Guangxicyon
| Guangxicyon Temporal range: 37–33Ma Late Eocene | |
|---|---|
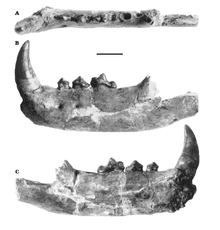 | |
| Lower jaw | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Caniformia |
| Family: | †Amphicyonidae |
| Subfamily: | Amphicyoninae |
| Genus: | Guangxicyon Zhai, 2003 |
| Species | |
| |
Guangxicyon is an extinct genus of amphicyonid mammal (also called bear dogs), which inhabited Central Asia from the Late Eocene subepoch to the Late Miocene subepoch 37—33 Ma, existing for approximately 4 million years.[1][2]
Guangxicyon was named by Zhai et al. in 2003. Its type and only known species is Guangxicyon sinoamericanus.
Fossil distribution
One site in Southern China.
Sources
- ↑ Zhai Renjie, Russell L. Ciochon, Tong Yongsheng, Donald E. Savage, Michael Morlo, Patricia A. Holroyd, and Gregg F. Gunnell. (2003) An aberrant amphicyonid mammal from the latest Eocene of the Bose Basin, Guangxi, China. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 48 (2), 293-300
- ↑ Paleobiology Database: Gobicyon, age range and collections