Groombridge 34
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Andromeda |
| Right ascension | 00h 18m 22.89s[1] |
| Declination | +44° 01′ 22.6″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.09/11.06 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M1.5V + M3.5V |
| U−B color index | 1.24 |
| B−V color index | 1.56 |
| Variable type | Flare stars |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +12.0 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +2888.92 ± 0.60[1] mas/yr Dec.: +410.10 ± 0.48[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 278.76 ± 0.77[1] mas |
| Distance | 11.70 ± 0.03 ly (3.587 ± 0.010 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 10.32/13.29 |
| Orbit | |
| Companion | Groombridge 34 B Gl 15 B |
| Period (P) | 2,600 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 41.15" |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.00 |
| Inclination (i) | 61.4° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 45.3° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 1745 |
| Details | |
| GX And | |
| Mass | 0.404[2] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.3863 ± 0.0021[3] R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 0.02589[note 1] L☉ |
| Luminosity (visual, LV) | 0.00637[note 2] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.89[2] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,730 ± 49[2] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | -0.32 dex |
| GQ And | |
| Mass | 0.163 M☉ |
| Radius | 0.19 R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | ~0.00262[note 1] L☉ |
| Luminosity (visual, LV) | 0.00041[note 2] L☉ |
| Temperature | ~3,000 K |
| Other designations | |
GX/GQ Andromedae, BD +43°44, GCTP 49, GJ 15 A/B, Gl 171-047/171-048, HD 1326, HIP 1475, LHS 3/4, LTT 10108/10109, LFT 31/32, SAO 36248, Vys 085 A/B. | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Groombridge 34 is a binary star system located about 11.7 light-years from the Sun. It consists of two red dwarfs in a nearly circular orbit with a separation of about 147 AU. Both stars in this pair exhibit variability due to random flares and they have been given variable star designations. (The brighter member Groombridge 34 A is designated GX And, and the other member is designated GQ And).
Distance
Groombridge 34 distance estimates
| Source | Parallax, mas | Distance, pc | Distance, ly | Distance, Pm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woolley et al. (1970) | 282±7 | 3.55±0.09 | 11.57+0.29 −0.28 |
109.4+2.8 −2.7 |
[4] |
| Gliese & Jahreiß (1991) | 289.5±4.9 | 3.45±0.06 | 11.27±0.19 | 106.6±1.8 | [5] |
| van Altena et al. (1995) | 282.0±2.2 | 3.546+0.028 −0.027 |
11.57±0.09 | 109.4+0.9 −0.8 |
[6] |
| Perryman et al. (1997) (Hipparcos) | 280.27±1.05 | 3.568±0.013 | 11.64±0.04 | 110.1±0.4 | [7] |
| Perryman et al. (1997) (Tycho) | 320.70±24.40 | 3.12+0.26 −0.22 |
10.2+0.8 −0.7 |
96.2+7.9 −6.8 |
[8] |
| van Leeuwen (2007) | 278.76±0.77 | 3.587±0.01 | 11.7±0.03 | 110.69+0.31 −0.3 |
[1] |
| Gatewood (2008) (MAP-based study) | 281.45±1.05 | 3.553±0.013 | 11.59±0.04 | 109.6±0.4 | [9] |
| RECONS TOP100 (2012) | 279.87±0.60[note 3] | 3.573±0.008 | 11.654±0.025 | 110.25±0.24 | [10] |
| Dittmann et al. (2014) (A) | 279.30±5.40 | 3.58±0.07 | 11.68+0.23 −0.22 |
110.5+2.2 −2.1 |
[11] |
| Dittmann et al. (2014) (B) | 313.90±9.30 | 3.19+0.1 −0.09 |
10.39+0.32 −0.3 |
98.3+3 −2.8 |
[11] |
Non-trigonometric distance estimates are marked in italic. The most precise estimate is marked in bold.
Planetary system
In August 2014, a planet orbiting around Groombridge 34 A was reported.[3] The planet's existence was deduced from analysis of the radial velocities of the parent Star by the Eta-Earth Survey using HIRES at Keck Observatory.
The planet is thought to have a minimum mass of 5.35 ± 0.75 Earth masses,[12] and at its discovery was the sixth nearest known exoplanet.
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | ≥ 5.35±0.75 M⊕ | 0.0717±0.0034 | 11.4433±0.0017 | 0.12? | — | — |
See also
- Groombridge 34 in fiction
- List of nearest stars
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 From
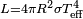 , where
, where 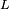 is the luminosity,
is the luminosity, 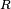 is the radius,
is the radius, 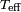 is the effective surface temperature and
is the effective surface temperature and  is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant
is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Using the absolute visual magnitude of Gliese 15 A,
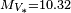 , and Gliese 15 B,
, and Gliese 15 B, 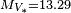 , with the absolute visual magnitude of the Sun,
, with the absolute visual magnitude of the Sun, 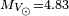 , the two visual luminosities of the stars can be calculated by
, the two visual luminosities of the stars can be calculated by 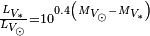
- ↑ Weighted parallax based on parallaxes from van Altena et al. (1995), van Leeuwen (2007) and Gatewood (2008).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 van Leeuwen F. (2007). "HIP 1475". Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction. Retrieved 2014-10-20.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Berger, D. H. et al. (2006). "First Results from the CHARA Array. IV. The Interferometric Radii of Low-Mass Stars". The Astrophysical Journal 644 (1): 475–483. arXiv:astro-ph/0602105. Bibcode:2006ApJ...644..475B. doi:10.1086/503318.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 http://arxiv.org/abs/1408.5645
- ↑ Woolley R.; Epps E. A.; Penston M. J.; Pocock S. B. (1970). "Woolley 15". Catalogue of stars within 25 parsecs of the Sun. Retrieved 2014-10-20.
- ↑ Gliese, W. and Jahreiß, H. (1991). "Gl 15". Preliminary Version of the Third Catalogue of Nearby Stars. Retrieved 2014-10-20.
- ↑ Van Altena W. F., Lee J. T., Hoffleit E. D. (1995). "GCTP 49". The General Catalogue of Trigonometric Stellar Parallaxes (Fourth ed.). Retrieved 2014-10-20.
- ↑ Perryman et al. (1997). "HIP 1475". The Hipparcos and Tycho Catalogues. Retrieved 2014-10-20.
- ↑ Perryman et al. (1997). "HIP 1475". The Hipparcos and Tycho Catalogues. Retrieved 2014-10-20.
- ↑ Gatewood, George (2008). "Astrometric Studies of Aldebaran, Arcturus, Vega, the Hyades, and Other Regions". The Astronomical Journal 136 (1): 452–460. Bibcode:2008AJ....136..452G. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/136/1/452.
- ↑ "RECONS TOP100". THE ONE HUNDRED NEAREST STAR SYSTEMS brought to you by RECONS (Research Consortium On Nearby Stars). 2012. Retrieved 2014-10-20.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Dittmann, Jason A.; Irwin, Jonathan M.; Charbonneau, David; Berta-Thompson, Zachory K. (2014). "Trigonometric Parallaxes for 1507 Nearby Mid-to-late M Dwarfs". The Astrophysical Journal 784 (2): 156. arXiv:1312.3241. Bibcode:2014ApJ...784..156D. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/784/2/156.
- ↑ Andrew Howard, Geoffrey Marcy, Debra A. Fischer, Howard Isaacson, Philip S. Muirhead, Gregory W. Henry, Tabetha S. Boyajian, Kaspar von Braun, Juliette C. Becker, Jason T. Wright, John Asher Johnson, Astrophysics Earth and Planetary Astrophysics : The NASA-UC-UH Eta-Earth Program: IV. A Low-mass Planet Orbiting an M Dwarf 3.6 PC from Earth.
- Lippincott, S. L., "Parallax and orbital motion of the 2 nearby long-period visual binaries Groombridge 34 and ADS 9090", 1972, Astronomical Journal, 77, 165.
External links
- SolStation entry
- www.richweb.f9.co.uk/
- Image Groombridge 34
- The One Hundred Nearest Star Systems, RECONS
Components
| NAME | Right ascension | Declination | Apparent magnitude (V) | Spectral type | Database references |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADS 246 B (ADS 246 AB) | 00h 18m 24s | +44° 01' 00 | 11.0 | Simbad | |
| ADS 246 C (V* GQ And) | 00h 18m 25.868s | +44° 01' 38.44 | 11.4 | M3.5 | Simbad |
| ADS 246 D (GJ 15 C) | 00h 18m 00.13s | +44° 00' 29.2 | 11.4 | M5 | Simbad |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||