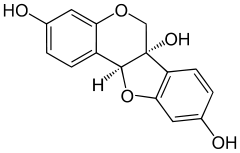
Glycinol (pterocarpan)
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
6H-[1]benzofuro[3,2-c]chromene-3,6a(11aH),9-triol | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | 114790 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 129648 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 272.25 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Glycinol is a pterocarpan, a type of natural phenol. It is a phytoalexin found in the soybean (Glycine max). It is formed by the cyclisation of daidzein. It has antiestrogenic activities.[1][2]
It can be synthethised chemically and possesses two chiral centers.[3]
Glycinol is the direct precursor of glyceollins through the action of a prenyltransferase.
Experiments show that the 6a oxygen of glycinol is derived from molecular oxygen.[4]
References
- ↑ Zimmermann, M. C.; Tilghman, S. L.; Boue, S. M.; Salvo, V. A.; Elliott, S.; Williams, K. Y.; Skripnikova, E. V.; Ashe, H. et al. (2009). "Glyceollin I, a Novel Antiestrogenic Phytoalexin Isolated from Activated Soy". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 332 (1): 35–45. doi:10.1124/jpet.109.160382. PMC 2802480. PMID 19797619.
- ↑ Qi Y., Moco S.I.A., Boeren S., Vos C.H. de and Bovy A.G. (2005). "Isolation and identification of glycinol from Glycine max L. Merri". Chinese Journal of Chromatography 23 (4): 353–357. PMID 16250441.
- ↑ Luniwal Amarjit, Khupse Rahul S, Reese Michael, Lei Fang and Erhardt Paul W (2009). "Total Syntheses of Racemic and Natural Glycinol". Journal of Natural Products 72 (11): 2072–2075. doi:10.1021/np900509f. PMID 19943626.
- ↑ Matthews, David E.; Plattner, Ronald D.; Vanetten, Hans D. (1989). "The 6a oxygen of the pterocarpan glycinol is derived from molecular oxygen". Phytochemistry 28: 113. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(89)85020-4.
| ||||||||||||||