Gowers' sign
Gowers' sign
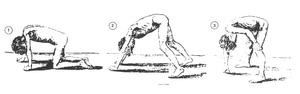
Gowers' sign is a medical sign that indicates weakness of the proximal muscles, namely those of the lower limb. The sign describes a patient that has to use his hands and arms to "walk" up his own body from a squatting position due to lack of hip and thigh muscle strength.
It is named after William Richard Gowers.[1][2]
Associations
Gowers' sign is classically seen in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, but also presents itself in centronuclear myopathy, myotonic dystrophy and various other conditions associated with proximal muscle weakness. For this maneuver, the patient is placed on the floor away from any objects that could otherwise be used to pull oneself to a standing position. It is also used in testing paraplegia.
See also
References
- ↑ synd/1228 at Who Named It?
- ↑ W. R. Gowers. A manual of the nervous system. Philadelphia; 2nd edition, volume 1, 1895.
|
|---|
| | CNS | |
|---|
| | PNS | Reflexes of extremities/
corticospinal tract | | Combination | |
|---|
| | Lower limb | |
|---|
| | Upper limb | |
|---|
|
|---|
| | Other torso/limbs | | Upper limb | |
|---|
| | Lower limb | |
|---|
| | Torso | |
|---|
| | General | |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | Mental/behavioral | |
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- meninges
- cortex
- association fibers
- commissural fibers
- lateral ventricles
- basal ganglia
- diencephalon
- mesencephalon
- pons
- cerebellum
- medulla
- spinal cord
- Physiology
- Development
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Cerebral palsy
- Meningitis
- Demyelinating diseases
- Seizures and epilepsy
- Headache
- Stroke
- Sleep
- Congenital
- Injury
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Other
- Symptoms and signs
- head and neck
- eponymous
- lesions
- Tests
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Drugs
- general anesthetics
- analgesics
- addiction
- epilepsy
- cholinergics
- migraine
- Parkinson's
- vertigo
- other
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- Nerves
- cranial
- trigeminal
- cervical
- brachial
- lumbosacral plexus
- somatosensory
- spinal
- autonomic
- Physiology
- reflexes
- proteins
- neurotransmitters
- transporters
- Development
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Autonomic
- Congenital
- Injury
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Other
- Symptoms and signs
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Local anesthetics
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | Description | |
|---|
| | Disorders |
- Mental and behavioral
- Mood
- Developmental
- pervasive
- dyslexia and specific
- Substance-related
- Emotional and behavioral
- Symptoms and signs
- Evaluation and testing
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Psychotherapy
- Drugs
- depression
- antipsychotics
- anxiety
- dementia
- hypnotics and sedatives
- psychostimulants, ADHD and nootropics
|
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Neuromuscular/
soft tissue | |
|---|
| | Collagen | |
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Development
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Infections
- Vesiculobullous
- Dermatitis and eczema
- Papulosquamous
- Urticaria and erythema
- Radiation-related
- Pigmentation
- Mucinoses
- Keratosis, ulcer, atrophy, and necrobiosis
- Vasculitis
- Fat
- Neutrophilic and eosinophilic
- Congenital
- Neoplasms and cancer
- nevi and melanomas
- epidermis
- dermis
- Symptoms and signs
- Terminology
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Drugs
- antibiotics
- disinfectants
- emollients and protectives
- itch
- psoriasis
- other
- Wound and ulcer
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- head
- neck
- arms
- chest and back
- diaphragm
- abdomen
- genital area
- legs
- Muscle tissue
- Physiology
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Myopathy
- Soft tissue
- Connective tissue
- Congenital
- abdomen
- muscular dystrophy
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Injury
- Symptoms and signs
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Drugs
- anti-inflammatory
- muscle relaxants
|
|---|
|
|
