated; this record represents the telomeric copy.[3]
Interactions
HIST2H3C has been shown to interact with NCOA6.[4]
References
- ↑ Marzluff WF, Gongidi P, Woods KR, Jin J, Maltais LJ (Oct 2002). "The human and mouse replication-dependent histone genes". Genomics 80 (5): 487–498. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(02)96850-3. PMID 12408966.
- ↑ Marashi F, Helms S, Shiels A, Silverstein S, Greenspan DS, Stein G et al. (Jul 1986). "Enhancer-facilitated expression of prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes using human histone gene 5' regulatory sequences". Biochem Cell Biol 64 (4): 277–289. doi:10.1139/o86-039. PMID 3013246.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Entrez Gene: HIST2H3C histone cluster 2, H3c".
- ↑ Goo YH, Sohn YC, Kim DH, Kim SW, Kang MJ, Jung DJ et al. (Jan 2003). "Activating signal cointegrator 2 belongs to a novel steady-state complex that contains a subset of trithorax group proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (1): 140–149. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.1.140-149.2003. PMC 140670. PMID 12482968.
Further reading
- Green L, Van Antwerpen R, Stein J, Stein G, Tripputi P, Emanuel B et al. (1984). "A major human histone gene cluster on the long arm of chromosome 1". Science 226 (4676): 838–840. doi:10.1126/science.6494913. PMID 6494913.
- Ohe Y, Iwai K (1982). "Human spleen histone H3. Isolation and amino acid sequence". J. Biochem. 90 (4): 1205–11. PMID 7309716.
- Díaz-Jullien C, Pérez-Estévez A, Covelo G, Freire M (1996). "Prothymosin alpha binds histones in vitro and shows activity in nucleosome assembly assay". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1296 (2): 219–27. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(96)00072-6. PMID 8814229. Vancouver style error (help)
- Albig W, Doenecke D (1998). "The human histone gene cluster at the D6S105 locus". Hum. Genet. 101 (3): 284–294. doi:10.1007/s004390050630. PMID 9439656.
- El Kharroubi A, Piras G, Zensen R, Martin MA (1998). "Transcriptional activation of the integrated chromatin-associated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (5): 2535–44. PMC 110633. PMID 9566873.
- Ahn J, Gruen JR (1999). "The genomic organization of the histone clusters on human 6p21.3". Mamm. Genome 10 (7): 768–770. doi:10.1007/s003359901089. PMID 10384058.
- Goto H, Tomono Y, Ajiro K, Kosako H, Fujita M, Sakurai M et al. (1999). "Identification of a novel phosphorylation site on histone H3 coupled with mitotic chromosome condensation". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (36): 25543–25549. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.36.25543. PMID 10464286.
- Deng L, de la Fuente C, Fu P, Wang L, Donnelly R, Wade JD et al. (2001). "Acetylation of HIV-1 Tat by CBP/P300 increases transcription of integrated HIV-1 genome and enhances binding to core histones". Virology 277 (2): 278–295. doi:10.1006/viro.2000.0593. PMID 11080476.
- Lachner M, O'Carroll D, Rea S, Mechtler K, Jenuwein T (2001). "Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins". Nature 410 (6824): 116–120. doi:10.1038/35065132. PMID 11242053.
- Shankaranarayanan P, Chaitidis P, Kühn H, Nigam S (2001). "Acetylation by histone acetyltransferase CREB-binding protein/p300 of STAT6 is required for transcriptional activation of the 15-lipoxygenase-1 gene". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (46): 42753–42760. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102626200. PMID 11509556. Vancouver style error (help)
- Deng L, Wang D, de la Fuente C, Wang L, Li H, Lee CG et al. (2001). "Enhancement of the p300 HAT activity by HIV-1 Tat on chromatin DNA". Virology 289 (2): 312–326. doi:10.1006/viro.2001.1129. PMID 11689053.
- Goto H, Yasui Y, Nigg EA, Inagaki M (2002). "Aurora-B phosphorylates Histone H3 at serine28 with regard to the mitotic chromosome condensation". Genes Cells 7 (1): 11–17. doi:10.1046/j.1356-9597.2001.00498.x. PMID 11856369.
- Ganesan S, Silver DP, Greenberg RA, Avni D, Drapkin R, Miron A et al. (2002). "BRCA1 supports XIST RNA concentration on the inactive X chromosome". Cell 111 (3): 393–405. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01052-8. PMID 12419249.
- Goo YH, Sohn YC, Kim DH, Kim SW, Kang MJ, Jung DJ et al. (2003). "Activating signal cointegrator 2 belongs to a novel steady-state complex that contains a subset of trithorax group proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (1): 140–149. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.1.140-149.2003. PMC 140670. PMID 12482968.
- Preuss U, Landsberg G, Scheidtmann KH (2003). "Novel mitosis-specific phosphorylation of histone H3 at Thr11 mediated by Dlk/ZIP kinase". Nucleic Acids Res. 31 (3): 878–885. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg176. PMC 149197. PMID 12560483.
- Yoon HG, Chan DW, Huang ZQ, Li J, Fondell JD, Qin J et al. (2003). "Purification and functional characterization of the human N-CoR complex: the roles of HDAC3, TBL1 and TBLR1". EMBO J. 22 (6): 1336–1346. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg120. PMC 151047. PMID 12628926.
- Lusic M, Marcello A, Cereseto A, Giacca M (2004). "Regulation of HIV-1 gene expression by histone acetylation and factor recruitment at the LTR promoter". EMBO J. 22 (24): 6550–6561. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg631. PMC 291826. PMID 14657027.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||