Graph cuts in computer vision
As applied in the field of computer vision, graph cuts can be employed to efficiently solve a wide variety of low-level computer vision problems (early vision[1]), such as image smoothing, the stereo correspondence problem, and many other computer vision problems that can be formulated in terms of energy minimization. Such energy minimization problems can be reduced to instances of the maximum flow problem in a graph (and thus, by the max-flow min-cut theorem, define a minimal cut of the graph). Under most formulations of such problems in computer vision, the minimum energy solution corresponds to the maximum a posteriori estimate of a solution. Although many computer vision algorithms involve cutting a graph (e.g., normalized cuts), the term "graph cuts" is applied specifically to those models which employ a max-flow/min-cut optimization (other graph cutting algorithms may be considered as graph partitioning algorithms).
"Binary" problems (such as denoising a binary image) can be solved exactly using this approach; problems where pixels can be labeled with more than two different labels (such as stereo correspondence, or denoising of a grayscale image) cannot be solved exactly, but solutions produced are usually near the global optimum.
History
The theory of graph cuts was first applied in computer vision in the seminal paper by Greig, Porteous and Seheult[2] of Durham University. In the Bayesian statistical context of smoothing noisy (or corrupted) images, they showed how the maximum a posteriori estimate of a binary image can be obtained exactly by maximizing the flow through an associated image network, involving the introduction of a source and sink. The problem was therefore shown to be efficiently solvable. Prior to this result, approximate techniques such as simulated annealing (as proposed by the Geman brothers[3]), or iterated conditional modes (a type of greedy algorithm as suggested by Julian Besag)[4] were used to solve such image smoothing problems.
Although the general 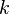 -colour problem remains unsolved for
-colour problem remains unsolved for 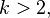 the approach of Greig, Porteous and Seheult[2] has turned out[5][6] to have wide applicability in general computer vision problems. Greig, Porteous and Seheult approaches are often applied iteratively to a sequence of binary problems, usually yielding near optimal solutions.
the approach of Greig, Porteous and Seheult[2] has turned out[5][6] to have wide applicability in general computer vision problems. Greig, Porteous and Seheult approaches are often applied iteratively to a sequence of binary problems, usually yielding near optimal solutions.
Notations
- Image:
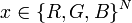
- Output: Segmentation (also called opacity)
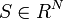 (soft segmentation). For hard segmentation
(soft segmentation). For hard segmentation 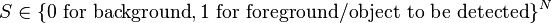
- Energy function:
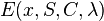 where C is the color parameter and λ is the coherence parameter.
where C is the color parameter and λ is the coherence parameter. -
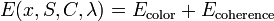
- Optimization: The segmentation can be estimated as a global minimum over S:
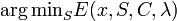
Existing methods
- Standard Graph cuts: optimize energy function over the segmentation (unknown S value).
- Iterated Graph cuts:
- First step optimizes over the color parameters using K-means.
- Second step performs the usual graph cuts algorithm.
- These 2 steps are repeated recursively until convergence.
- Dynamic graph cuts:
Allows to re-run the algorithm much faster after modifying the problem (e.g. after new seeds have been added by a user).
Energy function
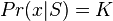
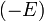 where the energy
where the energy 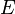 is composed of 2 different models (
is composed of 2 different models (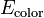 and
and 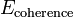 ):
):
Likelihood / Color model / Regional term
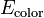 — unary term describing the likelihood of each color.
— unary term describing the likelihood of each color.
- This term can be modeled using different local (e.g. texons) or global (e.g. histograms, GMMs, Adaboost likelihood) approaches that are described below.
Histogram
- We use intensities of pixels marked as seeds to get histograms for object (foreground) and background intensity distributions: P(I|O) and P(I|B).
- Then, we use these histograms to set the regional penalties as negative log-likelihoods.
GMM (Gaussian Mixture Model)
- We usually use 2 distributions to model background and foreground pixels.
- Use a Gaussian mixture model (with 5-8 components) to model those 2 distributions.
- Goal: Try to pull apart those 2 distributions.
Texon
- A texon (or texton) is a set of pixels that has certain characteristics and is repeated in an image.
- Steps:
- Determine a good natural scale for the texture elements.
- Compute non-parametric statistics of the model-interior texons, either on intensity or on Gabor filter responses.
- References:
Prior / Coherence model / Boundary term
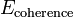 — binary term describing the coherence between neighborhood pixels.
— binary term describing the coherence between neighborhood pixels.
- In practice, pixels are defined as neighbors if they are adjacent either horizontally, vertically or diagonally (4 way connectivity or 8 way connectivity).
- Costs can be based on local intensity gradient, Laplacian zero-crossing, gradient direction, color mixture model,...
References
- Different energy functions have been defined:
- Standard Markov random field (MRF): Associate a penalty to disagreeing pixels by evaluating the difference between their segmentation label (crude measure of the length of the boundaries). See Boykov and Kolmogorov ICCV 2003
- Conditional random field (CRF): If the color is very different, it might be a good place to put a boundary. See Lafferty et al. 2001; Kumar and Hebert 2003
Criticism
Graph cuts methods have become popular alternatives to the level set-based approaches for optimizing the location of a contour (see[7] for an extensive comparison). However, graph cut approaches have been criticized in the literature for several issues:
- Metrication artifacts: When an image is represented by a 4-connected lattice, graph cuts methods can exhibit unwanted "blockiness" artifacts. Various methods have been proposed for addressing this issue, such as using additional edges[8] or by formulating the max-flow problem in continuous space.[9]
- Shrinking bias: Since graph cuts finds a minimum cut, the algorithm can be biased toward producing a small contour.[10] For example, the algorithm is not well-suited for segmentation of thin objects like blood vessels (see[11] for a proposed fix).
- Multiple labels: Graph cuts is only able to find a global optimum for binary labeling (i.e., two labels) problems, such as foreground/background image segmentation. Extensions have been proposed that can find approximate solutions for multilabel graph cuts problems.[6]
- Memory: the memory usage of graph cuts increase quickly as the image size increase. As an illustration, the Boykov-Kolmogorov max-flow algorithm v2.2 allocates
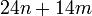 bytes (
bytes (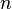 and
and 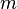 are respectively the number of nodes and edges in the graph). Nevertheless, some amount of work has been recently done in this direction for reducing the graphs before the maximum-flow computation.[12][13][14]
are respectively the number of nodes and edges in the graph). Nevertheless, some amount of work has been recently done in this direction for reducing the graphs before the maximum-flow computation.[12][13][14]
Algorithm
- Minimization is done using a standard minimum cut algorithm.
- Due to the Max-flow min-cut theorem we can solve energy minimization by maximizing the flow over the network. The Max Flow problem consists of a directed graph with edges labeled with capacities, and there are two distinct nodes: the source and the sink. Intuitively, it's easy to see that the maximum flow is determined by the bottleneck.
Implementation
| The Wikibook Algorithm Implementation has a page on the topic of: Graphs/Maximum flow/Boykov & Kolmogorov |
Boykov & Kolmogorov[15] published an efficient way to compute the max-flow for computer vision related graph.
Software
- http://pub.ist.ac.at/~vnk/software.html — An implementation of the maxflow algorithm described in "An Experimental Comparison of Min-Cut/Max-Flow Algorithms for Energy Minimization in Computer Vision" by Vladimir Kolmogorov
- http://vision.csd.uwo.ca/code/ — some graph cut libraries and MATLAB wrappers
- http://gridcut.com/ — fast multi-core max-flow/min-cut solver optimized for grid-like graphs
References
- ↑ Adelson, Edward H., and James R. Bergen (1991), "The plenoptic function and the elements of early vision", Computational models of visual processing 1.2 (1991).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 D.M. Greig, B.T. Porteous and A.H. Seheult (1989), Exact maximum a posteriori estimation for binary images, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B, 51, 271–279.
- ↑ D. Geman and S. Geman (1984), Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs distributions and the Bayesian restoration of images, IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 6, 721–741.
- ↑ J.E. Besag (1986), On the statistical analysis of dirty pictures (with discussion), Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B, 48, 259–302
- ↑ Y. Boykov, O. Veksler and R. Zabih (1998), "Markov Random Fields with Efficient Approximations", International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Y. Boykov, O. Veksler and R. Zabih (2001), "Fast approximate energy minimisation via graph cuts", IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 29, 1222–1239.
- ↑ Leo Grady and Christopher Alvino (2009), "The Piecewise Smooth Mumford-Shah Functional on an Arbitrary Graph", IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, pp. 2547-2561
- ↑ Yuri Boykov and Vladimir Kolmogorov (2003), "Computing Geodesics and Minimal Surfaces via Graph Cuts", Proc. of ICCV
- ↑ Ben Appleton and Hugues Talbot (2006), "Globally Minimal Surfaces by Continuous Maximal Flows", IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, pp. 106-118
- ↑ Ali Kemal Sinop and Leo Grady, "A Seeded Image Segmentation Framework Unifying Graph Cuts and Random Walker Which Yields A New Algorithm", Proc. of ICCV, 2007
- ↑ Vladimir Kolmogorov and Yuri Boykov (2005), "What Metrics Can Be Approximated by Geo-Cuts, or Global Optimization of Length/Area and Flux", Proc. of ICCV pp. 564-571
- ↑ Nicolas Lermé, François Malgouyres and Lucas Létocart (2010), "Reducing graphs in graph cut segmentation", Proc. of ICIP, pp. 3045-3048
- ↑ Herve Lombaert, Yiyong Sun, Leo Grady, Chenyang Xu (2005), "A Multilevel Banded Graph Cuts Method for Fast Image Segmentation", Proc. of ICCV, pp. 259-265
- ↑ Yin Li, Jian Sun, Chi-Keung Tang, and Heung-Yeung Shum (2004), "Lazy Snapping", ACM Transactions on Graphics, pp. 303-308
- ↑ Yuri Boykov, Vladimir Kolmogorov: An Experimental Comparison of Min-Cut/Max-Flow Algorithms for Energy Minimization in Vision. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(9): 1124-1137 (2004)
Further reading
- Dr. Simon Prince (2012). Computer Vision: Models, Learning, and Inference. New York: Cambridge. p. 295. ISBN 978-1107011793.