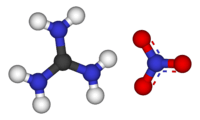
Guanidine nitrate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Guanidinium nitrate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 506-93-4 | |
| ChemSpider | 10049 |
| EC number | 208-060-1 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 10481 |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH6N4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 122.1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.436 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 213 °C (415 °F; 486 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes below boiling point |
| 160 g/l at 20 °C | |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | MSDS |
| EU classification | |
| R-phrases | R20 R21 R22 R36 R38 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Guanidine nitrate is a high energy fuel used in some gas generator and solid rocket propellant applications.
Overview
Guanidine nitrate is the salt formed from guanidine and nitric acid. It has the chemical formula C(NH2)3NO3. It has been used as a monopropellant in the Jetex engine for model airplanes. It is attractive because it has a high gas output and low flame temperature. It has a relatively high monopropellant specific impulse of 177 seconds (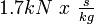 ).[note 1]
).[note 1]
Safety
Hazards:
- May explosively decompose on shock, friction, or concussion.
- May explode on heating.
- On combustion, forms toxic and corrosive fumes including nitric acid and nitrogen oxides.
- The substance is a strong oxidant and reacts with combustible and reducing materials.
Routes of exposure:
- The substance can be absorbed into the body by ingestion.
- A nuisance-causing concentration of airborne particles can be reached quickly when dispersed, especially if powdered.
Effects of short-term exposure:
- The substance is severely irritating to the eyes and the skin.
- Harmful if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through the skin.
See also
Notes
- ↑ 1000 lbf/in2 (700 kPa) chamber pressure, 14.7 lbf/in2 (101 kPa) exit pressure, shifting equilibrium theoretical performance
External links
- Jetex: Propellants
- PhysChem: Guanidine Nitrate MSDS
