Groupoid
In mathematics, especially in category theory and homotopy theory, a groupoid (less often Brandt groupoid or virtual group) generalises the notion of group in several equivalent ways. A groupoid can be seen as a:
- Group with a partial function replacing the binary operation;
- Category in which every morphism is invertible. A category of this sort can be viewed as augmented with a unary operation, called inverse by analogy with group theory.[1]
Special cases include:
- Setoids, that is: sets that come with an equivalence relation;
- G-sets, sets equipped with an action of a group G.
Groupoids are often used to reason about geometrical objects such as manifolds. Heinrich Brandt (1927) introduced groupoids implicitly via Brandt semigroups.[2]
Definitions
A groupoid is an algebraic structure (G,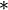 ) consisting of a non-empty set G and a binary operation '
) consisting of a non-empty set G and a binary operation '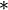 ' defined on G.
' defined on G.
Algebraic
A groupoid is a set G with a unary operation 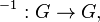 and a partial function
and a partial function 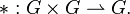 . Here * is not a binary operation because it is not necessarily defined for all possible pairs of G-elements. The precise conditions under which * is defined are not articulated here and vary by situation.
. Here * is not a binary operation because it is not necessarily defined for all possible pairs of G-elements. The precise conditions under which * is defined are not articulated here and vary by situation.
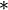 and −1 have the following axiomatic properties. Let a, b, and c be elements of G. Then:
and −1 have the following axiomatic properties. Let a, b, and c be elements of G. Then:
- Associativity: If a * b and b * c are defined, then (a * b) * c and a * (b * c) are defined and equal. Conversely, if either of these last two expressions is defined, then so is the other (and again they are equal).
- Inverse: a−1 * a and a * a−1 are always defined.
- Identity: If a * b is defined, then a * b * b−1 = a, and a−1 * a * b = b. (The previous two axioms already show that these expressions are defined and unambiguous.)
From these axioms, two easy and convenient properties follow:
- (a−1)−1 = a;
- If a * b is defined, then (a * b)−1 = b−1 * a−1.
Proof of first property: from 2. and 3. we obtain (a−1)−1 = (a−1)−1 * a−1 * a = a. ✓
Proof of second property: since a * b is defined, so is (a * b)−1 * a * b. Therefore (a * b)−1 * a * b * b−1 = (a * b)−1 * a is also defined. Moreover since a * b is defined, so is a * b * b−1 = a. Therefore a * b * b−1 * a−1 is also defined. From 3. we obtain (a * b)−1 = (a * b)−1 * a * a−1 = (a * b)−1 * a * b * b−1 * a−1 = b−1 * a−1. ✓
Category theoretic
A groupoid is a small category in which every morphism is an isomorphism, i.e. invertible.[1] More precisely, a groupoid G is:
- A set G0 of objects;
- For each pair of objects x and y in G0, there exists a (possibly empty) set G(x,y) of morphisms (or arrows) from x to y. We write f : x → y to indicate that f is an element of G(x,y).
- For every object x, a designated element
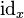 of G(x,x);
of G(x,x); - For each triple of objects x, y, and z, a function
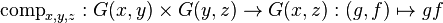 ;
; - For each pair of objects x, y a function
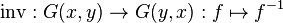 ;
;
satisfying, for any f : x → y, g : y → z, and h : z → w:
-
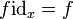 and
and 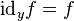 ;
; -
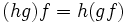 ;
; -
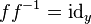 and
and 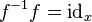 .
.
If f is an element of G(x,y) then x is called the source of f, written s(f), and y the target of f (written t(f)).
Comparing the definitions
The algebraic and category-theoretic definitions are equivalent, as follows. Given a groupoid in the category-theoretic sense, let G be the disjoint union of all of the sets G(x,y) (i.e. the sets of morphisms from x to y). Then 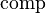 and
and 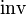 become partially defined operations on G, and
become partially defined operations on G, and 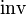 will in fact be defined everywhere; so we define * to be
will in fact be defined everywhere; so we define * to be 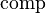 and
and 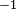 to be
to be 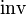 . Thus we have a groupoid in the algebraic sense. Explicit reference to G0 (and hence to
. Thus we have a groupoid in the algebraic sense. Explicit reference to G0 (and hence to 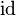 ) can be dropped.
) can be dropped.
Conversely, given a groupoid G in the algebraic sense, let G0 be the set of all elements of the form x * x−1 with x varying through G and define G(x*x−1,y*y−1) as the set of all elements f such that y * y−1 * f * x * x−1 exists. Given f∈G(x*x−1,y*y−1) and g∈G(y*y−1,z*z−1), their composite is defined as g * f ∈ G(x*x−1,z*z−1). To see this is well defined, observe that since z*z−1 * g * y*y−1 and y*y−1 * f * x*x−1 exist, so does z*z−1 * g * y*y−1 * y*y−1 * f * x*x−1 = z*z−1 * g*f * x*x−1. The identity morphism on x*x−1 is then x*x−1 itself, and the category-theoretic inverse of f is f−1.
Sets in the definitions above may be replaced with classes, as is generally the case in category theory.
Vertex groups
Given a groupoid G, the vertex groups or isotropy groups or object groups in G are the subsets of the form G(x,x), where x is any object of G. It follows easily from the axioms above that these are indeed groups, as every pair of elements is composable and inverses are in the same vertex group.
Category of groupoids
A subgroupoid is a subcategory that is itself a groupoid. A groupoid morphism is simply a functor between two (category-theoretic) groupoids. The category whose objects are groupoids and whose morphisms are groupoid morphisms is called the groupoid category, or the category of groupoids, denoted Grpd.
It is useful that this category is, like the category of small categories, cartesian closed. That is, we can construct for any groupoids 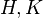 a groupoid
a groupoid 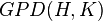 whose objects are the morphisms
whose objects are the morphisms 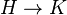 and whose arrows are the natural equivalences of morphisms. Thus if
and whose arrows are the natural equivalences of morphisms. Thus if 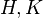 are just groups, then such arrows are the conjugacies of morphisms. The main result is that for any groupoids
are just groups, then such arrows are the conjugacies of morphisms. The main result is that for any groupoids 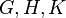 there is a natural bijection
there is a natural bijection
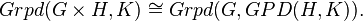
This result is of interest even if all the groupoids 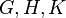 are just groups.
are just groups.
Fibrations, Coverings
Particular kinds of morphisms of groupoids are of interest. A morphism 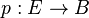 of groupoids is called a fibration if for each object
of groupoids is called a fibration if for each object 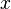 of
of 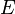 and each morphism
and each morphism 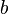 of
of 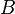 starting at
starting at  there is a morphism
there is a morphism  of
of 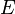 starting at
starting at 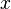 such that
such that 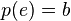 . A fibration is called a covering morphism or covering of groupoids if further such an
. A fibration is called a covering morphism or covering of groupoids if further such an  is unique. The covering morphisms of groupoids are especially useful because they can be used to model covering maps of spaces.[3]
is unique. The covering morphisms of groupoids are especially useful because they can be used to model covering maps of spaces.[3]
It is also true that the category of covering morphisms of a given groupoid 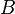 is equivalent to the category of actions of the groupoid
is equivalent to the category of actions of the groupoid 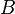 on sets.
on sets.
Examples
Linear algebra
Given a field K, the corresponding general linear groupoid GL*(K) consists of all invertible matrices whose entries range over K. Matrix multiplication interprets composition. If G = GL*(K), then the set of natural numbers is a proper subset of G0, since for each natural number n, there is a corresponding identity matrix of dimension n. G(m,n) is empty unless m=n, in which case it is the set of all nxn invertible matrices.
Topology
Given a topological space X, let G0 be the set X. The morphisms from the point p to the point q are equivalence classes of continuous paths from p to q, with two paths being equivalent if they are homotopic.
Two such morphisms are composed by first following the first path, then the second; the homotopy equivalence guarantees that this composition is associative. This groupoid is called the fundamental groupoid of X, denoted 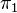 (X). The usual fundamental group
(X). The usual fundamental group 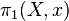 is then the vertex group for the point x.
is then the vertex group for the point x.
An important extension of this idea is to consider the fundamental groupoid 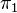 (X,A) where A is a set of "base points" and a subset of X. Here, one considers only paths whose endpoints belong to A.
(X,A) where A is a set of "base points" and a subset of X. Here, one considers only paths whose endpoints belong to A. 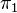 (X,A) is a sub-groupoid of
(X,A) is a sub-groupoid of 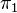 (X). The set A may be chosen according to the geometry of the situation at hand.
(X). The set A may be chosen according to the geometry of the situation at hand.
Equivalence relation
If X is a set with an equivalence relation denoted by infix 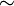 , then a groupoid "representing" this equivalence relation can be formed as follows:
, then a groupoid "representing" this equivalence relation can be formed as follows:
- The objects of the groupoid are the elements of X;
- For any two elements x and y in X, there is a single morphism from x to y if and only if x~y.
Group action
If the group G acts on the set X, then we can form the action groupoid representing this group action as follows:
- The objects are the elements of X;
- For any two elements x and y in X, there is a morphism from x to y corresponding to every element g of G such that gx = y;
- Composition of morphisms interprets the binary operation of G.
More explicitly, the action groupoid is the set 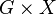 with source and target maps s(g,x) = x and t(g,x) = gx. It is often denoted
with source and target maps s(g,x) = x and t(g,x) = gx. It is often denoted 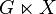 (or
(or 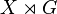 ). Multiplication (or composition) in the groupoid is then
). Multiplication (or composition) in the groupoid is then 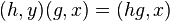 which is defined provided y=gx.
which is defined provided y=gx.
For x in X, the vertex group consists of those (g,x) with gx = x, which is just the isotropy subgroup at x for the given action (which is why vertex groups are also called isotropy groups).
Another way to describe G-sets is the functor category ![[\mathrm{Gr},\mathrm{Set}]](../I/m/daacf8a27c32c952629c05a48b16ae24.png) , where
, where 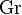 is the groupoid (category) with one element and isomorphic to the group G. Indeed, every functor F of this category defines a set X=F
is the groupoid (category) with one element and isomorphic to the group G. Indeed, every functor F of this category defines a set X=F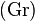 and for every g in G (i.e. for every morphism in
and for every g in G (i.e. for every morphism in 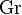 ) induces a bijection Fg : X→X. The categorical structure of the functor F assures us that F defines a G-action on the set X. The (unique) representable functor F :
) induces a bijection Fg : X→X. The categorical structure of the functor F assures us that F defines a G-action on the set X. The (unique) representable functor F : 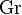 →
→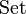 is the Cayley representation of G. In fact, this functor is isomorphic to
is the Cayley representation of G. In fact, this functor is isomorphic to 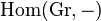 and so sends
and so sends 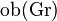 to the set
to the set 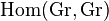 which is by definition the "set" G and the morphism g of
which is by definition the "set" G and the morphism g of 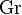 (i.e. the element g of G) to the permutation Fg of the set G. We deduce from the Yoneda embedding that the group G is isomorphic to the group {Fg | g∈G}, a subgroup of the group of permutations of G.
(i.e. the element g of G) to the permutation Fg of the set G. We deduce from the Yoneda embedding that the group G is isomorphic to the group {Fg | g∈G}, a subgroup of the group of permutations of G.
Fifteen puzzle
The symmetries of the fifteen puzzle form a groupoid (not a group, as not all moves can be composed).[4][5] This groupoid acts on configurations.
Mathieu groupoid
The Mathieu groupoid is a groupoid introduced by John Horton Conway acting on 13 points such that the elements fixing a point form a copy of the Mathieu group M12.
Relation to groups
| Group-like structures. The entries say whether the property is required. | |||||
| Totality* | Associativity | Identity | Divisibility | Commutativity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semicategory | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| Category | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Groupoid | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Magma | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Quasigroup | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| Loop | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| Semigroup | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Monoid | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Group | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Abelian Group | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| *Closure, which is used in many sources, is an equivalent axiom to totality, though defined differently. | |||||
If a groupoid has only one object, then the set of its morphisms forms a group. Using the algebraic definition, such a groupoid is literally just a group. Many concepts of group theory generalize to groupoids, with the notion of functor replacing that of group homomorphism.
If x is an object of the groupoid G, then the set of all morphisms from x to x forms a group G(x). If there is a morphism f from x to y, then the groups G(x) and G(y) are isomorphic, with an isomorphism given by the mapping g → fgf −1.
Every connected groupoid (that is, one in which any two objects are connected by at least one morphism) is isomorphic to an action groupoid (as defined above) (G, X) [by connectedness, there will only be one orbit under the action]. If the groupoid is not connected, then it is isomorphic to a disjoint union of groupoids of the above type (possibly with different groups G and sets X for each connected component).
Note that the isomorphism described above is not unique, and there is no natural choice. Choosing such an isomorphism for a connected groupoid essentially amounts to picking one object x0, a group isomorphism h from G(x0) to G, and for each x other than x0, a morphism in G from x0 to x.
In category-theoretic terms, each connected component of a groupoid is equivalent (but not isomorphic) to a groupoid with a single object, that is, a single group. Thus any groupoid is equivalent to a multiset of unrelated groups. In other words, for equivalence instead of isomorphism, one need not specify the sets X, only the groups G.
Consider the examples in the previous section. The general linear groupoid is both equivalent and isomorphic to the disjoint union of the various general linear groups GLn(F). On the other hand:
- The fundamental groupoid of X is equivalent to the collection of the fundamental groups of each path-connected component of X, but an isomorphism requires specifying the set of points in each component;
- The set X with the equivalence relation
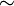 is equivalent (as a groupoid) to one copy of the trivial group for each equivalence class, but an isomorphism requires specifying what each equivalence class is:
is equivalent (as a groupoid) to one copy of the trivial group for each equivalence class, but an isomorphism requires specifying what each equivalence class is: - The set X equipped with an action of the group G is equivalent (as a groupoid) to one copy of G for each orbit of the action, but an isomorphism requires specifying what set each orbit is.
The collapse of a groupoid into a mere collection of groups loses some information, even from a category-theoretic point of view, because it is not natural. Thus when groupoids arise in terms of other structures, as in the above examples, it can be helpful to maintain the full groupoid. Otherwise, one must choose a way to view each G(x) in terms of a single group, and this choice can be arbitrary. In our example from topology, you would have to make a coherent choice of paths (or equivalence classes of paths) from each point p to each point q in the same path-connected component.
As a more illuminating example, the classification of groupoids with one endomorphism does not reduce to purely group theoretic considerations. This is analogous to the fact that the classification of vector spaces with one endomorphism is nontrivial.
Morphisms of groupoids come in more kinds than those of groups: we have, for example, fibrations, covering morphisms, universal morphisms, and quotient morphisms. Thus a subgroup H of a group G yields an action of G on the set of cosets of H in G and hence a covering morphism p from, say, K to G, where K is a groupoid with vertex groups isomorphic to H. In this way, presentations of the group G can be "lifted" to presentations of the groupoid K, and this is a useful way of obtaining information about presentations of the subgroup H. For further information, see the books by Higgins and by Brown in the References.
Lie groupoids and Lie algebroids
When studying geometrical objects, the arising groupoids often carry some differentiable structure, turning them into Lie groupoids. These can be studied in terms of Lie algebroids, in analogy to the relation between Lie groups and Lie algebras.
See also
- ∞-groupoid
- Inverse category
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Dicks & Ventura (1996). The Group Fixed by a Family of Injective Endomorphisms of a Free Group. p. 6.
- ↑ Brandt semigroup in Springer Encyclopaedia of Mathematics - ISBN 1-4020-0609-8
- ↑ J.P. May, A Concise Course in Algebraic Topology, 1999, The University of Chicago Press ISBN 0-226-51183-9 (see chapter 2)
- ↑ The 15-puzzle groupoid (1), Never Ending Books
- ↑ The 15-puzzle groupoid (2), Never Ending Books
References
- Brandt, H (1927), "Über eine Verallgemeinerung des Gruppenbegriffes", Mathematische Annalen 96 (1): 360–366, doi:10.1007/BF01209171
- Brown, Ronald, 1987, "From groups to groupoids: a brief survey," Bull. London Math. Soc. 19: 113-34. Reviews the history of groupoids up to 1987, starting with the work of Brandt on quadratic forms. The downloadable version updates the many references.
- —, 2006. Topology and groupoids. Booksurge. Revised and extended edition of a book previously published in 1968 and 1988. Groupoids are introduced in the context of their topological application.
- —, Higher dimensional group theory Explains how the groupoid concept has led to higher-dimensional homotopy groupoids, having applications in homotopy theory and in group cohomology. Many references.
- Dicks, Warren; Ventura, Enric (1996), The group fixed by a family of injective endomorphisms of a free group, Mathematical Surveys and Monographs 195, AMS Bookstore, ISBN 978-0-8218-0564-0
- Dokuchaev, M.; Exel, R.; Piccione, P. (2000). "Partial Representations and Partial Group Algebras". Journal of Algebra (Elsevier) 226: 505–532. arXiv:math/9903129. doi:10.1006/jabr.1999.8204. ISSN 0021-8693.
- F. Borceux, G. Janelidze, 2001, Galois theories. Cambridge Univ. Press. Shows how generalisations of Galois theory lead to Galois groupoids.
- Cannas da Silva, A., and A. Weinstein, Geometric Models for Noncommutative Algebras. Especially Part VI.
- Golubitsky, M., Ian Stewart, 2006, "Nonlinear dynamics of networks: the groupoid formalism", Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 43: 305-64
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Groupoid", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- Higgins, P. J., "The fundamental groupoid of a graph of groups", J. London Math. Soc. (2) 13 (1976) 145—149.
- Higgins, P. J. and Taylor, J., "The fundamental groupoid and the homotopy crossed complex of an orbit space", in Category theory (Gummersbach, 1981), Lecture Notes in Math., Volume 962. Springer, Berlin (1982), 115—122.
- Higgins, P. J., 1971. Categories and groupoids. Van Nostrand Notes in Mathematics. Republished in Reprints in Theory and Applications of Categories, No. 7 (2005) pp. 1–195; freely downloadable. Substantial introduction to category theory with special emphasis on groupoids. Presents applications of groupoids in group theory, for example to a generalisation of Grushko's theorem, and in topology, e.g. fundamental groupoid.
- Mackenzie, K. C. H., 2005. General theory of Lie groupoids and Lie algebroids. Cambridge Univ. Press.
- Weinstein, Alan, "Groupoids: unifying internal and external symmetry — A tour through some examples." Also available in Postscript., Notices of AMS, July 1996, pp. 744–752.
- Weinstein, Alan, "The Geometry of Momentum" (2002)
- R.T. Zivaljevic. "Groupoids in combinatorics—applications of a theory of local symmetries". In Algebraic and geometric combinatorics, volume 423 of Contemp. Math., 305–324. Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, RI (2006)